Contents
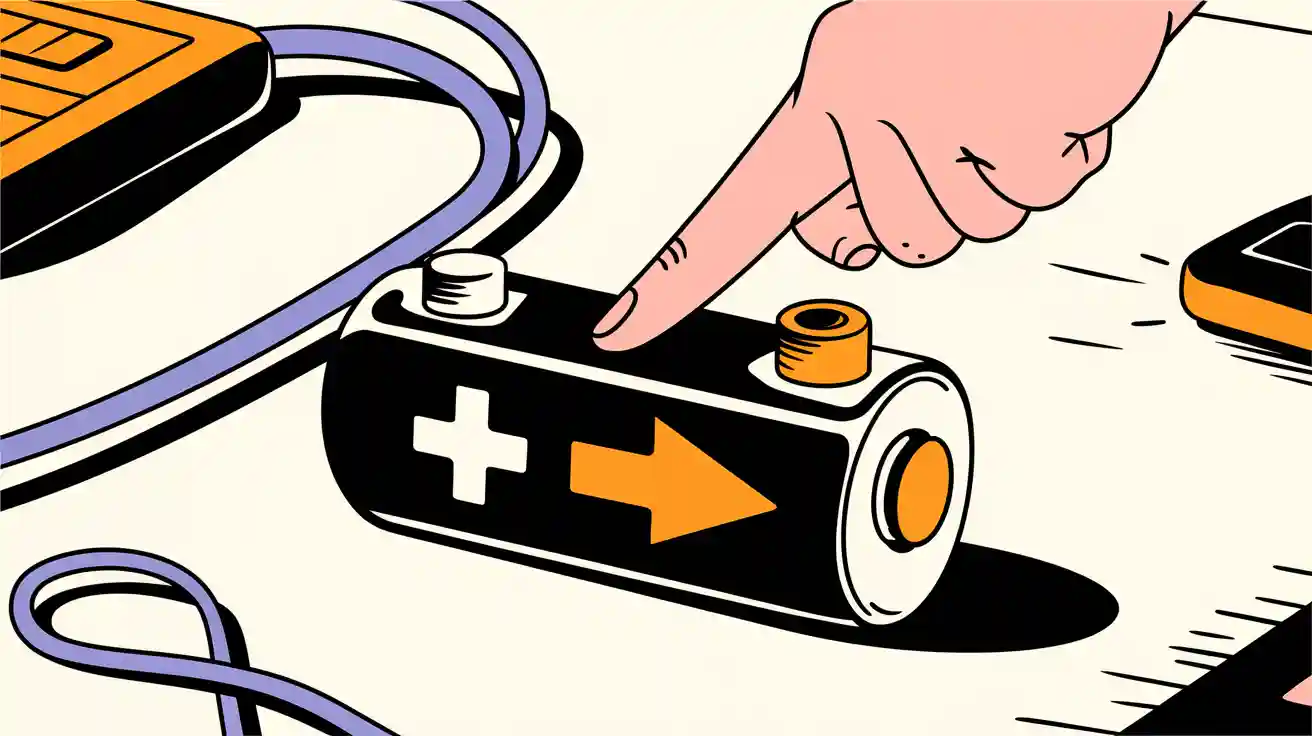
You can quickly identify the positive or negative lithium battery terminals using visual cues. Look for markings like a “+” or “-” symbol near the terminals. These labels are standard on most lithium batteries. For safety, use caution when handling battery packs, especially in professional settings where accuracy is crucial. Misidentifying the positive or negative lithium battery terminals can lead to damage or hazards.
Key Takeaways
You can find battery terminals by checking their colors. Red means positive, and black means negative.
If labels are hard to see, use a multimeter. A positive number means the red probe is on the positive terminal.
Be safe when working with batteries. Wear safety gear and avoid short circuits to stay safe.
Part 1: Visual Identification Methods

1.1 Color Coding and Labels
Color coding and labels are the most straightforward ways to identify the positive and negative terminals on a lithium-ion battery. Manufacturers often use red to indicate the positive terminal and black for the negative terminal. These colors are universally recognized and help you quickly determine the polarity of the battery.
In addition to color coding, most lithium-ion batteries feature clear labels near the terminals. Look for a “+” symbol to mark the positive terminal and a “-” symbol for the negative terminal. These markings are typically printed or engraved directly onto the battery casing. If you are working with a battery pack, check the user manual or the manufacturer’s specifications for additional guidance.
When the labels or colors are unclear due to wear or damage, you may need to rely on alternative methods, such as using a multimeter, which will be discussed later in this blog.
1.2 Physical Features of Terminals
The physical design of the terminals can also help you identify the positive and negative sides of a lithium-ion battery. In many cases, the positive terminal is slightly larger or more prominent than the negative terminal. This design difference ensures proper alignment when connecting the battery to a device or circuit.
Some lithium battery packs include unique connectors or terminal shapes to prevent incorrect connections. For example, the positive terminal may have a rounded or protruding shape, while the negative terminal might appear flat or recessed. These physical features act as a safeguard against polarity errors, which can damage the battery or connected equipment.
If you are unsure about the terminal design, consult the technical documentation provided by the manufacturer. This step is especially important for custom battery packs used in industrial or professional applications.
1.3 Identifying Terminals on Lithium Battery Packs
Lithium battery packs often combine multiple cells to achieve higher voltage or capacity. Identifying the positive and negative terminals on these packs can be more complex than on individual cells. Manufacturers typically label the main terminals on the pack with “+” and “-” symbols. However, the internal wiring of the pack may include additional connections for balancing or monitoring purposes.
To accurately identify the terminals, examine the pack’s wiring diagram, which is usually included in the product manual. If the diagram is unavailable, you can use a multimeter to test the polarity of the terminals. Set the multimeter to the DC voltage setting and connect the probes to the terminals. A positive reading indicates that the red probe is on the positive terminal, while a negative reading shows the opposite.
For custom battery packs, consider consulting experts or the manufacturer directly. Companies like Large Power specialize in custom battery solutions and can provide detailed guidance for your specific application. You can learn more about their services here: Custom Battery Solutions.
Tip: Always handle lithium battery packs with care. Incorrectly identifying the terminals can lead to short circuits, overheating, or even fire hazards.
Part 2: Alternative Methods for Identifying Terminals
2.1 Using a Simple Circuit to Identify Positive or Negative Lithium Battery Terminals
When visual cues or labels are missing, a simple circuit can help you determine the polarity of a lithium battery. This method is particularly useful for professionals working with custom battery packs or damaged batteries. To perform this test, you will need a small light bulb or an LED, along with two wires.
Connect one wire to each terminal of the battery.
Attach the other ends of the wires to the light bulb or LED.
Observe the behavior of the light source. If the bulb lights up or the LED glows, the terminal connected to the positive lead of the light source is the positive terminal.
This approach works because the current flows from the positive to the negative terminal in a closed circuit. For lithium-ion battery packs, this method can also help verify the main terminals when dealing with complex wiring systems. Always ensure that the circuit components are rated for the battery’s voltage to avoid damage or hazards.
Tip: Use this method only for low-voltage batteries or packs. For high-voltage systems, consult a professional or use specialized equipment to ensure safety.
2.2 Multimeter-Free Techniques for Terminal Testing
If you lack access to a multimeter, several alternative techniques can help you identify the positive and negative terminals of a lithium battery. These methods rely on simple tools or household items and are particularly useful in fieldwork or emergency situations.
Color Coding: Some batteries use brown for the positive terminal and gray for the negative terminal.
Chemical Reaction Test: Immerse wires connected to the terminals in a dilute sulfuric acid solution. Bubbles will form at the negative terminal due to the release of hydrogen gas.
Light Bulb Test: Similar to the simple circuit method, connect the terminals to a light bulb and observe the current flow.
Potato Test: Insert the battery leads into a potato. The green wire will indicate the positive terminal.
Saltwater Method: Submerge wires connected to the terminals in saltwater. The terminal producing more bubbles is the negative one.
Copper Sulfate Solution: Use carbon rods in a copper sulfate solution. Copper will deposit on the negative terminal.
LED Test: Connect an LED to the terminals. If it lights up, the connected terminal is positive.
These techniques provide quick and practical solutions for identifying polarity without specialized tools. However, they may not be suitable for all battery types or professional applications. Always verify the results using a multimeter or consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for critical systems.
2.3 Identifying Terminals with Household Items
Household items can serve as a last resort for identifying the positive and negative terminals of a lithium battery. While these methods are less precise, they can be effective in non-critical scenarios.
Aluminum Foil and Saltwater: Create a makeshift circuit using aluminum foil and a saltwater solution. Connect the battery terminals to the foil and immerse them in the solution. The terminal producing more bubbles is the negative one.
LED Flashlight: Disassemble an LED flashlight and use its components to test the battery terminals. The LED will light up when connected to the correct polarity.
Paper Clip Test: Straighten two paper clips and connect them to the battery terminals. Place the other ends in a small amount of water. The terminal causing more bubbling is the negative one.
These methods are not recommended for high-capacity lithium-ion battery packs or professional applications due to their limited accuracy. For industrial or custom battery solutions, consider consulting experts like Large Power for reliable guidance.
Note: Always prioritize safety when using unconventional methods. Avoid prolonged contact with battery terminals to prevent overheating or damage.
Part 3: Safety Precautions When Identifying Terminals
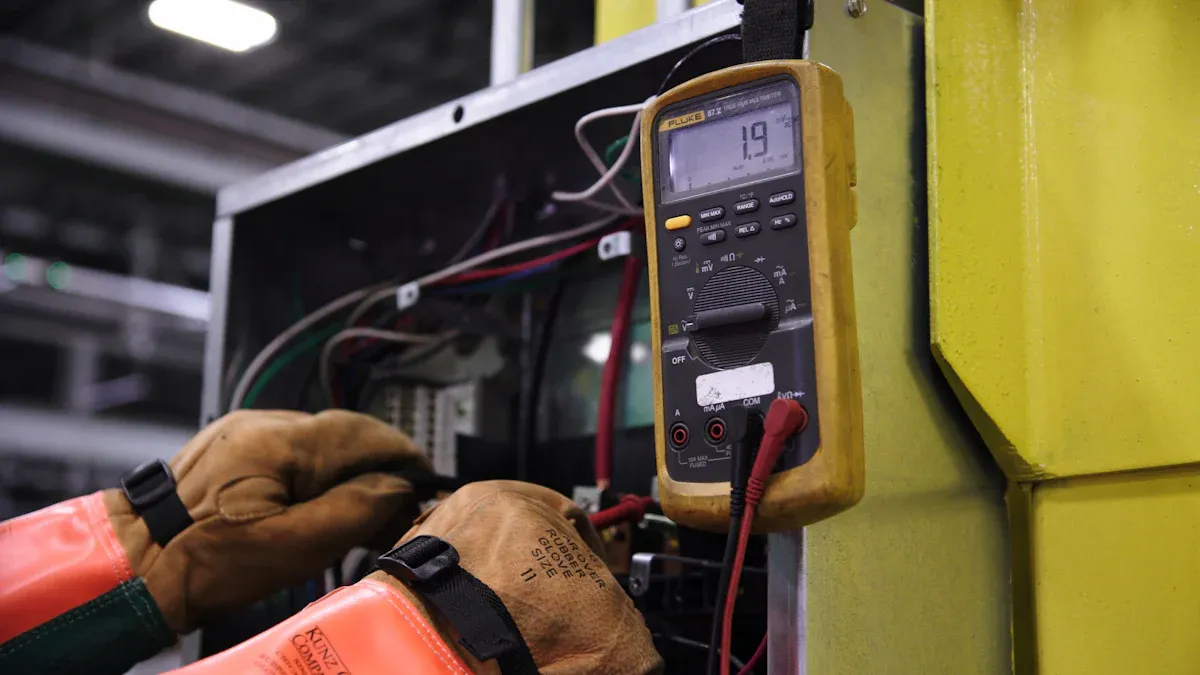

3.1 Avoiding Short Circuits in Battery Packs
Short circuits in lithium-ion battery packs can lead to overheating, fires, or even explosions. To prevent this, you should always avoid direct contact between the positive and negative terminals. Use insulated tools when working with battery packs to minimize the risk of accidental connections. If you’re handling a custom battery pack, ensure the terminals are properly covered with insulating materials like heat-shrink tubing or terminal caps.
Regular inspection of the battery pack is also essential. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or exposed wiring that could cause a short circuit. Proper storage plays a critical role as well. Keep batteries in a dry, cool environment and avoid stacking them in a way that could damage the terminals.
Tip: Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for safe handling and storage. For custom solutions, consult experts like Large Power to ensure compliance with safety standards.
3.2 Safe Handling of Lithium Batteries
Handling lithium batteries requires a clear understanding of their potential hazards. Always wear personal protective equipment (PPE), such as insulated gloves and safety goggles, to protect yourself from electrical shocks or leaks. Avoid using damaged batteries, as they can release harmful chemicals or catch fire.
When connecting or disconnecting a battery, ensure the power is off to reduce the risk of electrical arcs. Use tools specifically designed for battery work, as regular tools may not provide adequate insulation. Additionally, never force a connection if the terminals do not align properly. This could damage the battery or the device.
Note: Awareness of hazardous voltage levels is critical. Even small lithium-ion batteries can deliver a dangerous shock if mishandled.
3.3 Proper Disposal of Damaged or Misidentified Batteries
Damaged or misidentified batteries pose significant risks to both safety and the environment. Never dispose of lithium batteries in regular trash, as they can ignite under pressure or heat. Instead, take them to a certified recycling facility. Many local governments and retailers offer battery recycling programs to ensure safe disposal.
If you’re unsure about a battery’s condition, consult a professional before attempting to dispose of it. Proper packaging is also crucial. Place the battery in a non-conductive container, such as a plastic bag, to prevent accidental short circuits during transport.
For businesses handling large quantities of batteries, having an emergency plan in place is vital. This includes training employees on proper disposal methods and maintaining a list of certified recycling partners. You can learn more about sustainable practices for lithium batteries here: Sustainability at Large Power.
Callout: Proper disposal not only ensures safety but also supports environmental sustainability by reducing electronic waste.
Identifying the positive and negative terminals of a lithium battery is essential for safe and effective use. You can rely on visual cues, simple circuits, or household items to determine polarity. Always prioritize safety by following best practices. For complex systems, consult experts to ensure proper handling and avoid potential hazards.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between the anode and cathode in a lithium battery?
The anode is the negative terminal, while the cathode is the positive terminal. Understanding how to determine anode and cathode ensures proper battery usage.
2. How to determine anode and cathode if the labels are missing?
Use a multimeter or a simple circuit. The anode connects to the negative probe, and the cathode connects to the positive probe.
3. Why is it important to know how to determine anode and cathode?
Identifying the anode and cathode prevents polarity errors. Misconnections can damage the battery or connected devices, leading to safety hazards.