IEC 60601-1 stands as the global standard for medical power supply safety. You need to meet this standard if you manufacture or regulate medical devices, especially those using lithium battery packs. IEC 60601-1 covers insulation, leakage current, shock, creepage, air clearances, product layout, and risk management. Regulatory agencies in the U.S., Canada, EU, Japan, Brazil, and Australia require compliance, as shown below:
Country | Compliance Requirement |
|---|---|
U.S. | Required |
Canada | Required |
EU | Required |
Japan | Required |
Brazil | Required |
Australia | Required |
Meeting IEC 60601-1 ensures you achieve market access and maintain high safety standards for your medical device.
Key Takeaways
IEC 60601-1 is the global standard for medical power supply safety, essential for manufacturers and regulators of medical devices.
Compliance with IEC 60601-1 ensures market access and high safety standards, protecting both patients and operators.
The standard covers critical aspects like insulation, leakage current, and risk management, which are vital for lithium battery-powered devices.
Meeting IEC 60601-1 requirements helps avoid costly product recalls, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage.
Adhering to IEC 60601-1 builds trust with healthcare providers and opens doors to new market opportunities.
Part 1: IEC 60601-1 Overview
1.1 Standard Definition
You encounter IEC 60601-1 as the primary standard for medical electrical equipment. This standard sets the foundation for safety and performance in devices that support patient care. IEC 60601-1 defines requirements for insulation, leakage current, shock protection, and product layout. You rely on these standards to guide your design and testing processes. The standard applies to a wide range of medical devices, including those powered by advanced lithium battery chemistries such as LiFePO4, NMC, LCO, LMO, LTO, solid-state, and lithium metal. You see IEC 60601-1 referenced in regulatory documents and product certifications across global markets.
1.2 Scope for Medical Power Supply
IEC 60601 covers the essential aspects of medical power supply systems. You must address isolation, leakage current, and fault conditions during product development. The standard divides medical power supplies into three main classifications: Type B, Type BF, and Type CF. Each classification has specific isolation and leakage current requirements. You can review the table below for a quick comparison:
Classification | Isolation Requirements | Leakage Current Limits |
|---|---|---|
Type B | 4,000 VAC input-to-output, 1,500 VAC input-to-ground, 500 VAC output-to-ground | 100 µA (normal), 500 µA (single fault) |
Type BF | 4,000 VAC input-to-output, 1,500 VAC input-to-ground, 1,500 VAC output-to-ground | 100 µA (normal), 500 µA (single fault) |
Type CF | 4,000 VAC input-to-output, 1,500 VAC input-to-ground, 1,500 VAC output-to-ground | 10 µA (normal), 50 µA (single fault) |
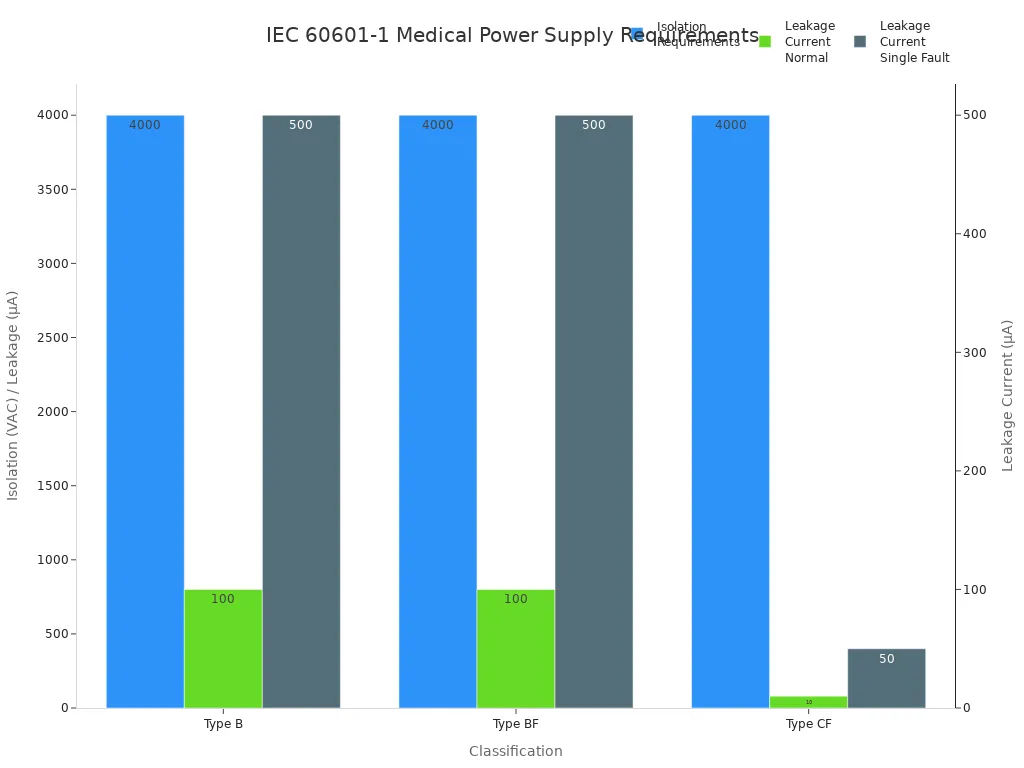
You use these requirements to ensure your products meet strict safety standards. IEC 60601 influences your design choices, component selection, and testing protocols. You find these standards critical in medical, robotics, security, infrastructure, and industrial applications.
1.3 Lithium Battery Pack Relevance
You recognize the growing importance of lithium battery packs in medical devices. IEC 60601-1 addresses the safety requirements for batteries, including LiFePO4, NMC, LCO, LMO, LTO, solid-state, and lithium metal chemistries. You must comply with IEC 60601-1 and related standards to ensure safe operation and market acceptance.
You need to verify insulation and leakage current for battery-powered systems.
You must test for shock protection and creepage distances.
You ensure your lithium battery packs meet IEC 60601-1 requirements before deployment.
You see these standards applied in medical monitoring equipment, surgical robots, security systems, and industrial automation. IEC 60601-1 provides the framework you need to deliver reliable, safe, and compliant products.
Part 2: Safety Requirements in IEC 60601

2.1 Insulation and Leakage Current
You rely on IEC 60601-1 to set strict insulation and leakage current standards for medical equipment, especially those powered by lithium battery packs such as LiFePO4, NMC, LCO, LMO, LTO, solid-state, and lithium metal. Insulation prevents unintended current flow, protecting both patients and operators. Leakage current limits ensure that even under fault conditions, your device does not expose patients to dangerous electrical levels.
IEC 60601 mandates maximum allowable leakage current for patient-connected devices. You must verify these values during testing and certification:
Type | Normal Conditions | Single-Fault Conditions |
|---|---|---|
Type B | 100µA | 500µA |
Type BF | 100µA | 500µA |
Type CF | 10µA | 50µA |
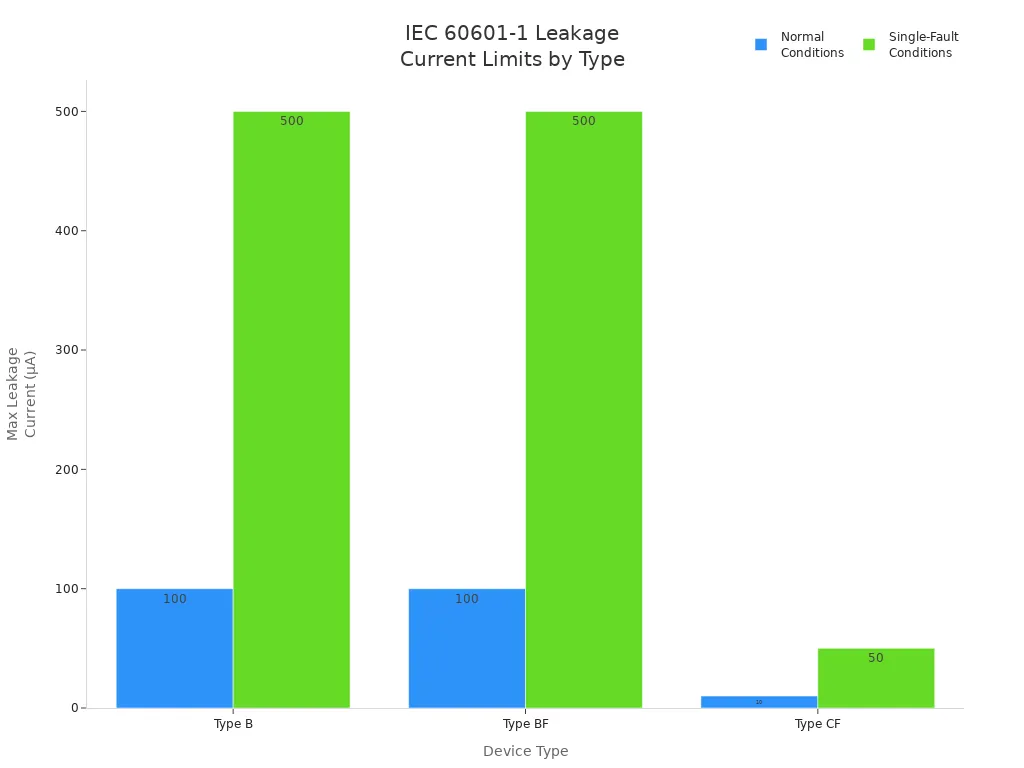
You see these requirements applied in medical monitoring systems, surgical robots, and industrial automation platforms. For lithium battery-powered devices, you must ensure insulation integrity and manage leakage current, regardless of battery chemistry. IEC 60601-1 does not differentiate between inside and outside the patient environment, which means you must maintain safety across all use cases.
2.2 Shock and Creepage Protection
IEC 60601-1 defines protection against electric shock through equipment classification and insulation requirements. You must implement Means of Patient Protection (MOPP) and Means of Operator Protection (MOOP) to minimize risk. For devices in contact with patients, you need to provide two levels of MOPP, ensuring that even minimal leakage currents are controlled.
IEC 60601-1 defines protection against electric shock through the classification of medical electrical equipment into different classes, each with specific safety requirements. It emphasizes the importance of Means of Patient Protection (MOPP) and Means of Operator Protection (MOOP) to minimize the risk of electric shock. For devices in contact with patients, a higher level of protection (2 MOPP) is mandated, ensuring that even minimal leakage currents are managed to protect vulnerable individuals.
You classify medical electrical equipment as Class I or Class II:
Class I: Requires basic insulation and protective earth ground.
Class II: Utilizes reinforced or double insulation, without relying on grounding.
Creepage and clearance distances are critical for preventing shock and ensuring insulation performance. IEC 60601-1 specifies strict requirements for medical power supply circuits:
Equipment Type | Isolation Voltage | Creepage Distance | Insulation Type |
|---|---|---|---|
Type B | 1500 Vac | 2.5 mm | Basic Insulation |
Type BF | 3000 Vac | 5 mm | Double Insulation |
Type CF | 4000 Vac | 8 mm | Double Insulation |
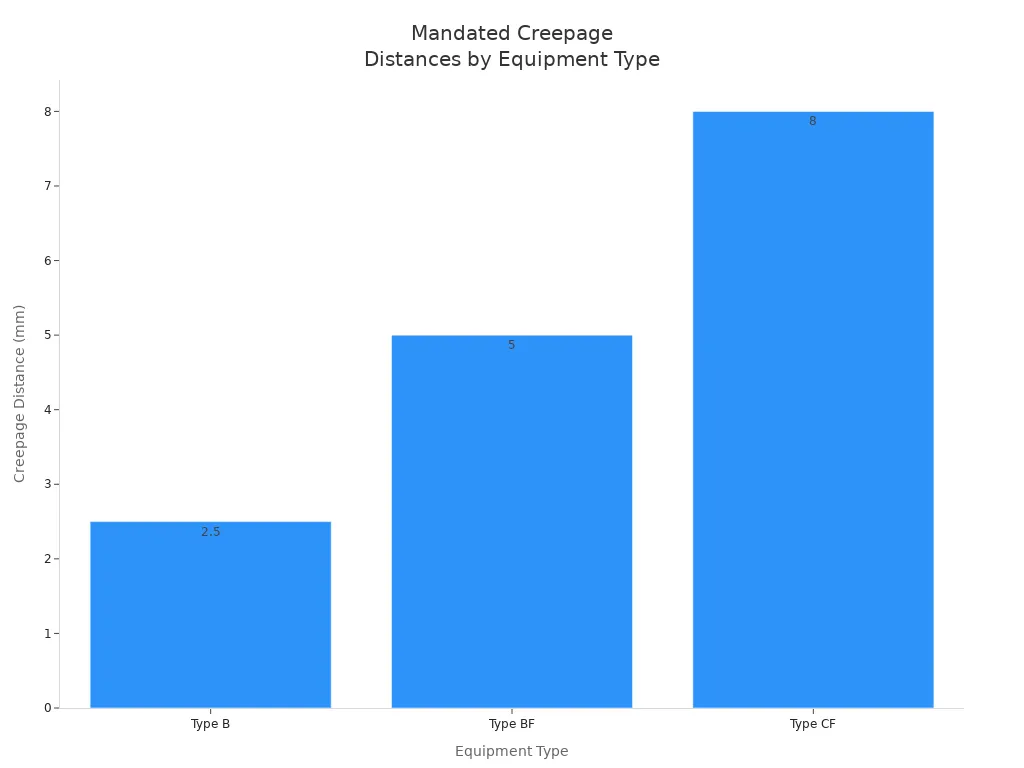
You must ensure that lithium battery-powered medical equipment meets these creepage and clearance distances, especially for high-voltage battery chemistries. For working voltages above 125 V rms, you need greater than 6 mm of creepage. For 250 V rms, you require more than 8 mm. These standards apply across medical, robotics, security, and industrial sectors.
2.3 Risk Management
IEC 60601-1 integrates risk management into product design and certification. You must identify, quantify, and mitigate risks associated with lithium battery-powered medical devices. The standard requires you to comply with ISO 14971, which guides risk management for medical equipment.
Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
ISO 14971 | An international standard for risk management of medical devices, essential for compliance with IEC 60601-1. |
Risk Management Process | Manufacturers must identify, quantify, and mitigate risks associated with the device’s intended use and foreseeable misuse. |
Compliance Evaluation | Compliance is assessed through documentation review rather than on-site audits. |
You must also ensure lithium rechargeable batteries comply with IEC 62133, which covers mechanical, environmental, and electrical safety tests. For primary lithium batteries, IEC 60086-4 applies. Clause 15.4.3.4 of IEC 60601-1 requires strict adherence to these standards for all lithium battery chemistries.
The 3rd edition of IEC 60601-1 mandates that you integrate risk management into product design and certification submission. You conduct thorough analyses, such as Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA), to identify and mitigate potential risks. This process enhances the safety and reliability of your medical electrical equipment, ensuring compliance and market acceptance.
Tip: You should document every step of your risk management process. This documentation supports your certification and demonstrates your commitment to safety for regulators and B2B partners.
You see risk management requirements applied in medical, robotics, security, infrastructure, and industrial applications. By following IEC 60601-1, you deliver safe, reliable, and compliant lithium battery-powered devices to the market.
Part 3: Regulatory and Market Impact
3.1 International Recognition
You operate in a global market where regulatory agencies demand strict adherence to standards. IEC 60601-1 stands as the recognized medical device standard for medical electrical equipment. You see regulatory bodies in the United States, European Union, Japan, Brazil, Canada, and Australia require products to be certified to IEC 60601. This international acceptance means you can design external and embedded medical power supplies for worldwide distribution without needing to meet separate national standards.
You benefit from this harmonization. When you comply with IEC 60601, you reduce the risk of regulatory delays and avoid costly redesigns. Healthcare providers and B2B partners trust devices that meet IEC 60601-1 requirements. You build credibility and demonstrate your commitment to safety and reliability. This recognition extends to lithium battery packs, including LiFePO4, NMC, LCO, LMO, LTO, solid-state, and lithium metal chemistries, which are increasingly used in medical, robotics, and industrial applications.
3.2 Compliance and Certification
You face a complex path when seeking certification for your medical power supply. IEC 60601-1 compliance requires you to meet rigorous safety and performance standards. You must interpret and apply the requirements to your device design, which often demands specialized expertise in electrical engineering and regulatory affairs. You also need to keep up with frequent updates to IEC 60601, which can impact your product development timeline.
You encounter several common challenges during certification:
Accurately interpreting and applying the complex requirements of IEC 60601-1 to your medical device design.
Navigating the need for specialized knowledge in electrical engineering and regulatory standards.
Adapting to ongoing updates and revisions to IEC 60601, which require continuous regulatory surveillance.
Managing the extensive documentation required for certification, which demands meticulous attention to detail.
You must invest in thorough testing and documentation to achieve compliance. This process can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, especially for new companies entering the market. However, when you achieve certification, you minimize the likelihood of delays in product approvals. Compliance streamlines regulatory processes and builds confidence among healthcare providers, facilitating faster market access for your lithium battery-powered medical devices.
Tip: You can further strengthen your market position by aligning your compliance efforts with sustainability initiatives. Review our approach to sustainability and ensure your supply chain meets conflict minerals requirements.
3.3 Market Access for Medical Power Supply
You recognize that compliance with IEC 60601-1 is essential for market access. Regulatory agencies will not approve your medical electrical equipment unless it meets the standard. Failure to comply can prevent your device from entering the market and expose your company to significant financial risks.
Consequence | Description |
|---|---|
Product recalls | Products may be recalled from the market due to non-compliance. |
Liability in lawsuits | Manufacturers may face lawsuits for injuries caused by their products. |
Regulatory penalties | Non-compliance can lead to fines and other regulatory actions. |
Reputational damage | Companies may suffer damage to their reputation, affecting future sales. |
You avoid these risks by ensuring your external and embedded medical power supplies are certified to IEC 60601. You protect your business from lawsuits, regulatory penalties, and reputational harm. You also gain a competitive advantage by demonstrating your commitment to safety and quality.
You see the impact of IEC 60601 compliance across medical, robotics, security, infrastructure, consumer electronics, and industrial sectors. You deliver lithium battery-powered devices that meet global standards, ensuring reliable performance and patient safety. You build trust with B2B partners and healthcare providers, opening doors to new markets and opportunities.
Part 4: IEC 60601 vs Other Standards
4.1 Key Differences
You often compare IEC 60601-1 with other standards such as UL 60601-1 and EN 60601-1 when evaluating medical power supply requirements. Each standard addresses medical electrical equipment, but you notice important differences in component approval, leakage current, and protection features. The table below highlights how UL 60601-1 and IEC 60601-1 differ in their approach to safety and compliance for lithium battery-powered devices:
Aspect | UL 60601-1 Requirements | IEC 60601-1 Requirements |
|---|---|---|
Components | Must comply with ANSI/UL standards; UL approved components preferred | More flexible component approval policies |
Leakage Current | More stringent leakage current requirements | Less stringent requirements |
Moving Parts | Must have end stops or mechanical means to limit travel | No specific requirement |
Oxygen | Additional constructional requirements for oxygen use | Standard requirements |
Conductive Coatings | Nonmetallic surfaces must comply with UL 746C | No specific requirement |
Flammability | Polymeric enclosures must meet flammability requirements | Standard flammability requirements |
Mains Plug | “Hospital Grade” or “Hospital Only” plugs required if available | No specific requirement |
Power Supply Cords | Specifies types of power supply cords | General requirements |
Markings | Additional marking requirements | Standard marking requirements |
You see that IEC 60601 offers more flexibility in component selection and general requirements, which benefits manufacturers working with advanced lithium battery chemistries like LiFePO4, NMC, LCO, LMO, LTO, solid-state, and lithium metal. When you evaluate EN 60601-1, you notice that its scope for battery chargers depends on labeling and intended use. If a charger is labeled only as a charger, it may fall under low voltage and EMC directives instead of medical standards. This can create confusion in regulatory interpretation.
Note: IEC 60601-1 applies consistently to medical electrical equipment, including lithium battery-powered devices, while other standards may have inconsistent definitions for accessories and scope.
4.2 Why IEC 60601-1 Leads in Safety
You choose IEC 60601-1 because it provides unique safety features not found in other standards. You benefit from requirements that address sharp edges, pinch points, and stability under various conditions. IEC 60601-1 emphasizes electrical safety, means of protection, and essential performance in medical environments. The table below summarizes these features:
Safety Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Sharp edges | Prevents injury from sharp edges on medical carts |
Pinch points | Avoids areas where users could get pinched |
Stability under conditions | Ensures stability during use and transport |
Leakage current | Prevents stray voltage that could harm patients |
Durability of markings | Ensures safety markings remain legible |
Tensile safety factor | Ensures carts withstand expected loads |
You rely on IEC 60601 for rigorous testing and risk management. The standard includes a risk management model and a framework for essential performance, which are critical for lithium battery-powered medical devices. Leading manufacturers prefer IEC 60601-1 because it allows you to demonstrate compliance and deliver safe, reliable products for medical, robotics, security, infrastructure, and industrial sectors.
Tip: When you design lithium battery packs for medical electrical equipment, you should prioritize IEC 60601-1 compliance to ensure protection for both patients and operators.
You see IEC 60601-1 as the leading standard for medical power supply across global markets. The table below highlights its widespread adoption and influence:
Compliance Framework | Based on IEC 60601-1 | Market Entry Requirement | Global Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
UL 60601-1 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
EN 60601-1 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
CSA C22.2 No. 606.1 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
You rely on this standard to deliver safe, reliable medical devices for healthcare, robotics, security, infrastructure, and industrial sectors. IEC 60601-1 requires you to implement risk management protocols that help you identify hazards and reduce safety incidents. You protect patients and operators by prioritizing compliance, especially when designing lithium battery packs. You should make IEC 60601-1 your foundation for every medical device project.
FAQ
What makes IEC 60601-1 critical for lithium battery-powered medical devices?
You rely on IEC 60601-1 to ensure safe operation and global market access for lithium battery-powered medical devices. The standard covers insulation, leakage current, and risk management, protecting both patient and operator in medical, robotics, and industrial sectors.
How does IEC 60601-1 address operator safety with lithium battery packs?
You must follow IEC 60601-1 requirements for insulation and creepage distances. These measures protect the operator from electric shock and leakage current. You see these protections applied in medical monitoring, security systems, and industrial automation platforms.
Which lithium battery chemistries are covered under IEC 60601-1?
You use lithium battery chemistries such as LiFePO4, NMC, LCO, LMO, LTO, solid-state, and lithium metal. IEC 60601-1 applies to all these types, ensuring safe integration in medical, robotics, infrastructure, and consumer electronics applications.
What happens if your device fails IEC 60601-1 compliance?
You risk product recalls, regulatory penalties, and lawsuits. Non-compliance can damage your reputation and block market access for lithium battery-powered devices in medical, security, and industrial sectors.
How do you verify IEC 60601-1 compliance for lithium battery packs?
You conduct insulation, leakage current, and shock protection tests. You document risk management processes and ensure operator safety. You must meet strict standards before deploying devices in medical, robotics, and infrastructure environments.




