
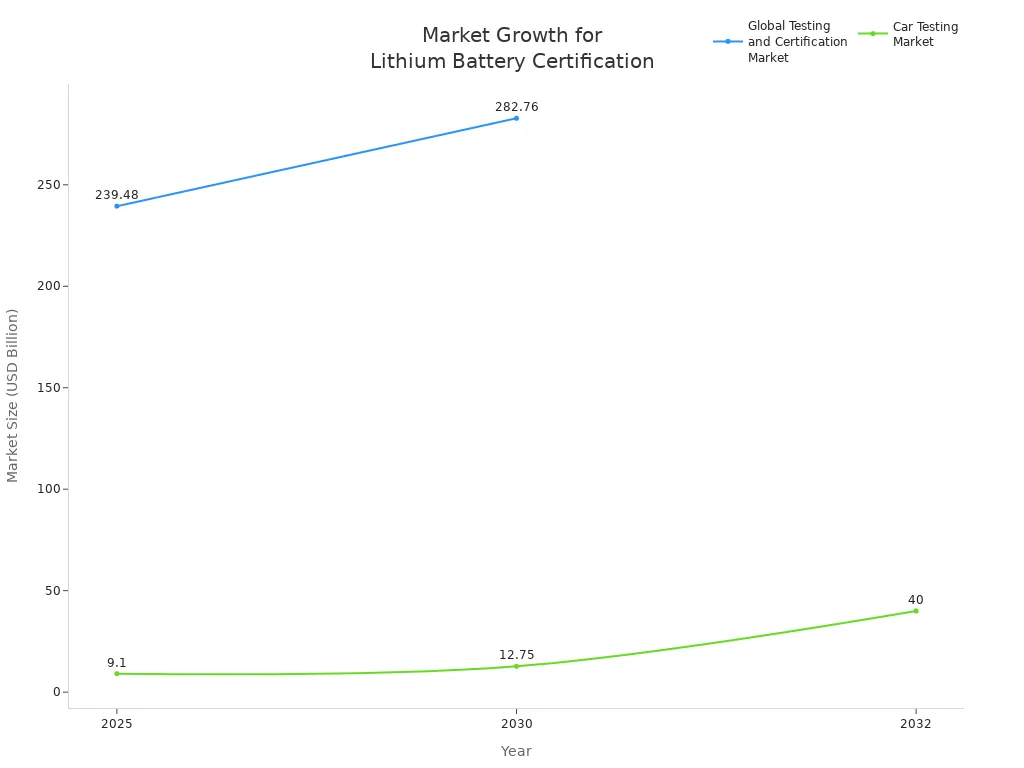
You face strict certification requirements when bringing lithium battery packs to global markets. Each region demands specific certifications, like UL in North America and CB vs IEC standards internationally, to ensure safety and performance. UN38.3 certification remains mandatory for battery transport worldwide.
Different countries enforce unique certification rules for battery market access.
Certifications focus on safety, transport, and industry standards.
UN38.3 ensures batteries withstand shipping risks like vibration and shock.
Choosing the right certification strategy, especially understanding the differences in CB vs IEC standards, helps you avoid market barriers and supports compliance in the evolving lithium battery industry.
Key Takeaways
CB and IEC certifications focus on product safety, ensuring lithium batteries meet electrical and mechanical safety standards for global market access.
UL certification is essential for North American markets, demonstrating compliance with strict safety and performance rules in the US and Canada.
UN38.3 certification is mandatory for safely transporting lithium batteries worldwide, protecting against risks like shock, vibration, and temperature changes during shipping.
Part 1: Lithium Battery Standards

1.1 CB Certification
CB certification serves as a globally recognized framework for lithium battery safety. You rely on the IECEE CB Scheme, which is built on IEC standards, to streamline international market access. The CB certificate confirms that your lithium batteries meet harmonized safety standards, including electrical, mechanical, and thermal safety. IEC 62133-2:2017 is the core standard for CB certification, covering portable sealed secondary cells and batteries with lithium-ion and lithium-polymer chemistries. This standard applies to all rechargeable, portable, or user-replaceable batteries, regardless of capacity.
CB certification focuses on electrical safety, functional safety, and design considerations. You submit your batteries to accredited CB Testing Laboratories (CBTLs) for rigorous testing. The process includes overcharge, short circuit, vibration, crush, temperature cycling, and thermal abuse tests. After successful testing, you receive a CB Test Certificate, which national certification bodies (NCBs) in over 50 countries accept. This mutual recognition reduces redundant testing and accelerates compliance.
CB certification does not cover transportation safety. You must obtain separate certifications, such as UN38.3, for shipping lithium batteries.
Focus Area / Test Category | Description / Purpose |
|---|---|
Electrical Safety Tests | Overcharge, external short circuit, forced discharge |
Mechanical Safety Tests | Vibration, crush, free fall |
Environmental Adaptability Tests | Temperature cycling, low-pressure, constant damp heat |
Thermal Abuse Test | Exposure to high temperatures (e.g., 130°C) |
Specialized Tests | Electrostatic discharge, high-rate charge protection |
1.2 IEC Certification
IEC certification is based on IEC 62133, the international safety standard for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries used in portable electronic devices. You use IEC certification to verify that your batteries meet electrical, mechanical, and chemical safety requirements. The standard addresses hazards such as overcharging, over-discharging, short-circuiting, and thermal runaway. IEC 62133 applies to sealed secondary cells and batteries used in consumer electronics, IT equipment, laboratory devices, and medical equipment.
The scope of IEC certification includes requirements for labeling, documentation, and testing. You must ensure your batteries pass tests for safe operation and quality improvement. IEC 62133 has two main versions: the 2nd Edition and IEC 62133-2 1st Edition, which differ in chemistry focus and test conditions. The EU made IEC 62133-2 mandatory for new portable lithium-ion batteries in 2021. Certification under IEC 62133 helps you meet global regulatory requirements and gain market access.
IEC 62133 defines safety requirements and testing procedures for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries.
The scope includes electrical, mechanical, and chemical safety aspects.
Applies to sealed secondary cells and batteries in consumer electronics, IT, tools, labs, and medical devices.
Requires labeling, documentation, and testing for compliance.
Two main versions: IEC 62133 2nd Edition and IEC 62133-2 1st Edition.
EU adopted IEC 62133-2 in 2021; US and Canada have related standards.
Certification improves product safety and market access.
Global certification bodies provide IEC 62133 services.
The CB vs IEC relationship is critical. CB certification is an internationally recognized conformity assessment system based on IEC standards. You test your batteries once under IEC 62133, and the CB certificate allows acceptance in multiple countries. IEC certification alone does not offer mutual recognition, but CB certification does.
The IECEE CB Scheme is built on IEC International Standards and recognized internationally.
CB certification enables mutual recognition of test results and certificates among over 50 countries.
CB certification requires compliance with IEC 62133 for rechargeable lithium batteries.
CB certification accelerates market entry and reduces costs.
IEC certification alone is not a formal international certification scheme with mutual recognition.
1.3 UL Standards
UL certification is essential for lithium battery safety in North America. You use UL standards to demonstrate that your batteries meet strict safety and performance criteria. UL Listed, UL Recognized Component, and UL Certified marks indicate compliance with electrical, mechanical, and thermal safety standards. UL 2054 and UL/CSA 62133 are commonly required for battery packs sold on platforms like Amazon.
UL standards focus on product safety, including electrical performance, temperature cycling, and abuse scenarios. You must provide UL test reports and follow packaging and shipping requirements. UL standards such as UL 1973, UL 9540A, and UL 9540 address stationary and motive battery systems, fire safety, and integrated energy storage systems.
UL Standard | Scope | Key Requirements and Testing Protocols | Primary Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
UL 1973 | Stationary and motive battery systems | Electrical safety, thermal management, mechanical durability, chemical safety | Energy storage, forklifts |
UL 9540A | Thermal runaway fire propagation | Fire containment, mitigation of fire spread | Fire safety in energy storage |
UL 9540 | Energy storage systems | Integrated safety evaluation, thermal management | Overall system safety |
NFPA 855 | Installation requirements | Ventilation, spacing, hazard mitigation | Safe installation and operation |
Certification Type | Key Standards | Safety Focus | Geographic Focus | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
UL Standards | UL 1642, UL 2054, UL 2580 | Product safety, electrical performance, temperature cycling | North America | Consensus-based, recognized as equivalent to IEC in some contexts |
IEC Standards | IEC 62133, IEC 60086-4, IEC 61960, IEC 62281 | Safety requirements for portable batteries and transport | International | Basis for CB certification, broader safety and transport requirements |
CB Certification | IEC 62133 | Compliance with IEC safety standards | International | Requires additional testing to comply with IEC 62133 |
UL certification is often considered equivalent to IEC compliance, but acceptance depends on certification bodies. Both UL and IEC require testing after transport certification, such as UN38.3.
1.4 UN38.3 Certification
UN38.3 certification is mandatory for transporting lithium batteries by air, sea, and land. You must ensure your batteries pass eight rigorous tests simulating transport conditions, including altitude simulation, thermal cycling, vibration, shock, external short circuit, impact, overcharge, and forced discharge. These tests confirm that your batteries do not leak, rupture, catch fire, or lose integrity during shipment.
UN38.3 applies to all lithium battery types, including lithium-ion, lithium-polymer, LiFePO4, NMC, LCO, LMO, LTO, solid-state, and lithium metal batteries. You must comply with packaging, labeling, and documentation requirements to meet international transport safety regulations. UN38.3 complements other standards, such as the Globally Harmonized System (GHS).
Test Code | Test Name | Purpose / Simulation Description | Battery Types Covered |
|---|---|---|---|
T1 | Altitude Simulation | Simulates low pressure conditions to check battery integrity under low pressure. | Primary and Secondary cells/batteries |
T2 | Thermal Test | Tests battery integrity under rapid and extreme temperature changes. | Primary and Secondary cells/batteries |
T3 | Vibration | Simulates vibration during transportation to verify battery durability. | Primary and Secondary cells/batteries |
T4 | Shock | Simulates shocks experienced during transport to check battery robustness. | Primary and Secondary cells/batteries |
T5 | Short Circuit | Simulates an external short circuit to ensure battery safety mechanisms prevent fire or rupture. | Primary and Secondary cells/batteries |
T6 | Impact | Simulates impact/crush to the battery case to verify mechanical safety. | Primary and Secondary cells |
T7 | Overcharge | Simulates overcharging conditions to ensure rechargeable batteries do not catch fire or rupture. | Secondary (rechargeable) batteries |
T8 | Forced Discharge | Simulates forced discharge conditions to verify battery safety under abnormal discharge. | Primary and Secondary cells |
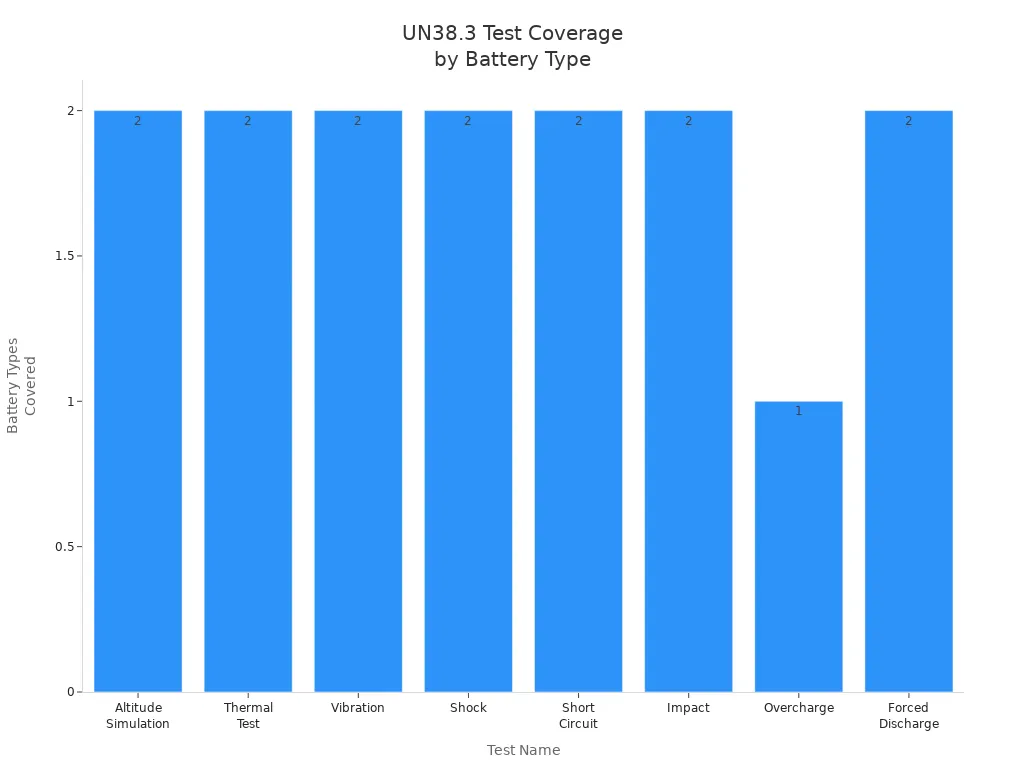
UN38.3 certification is a legal requirement for shipping lithium batteries. You must send battery samples to approved labs for testing and obtain a test report verifying compliance.
CB vs IEC: Relationship and Distinction
You must understand the CB vs IEC distinction when selecting battery certification paths. CB certification is part of the IECEE CB Scheme, which relies on IEC standards such as IEC 62133 for rechargeable lithium batteries. CB certification enables mutual acceptance of test reports and certificates across multiple countries, reducing redundant testing and accelerating market access. IEC certification alone does not offer this structured international recognition.
CB certification is internationally recognized and allows entry into multiple markets.
IEC certification is the basis for CB certification but lacks mutual recognition.
CB certification requires compliance with IEC 62133 for lithium batteries.
National Certification Bodies handle country-specific differences, simplifying compliance.
Product Safety vs Transport Safety
You must distinguish between product safety and transport safety when certifying lithium batteries. Product safety standards, such as IEC 62133 and UL 2054, focus on electrical, mechanical, and chemical hazards during everyday use. Transport safety standards, such as UN38.3, address risks during shipment, including vibration, shock, and temperature extremes.
Certification | Scope | Purpose | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
UN38.3 | Safe transportation of lithium batteries | Mitigate transport hazards | Mandatory for all lithium batteries during shipment |
IEC 62133 | Safety of portable lithium batteries | Prevent hazards in consumer use | Certification for consumer electronics batteries |
Comparison Table: Scope, Purpose, and Application
Certification | Scope | Purpose | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
CB Certification | International conformity assessment based on IEC standards | Ensure electrical and functional safety | Global market access for lithium batteries |
IEC Certification | Safety requirements for portable lithium batteries | Prevent hazards in everyday use | Consumer electronics, IT, medical, industrial |
UL Certification | North American safety standards for lithium batteries | Demonstrate product safety and performance | Market access in US and Canada, Amazon compliance |
UN38.3 Certification | United Nations transport safety standards for lithium batteries | Ensure safe shipment and handling | Mandatory for air, sea, and land transport |
You must update your battery certification strategy as standards evolve.
Part 2: Certification Requirements and Battery Pack Certifications
2.1 Certification Requirements
Selecting the right battery certification for your lithium battery pack depends on several factors: product type, target market, and shipping method. Each standard has unique certification requirements and addresses specific aspects of lithium-ion battery safety, performance, and regulatory compliance.
You must first identify the chemistry and application of your battery. For example, lithium-ion, lithium-polymer, and lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries require different testing protocols. The certification requirements for lithium batteries are more stringent than those for other chemistries, such as nickel-metal hydride or lead acid, due to higher energy density and associated risks.
The following table summarizes the main certification requirements for each standard:
Standard | Certification Requirements / Tests | Notes |
|---|---|---|
IEC 62133 | – External Short-Circuit (cell and battery level) | Covers safety and abuse testing for lithium-ion batteries, including automotive and electronics applications. |
UN 38.3 | – Vibration | Mandatory testing before shipping lithium batteries to ensure safety during transport. |
CB | – General certification context provided by TÜV SÜD as an accredited CB Test Lab | TÜV SÜD offers CB Test Reports and Certificates, but specific test details are not provided. |
UL | – No explicit detailed information found in the source regarding UL certification requirements | UL certification requirements are not detailed in the retrieved documents. |
You must also consider the shipment scenario. Shipping lithium batteries independently requires full UN38.3 certification and compliance with IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations. Shipping batteries installed in devices may have less stringent requirements, but you still need proper packaging and labeling. Any modification to a certified battery, such as repackaging or changing cells, may require recertification.
Tip: Always verify the latest regulatory updates for your target market. Regulatory requirements change frequently, impacting your battery certification process and market access.
2.2 Battery Pack Certifications
Battery pack certifications ensure your products meet global safety standards and regulatory requirements. You must select the appropriate certification set based on your application area, such as consumer electronics, automotive, industrial, or medical devices. The following table outlines the most common battery pack certifications and their application areas:
Certification/Standard | Application Area | Description |
|---|---|---|
UL 1642 | Lithium batteries | Safety requirements and tests for hazardous conditions |
UL 2054 | Household/commercial lithium batteries | Safety during use, handling, and storage |
UL 4200A | Secondary lithium batteries | Requirements for high-performance batteries (e.g., EVs, robotics, industrial) |
UL 60086-4 | Primary lithium batteries | Safety and performance for consumer electronics and industrial devices |
UL Listed Mark | Consumer electronics | Indicates battery passed rigorous safety testing |
UL Recognized Component Mark | Battery components (cells/modules) | Certifies safety and performance of individual components |
UL Certified Mark | Lithium battery products | Combines multiple UL certifications for global compliance |
IEC/EN 62133 | General battery safety | International standard for portable rechargeable cells and batteries |
IEC 62660 series | Secondary lithium-ion cells | Propulsion batteries for electric road vehicles |
ISO 12405 series | Lithium-ion traction battery packs | Test specifications for EV battery packs and systems |
UN/DOT 38.3 | Transport safety | Testing for safe transportation of lithium batteries |
You must also address industry-specific requirements. For example, the medical sector demands compliance with IEC 60601-1, while robotics and security systems often require UL 2054 and IEC 62133. Infrastructure projects and industrial applications rely on ISO 12405 and IEC 62660. Consumer electronics typically use UL 1642, UL 2054, and IEC 62133.
Battery pack certifications play a critical role in lithium-ion battery safety, reliability, and market acceptance. Certified batteries undergo rigorous abuse, environmental, and lifecycle testing to ensure they meet safety standards and regulatory compliance. Third-party laboratories, such as TÜV SÜD, provide comprehensive testing and documentation, supporting your declaration of conformity and global battery pack certifications.
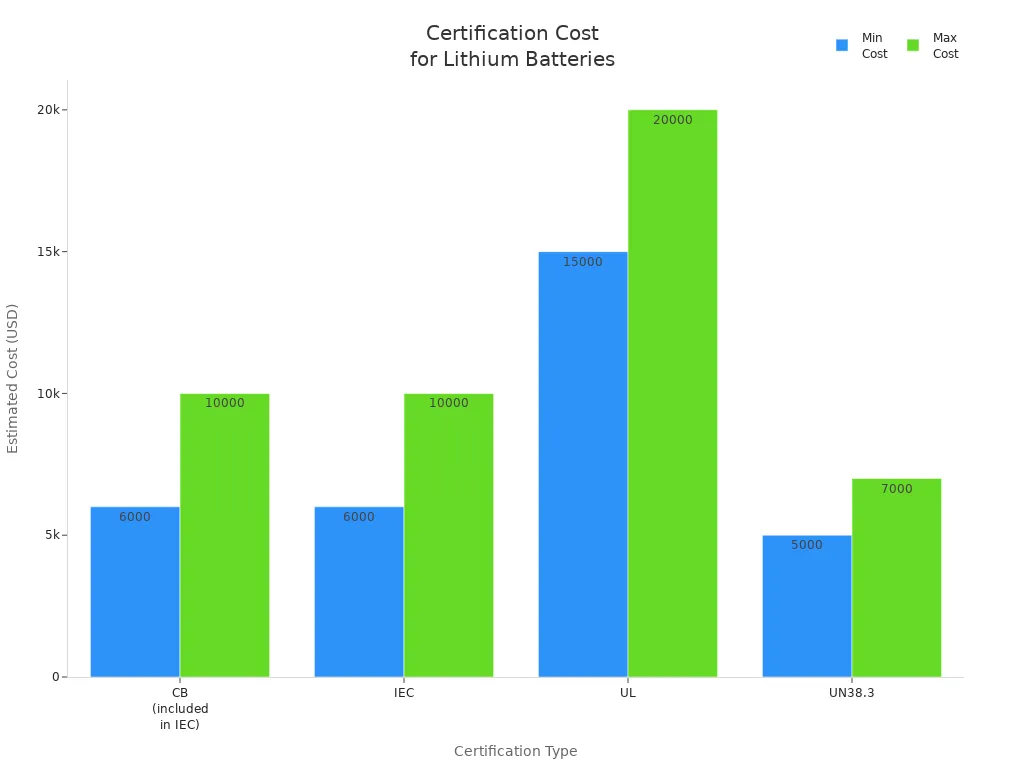
Note: Certification costs and lead times vary by battery design, chemistry, and pack size. For example, UL certification may cost $15,000–$20,000 and take up to 12 weeks, while UN38.3 certification typically costs $5,000–$7,000 and takes 4–6 weeks.
2.3 Application Scenarios
You must align your battery certification strategy with your product’s application scenario and market requirements. The following table summarizes typical application scenarios for each certification:
Certification | Typical Application Scenarios |
|---|---|
UL | Safety and performance testing for lithium cells, battery packs in portable electronics, stationary batteries, energy storage systems, robotics, and security systems. Includes standards like UL 1642 (lithium cells), UL 2054 (portable battery packs), UL 1973 (stationary batteries), and UL 9540 (energy storage systems). |
IEC | International safety standards for portable sealed cells and lithium-ion batteries, especially in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, medical devices, and energy storage systems. Key standards include IEC 62133 (portable sealed cells) and IEC 62619 (lithium-ion batteries for EVs and ESS). |
UN38.3 | Mandatory certification for safe transportation of lithium batteries by air and sea, ensuring batteries do not pose fire or explosion risks during shipment. |
CB Scheme | Facilitates international trade by providing a single certification recognized in over 50 countries, ensuring global safety compliance and easing market entry for manufacturers. Supports various trade agreements to reduce barriers. |
For example, if you manufacture lithium battery packs for medical devices, you must comply with IEC 60601-1 and IEC 62133, in addition to UN38.3 for transport. Robotics and industrial battery packs require UL 2054, IEC 62133, and ISO 12405. Security systems and infrastructure projects demand robust battery certification sets, including UL, IEC, and UN38.3, to ensure uninterrupted operation and regulatory compliance.
Callout: Non-compliance with battery certification requirements can result in shipment rejection, legal penalties, and brand damage. Always maintain up-to-date documentation, including your declaration of conformity and test reports.
Market and Shipping Requirements
You must distinguish between market and shipping requirements. Market requirements focus on product safety, performance, and consumer protection, using standards like UL 2054 and IEC 62133. Shipping requirements prioritize safe transport, with UN38.3 certification and IATA regulations as mandatory elements. The following table highlights these differences:
Aspect | Market Requirements (e.g., Amazon) | Shipping Requirements (International Transport) |
|---|---|---|
Focus | Product safety, performance, consumer protection | Safe transport of hazardous materials |
Key Certifications | UL standards (UL 2054, UL/CSA 62133), UL test reports | UN 38.3 certification, IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations, HMR |
Packaging Requirements | Protection, clear labeling, documentation for consumer awareness | Specific packaging, marking, labeling, and documentation protocols |
Quantity Restrictions | Limits on sale and shipment quantities, prohibition of damaged batteries | Quantity limitations per transport regulations |
Testing Emphasis | Product safety and performance testing | Rigorous transport safety tests (altitude, thermal, vibration, shock) |
Special Provisions | Consumer compliance and trust maintenance | Regulations for smart luggage, small lithium battery-powered vehicles |
Regulatory Goal | Consumer safety and market compliance | Hazard mitigation and regulatory adherence during logistics |
2.4 Importance of Compliance for International Trade and Transport
You must prioritize compliance with global battery pack certifications to access international markets and ensure smooth logistics. Regulatory compliance with CB, IEC, UL, and UN38.3 standards guarantees your lithium batteries meet safety, performance, and transport requirements. Failure to comply can lead to shipment detention, import bans, legal fines, and loss of buyer trust.
Certification | Importance for International Trade and Transport | Main Market | Applicability |
|---|---|---|---|
UN38.3 | Mandatory for safe air and sea transport; prevents shipment rejection and legal penalties | Global | All lithium batteries shipped internationally |
IEC 62133 | Ensures safety performance and structural standards; widely accepted internationally | Global (especially EU, Asia) | Rechargeable lithium batteries |
UL (e.g., UL2054) | Focuses on consumer safety, fire, and shock protection; required for US market access | United States | Consumer and industrial battery products |
CB | Facilitates international market access by harmonizing safety standards | Global | Electrical and electronic products including batteries |
You must also manage supply chain risks by maintaining up-to-date knowledge of regulatory changes, training staff on certification processes, and collaborating with experienced logistics partners. Strong compliance programs help you avoid shipment delays and regulatory penalties.
For custom consultation on battery certification, regulatory compliance, or battery pack design, click here for a custom battery solution.
You must select the right certification for your lithium battery packs based on application, market, and transport needs. The table below highlights the main differences:
Certification | Focus | Application |
|---|---|---|
CB/IEC | Product safety | Global market access |
UL | North American safety | US/Canada compliance |
UN38.3 | Transport safety | International shipping |
Review target market regulations and customer expectations.
Consult experts for guidance.
Prepare accurate documentation and test reports.
FAQ
1. What is the main difference between CB, IEC, UL, and UN38.3 certifications?
Certification | Main Focus | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
CB/IEC | Product safety | Global market entry |
UL | North American safety | US/Canada compliance |
UN38.3 | Transport safety | International shipping |
2. Do you need both UN38.3 and UL/IEC certification for lithium battery packs?
Yes. You need UN38.3 for transport safety and UL or IEC for product safety. Both are mandatory for international trade and compliance.
3. How can Large Power help with lithium battery pack certification?
Large Power provides technical support, testing, and documentation for all major certifications. Request a custom battery solution for expert compliance guidance.




