Contents

Lithium batteries leak when their internal electrolyte escapes due to damage, overcharging, or aging. This leakage can harm devices, create safety risks, and reduce battery efficiency. To ensure safety, inspect batteries regularly and store batteries properly. If leakage occurs, protect yourself and clean up spills immediately. Can you clean battery leaks safely? Yes, with proper precautions.
Key Takeaways
Check lithium batteries often for leaks like swelling or rust. Finding problems early stops more damage to devices.
Keep batteries in a cool, dry spot and don’t overcharge. Storing and using them right makes them last longer and leak less.
If a battery leaks, be careful with it. Wear gloves, keep it away from other things, and call waste services to throw it away safely.
Part 1: Why Lithium Batteries Leak

1.1 Key Components of Lithium Batteries and Their Vulnerabilities
Lithium batteries consist of several critical components, including the anode, cathode, separator, electrolyte, and casing. Each of these plays a vital role in the battery’s functionality but also introduces potential vulnerabilities that can lead to leakage.
Anode and Cathode: These electrodes facilitate the flow of lithium ions during charging and discharging. However, impurities or defects in the electrode materials can trigger chemical reactions that compromise the battery’s integrity.
Separator: This thin membrane prevents direct contact between the anode and cathode. If the separator becomes damaged due to overheating or physical stress, it can lead to internal short circuits and leakage.
Electrolyte: The electrolyte, often a liquid or gel, enables ion transport between the electrodes. Its chemical composition makes it highly reactive, especially under extreme conditions like high temperatures or overcharging.
Casing: The outer shell protects the internal components. Physical damage to the casing, such as dents or punctures, can expose the electrolyte and lead to leakage.
“The study introduces a new class of side-channel attacks that utilize electric vehicle (EV) battery data to extract sensitive user information. By analyzing battery consumption patterns, the research demonstrates a method to accurately identify the EV driver, their driving style, and even infer the vehicle’s start and end locations. The attacks achieved an average success rate of 95.4%, highlighting significant privacy risks associated with EV battery data.”
Understanding these vulnerabilities helps you identify why lithium batteries leak and underscores the importance of proper handling and maintenance.
1.2 Common Causes of Lithium Battery Leakage
Several factors contribute to lithium battery leakage. Recognizing these causes can help you take preventive measures to avoid potential hazards.
Overcharging: When a battery is charged beyond its recommended voltage, the electrolyte can break down, generating gas and heat. This increases internal pressure, leading to leakage.
Physical Damage: Impact or puncture can disrupt the separation between the anode and cathode, causing internal short circuits. Visible signs like swelling, dents, or deformation often indicate damage.
Exposure to Extreme Heat: High temperatures can decompose the electrolyte and damage the separator, increasing the risk of leakage.
Improper Storage: Storing batteries in fluctuating temperatures or humid environments can cause moisture to react with the electrolyte, leading to corrosion and leakage.
Additional common causes include:
Poor manufacturing quality
Mixing different battery models
Improper use
Regular inspections and adherence to usage guidelines can mitigate these risks and ensure the longevity of your lithium battery packs.
1.3 How Manufacturing Defects Contribute to Leakage
Manufacturing defects significantly impact the structural integrity of lithium batteries, increasing the likelihood of leakage. Research shows that improper assembly, contamination, and material inconsistencies are common culprits. These issues can lead to thermal runaway, a dangerous condition where the battery’s temperature rapidly escalates, causing leakage or even fire.
Key insights into manufacturing standards:
Clean manufacturing environments are essential to prevent contamination.
Approximately 4 billion lithium-ion cells were produced in 2012, highlighting the scale of production and the potential for occasional defects.
The failure rate for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries is about one in 10 million cells, indicating that while rare, defects can have severe consequences.
Investing in high-quality batteries from reputable manufacturers reduces the risk of defects. For businesses relying on lithium battery packs, ensuring compliance with stringent quality standards is crucial. If you require custom battery solutions tailored to your specific needs, consider consulting with Large Power.
Part 2: How to Deal with Leaking Battery Safely
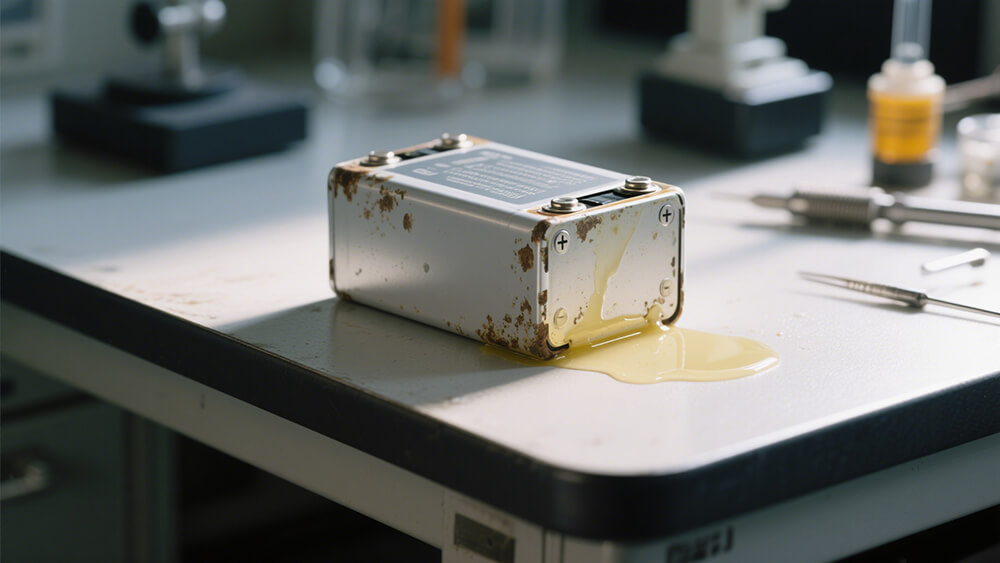

2.1 Signs of Lithium Battery Leakage
Identifying the early signs of a leaking lithium battery is crucial for preventing further damage to your equipment and ensuring safety. Here are the most common indicators:
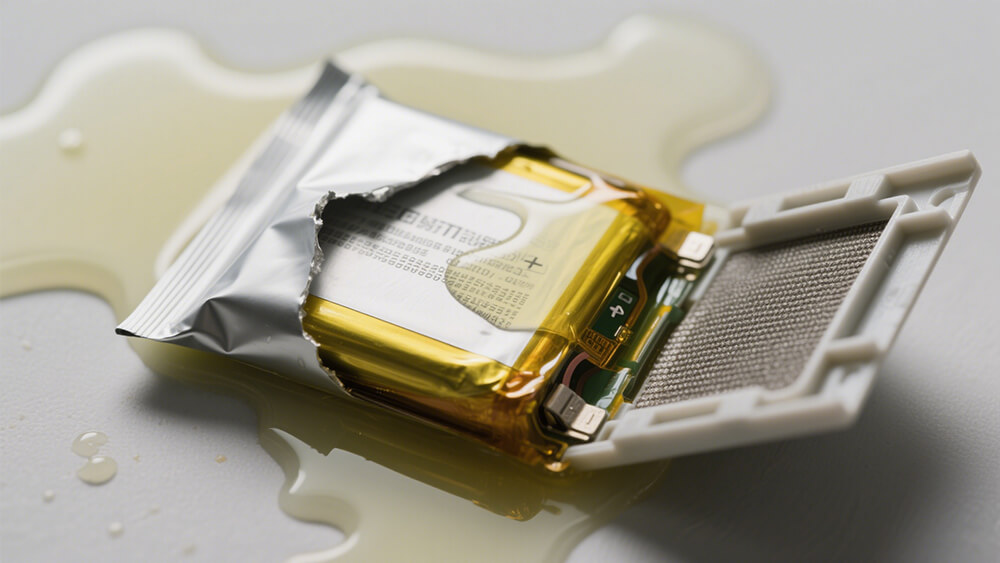
Physical Deformation: Swelling, bulging, or warping of the battery casing often signals internal pressure buildup caused by electrolyte leakage.
Liquid Residue: A sticky or oily substance on the battery surface or nearby areas may indicate electrolyte seepage. This residue can sometimes emit a sweet or chemical odor.
Corrosion: White or green crystalline deposits around the battery terminals or contacts suggest a chemical reaction between the leaked electrolyte and metal components.
Performance Issues: A sudden drop in battery capacity, abnormal heating during use, or erratic voltage readings could point to internal damage caused by leakage.
Unusual Smell: A sharp, solvent-like odor is a telltale sign of electrolyte vapor escaping from the battery.
Tip: Regularly inspect your lithium battery packs for these signs, especially if they are used in critical applications like robotics, medical devices, or industrial equipment. Early detection can save your electronics from irreversible damage.
2.2 Risks and Dangers of Battery Leakage
When lithium batteries leak, the consequences can be severe, affecting both safety and functionality. Understanding these risks helps you take appropriate precautions.
Fire and Explosion Hazards
Leaking electrolyte is highly flammable. If exposed to heat or sparks, it can ignite, leading to fires or explosions. This risk is particularly high in environments with poor ventilation or near flammable materials.Corrosion of Electronics
The leaked electrolyte can corrode circuit boards, connectors, and other sensitive components in your devices. This damage is often irreversible, rendering the equipment unusable.Toxic Exposure
Electrolyte vapors contain harmful chemicals that can irritate the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. Prolonged exposure may lead to more severe health issues.Environmental Impact
Improper disposal of leaking batteries can contaminate soil and water, posing long-term environmental risks.
Note: Always prioritize safety when dealing with a leaking lithium battery. If you notice signs of fire or excessive heat, evacuate the area and contact emergency services immediately.
2.3 Safe Steps to Handle a Leaking Battery
Handling a leaking lithium battery requires careful attention to minimize risks. Follow these steps to ensure safety:
Do Not Touch the Leak Directly
Avoid direct contact with the leaked material. Electrolyte is corrosive and can cause skin burns or irritation. Use gloves and protective eyewear when handling the battery.Isolate the Battery
Remove the battery from the device or equipment, if safe to do so. Place it in a non-flammable container, such as a metal box, to contain the leak.Neutralize the Spill
Use an absorbent material, like baking soda or sand, to neutralize and contain the leaked electrolyte. Avoid using water, as it can react with the chemicals and worsen the situation.Ventilate the Area
Ensure proper ventilation to disperse any harmful vapors. This step is especially important in confined spaces.Dispose of the Battery Properly
Contact your local hazardous waste disposal service or Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) department for guidance. Never throw a leaking battery in regular trash or attempt to incinerate it.
Step | Procedure |
|---|---|
1 | Open the lid of a crash bin. |
2 | Remove a Ziploc bag containing inert beads. |
3 | Place the damaged battery in the crash bin. |
4 | Cover the battery with inert beads if it shows signs of imminent failure. |
5 | Secure the bin with a metal lid. |
6 | Move the bin to a safe location, if possible. |
7 | Contact emergency services if fire or excessive heat is observed. |
Reminder: Always wait until the battery cools to room temperature before handling it. If you are unsure about the procedure, consult professionals for assistance.
For businesses relying on lithium battery packs, investing in custom solutions tailored to your operational needs can enhance safety and reliability. Explore Large Power’s custom battery solutions for expert guidance.
Part 3: How to Prevent Battery from Leaking
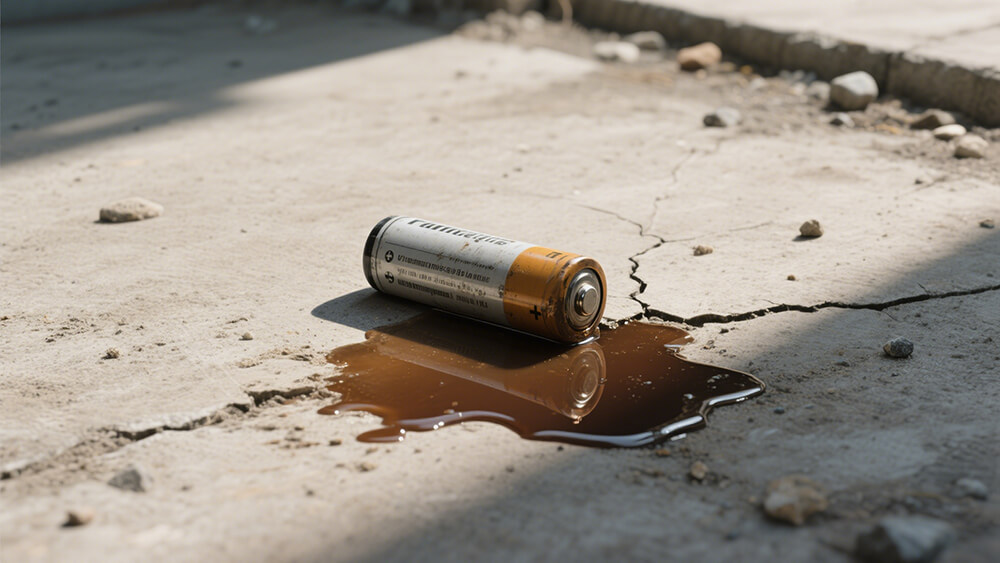

3.1 Best Practices for Lithium Battery Maintenance
Proper maintenance is essential to prevent lithium battery leakage and extend its lifespan. Following these best practices ensures safety and reliability:
Avoid overcharging by using chargers that stop at peak voltage. Overcharging can degrade the electrolyte and increase leakage risks.
Regularly inspect batteries for physical damage, swelling, or leaks. Early detection prevents further battery leakage damage electronics.
Charge batteries in a safe environment equipped with fire alarms and extinguishers. Use nonflammable surfaces like steel shelving to minimize fire hazards.
Monitor battery temperature during charging. If the battery or charger becomes excessively warm, discontinue use immediately.
Tip: Handle batteries gently to avoid casing damage. Never attempt to repair or modify a leaky battery, as this can worsen the issue.
3.2 Proper Storage and Usage Guidelines for Battery Packs
Storing and using lithium batteries correctly reduces the risk of leakage and ensures optimal performance. Follow these guidelines:
Store batteries in a cool, dry place at room temperature. Avoid exposure to direct sunlight or heat sources.
Keep batteries partially charged (around 50%) for long-term storage. This prevents over-discharge and electrolyte degradation.
Remove batteries from devices if not in use for extended periods. This prevents accidental discharge and leakage.
Separate fresh and depleted cells to avoid mixing, which can lead to performance issues.
Use metal storage cabinets for additional safety, especially in industrial environments.
Note: Always purchase batteries from reputable manufacturers to ensure quality and reliability. For custom battery solutions tailored to your needs, consult Large Power.
3.3 Importance of Quality Assurance in Battery Manufacturing
Stringent quality assurance protocols during manufacturing play a critical role in reducing leakage occurrences. Industry analysis reveals that defects like off-spec separators can increase leakage rates from less than 1% to as high as 3-4%. Manufacturers must maintain clean production environments and adhere to strict standards to minimize defects.
Investing in high-quality batteries ensures better performance and safety. Businesses relying on lithium battery packs should prioritize suppliers with proven quality assurance practices. For reliable and durable battery solutions, explore Large Power’s custom battery solutions.
3.4 Addressing Misconceptions: Can a Leaking Battery Be Used?
Using a leaky battery poses significant risks. The leaked electrolyte is highly corrosive and can damage electronics, cause short circuits, or even ignite fires. Attempting to use or repair a leaking battery is unsafe and can lead to severe consequences.
Reminder: Dispose safely of leaking batteries at hazardous waste collection sites. Never throw them in regular trash or incinerate them. Proper disposal protects both the environment and your safety.
For more information on sustainable battery practices, visit Sustainability at Large Power.
Lithium battery leakage poses serious risks to safety and equipment performance. Fires caused by these batteries have resulted in over 660 incidents, 12 deaths, and more than 260 injuries since 2019.
Understanding the causes of leakage and taking preventive measures ensures safer battery usage. High-quality lithium batteries offer longer lifespans, rigorous testing, and built-in safety features, reducing leakage risks significantly.
Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
Rigorous Testing | High-quality lithium batteries undergo extensive testing to ensure durability. |
Longer Lifespan | These batteries last two to three times longer than other types. |
Built-in Safety Features | Mechanisms prevent overcharging and overheating, enhancing safety. |
Invest in reliable batteries and follow proper handling practices to ensure long-term safety and performance.
FAQ
1. How can you safely dispose of a leaking lithium-ion battery?
Dispose of leaking lithium-ion batteries at designated hazardous waste facilities. Never throw them in regular trash or incinerate them. For guidance, consult local waste management services.
2. Can a leaking battery damage industrial equipment?
Yes, leaked electrolyte can corrode sensitive components in industrial equipment. Regular inspections and proper maintenance reduce this risk. Learn more about industrial battery solutions.
3. Why should you choose Large Power for custom battery solutions?
Large Power offers tailored lithium battery solutions with rigorous quality assurance, ensuring safety and reliability. Explore our custom battery solutions for your specific needs.