 OEM batteries represent a specialized manufacturing approach where original equipment manufacturers produce battery cells and packs according to precise specifications provided by device manufacturers. Engineers consistently specify OEM batteries for critical applications due to their documented reliability, verified compatibility, and adherence to established quality standards. These power solutions are manufactured specifically for designated devices including laptops, smartphones, and industrial equipment.
OEM batteries represent a specialized manufacturing approach where original equipment manufacturers produce battery cells and packs according to precise specifications provided by device manufacturers. Engineers consistently specify OEM batteries for critical applications due to their documented reliability, verified compatibility, and adherence to established quality standards. These power solutions are manufactured specifically for designated devices including laptops, smartphones, and industrial equipment.
The fundamental distinction lies in the manufacturing process itself. OEM batteries undergo comprehensive testing protocols to verify they meet the exact quality and safety parameters established by the original device manufacturer. Performance data consistently demonstrates that OEM batteries outperform non-OEM alternatives, primarily due to the stringent manufacturing controls and material specifications required during production.
For engineers evaluating OEM battery versus aftermarket options, the decision involves balancing compatibility requirements against cost considerations. OEM batteries deliver precise voltage matching and thermal characteristics, though they typically require higher initial investment. The OEM battery manufacturing model operates on a build-to-specification basis where device manufacturers provide detailed requirements including voltage parameters, capacity specifications, physical dimensions, and thermal management requirements, which the battery manufacturer then implements through controlled production processes.
OEM battery selection becomes particularly critical in applications where power system reliability directly affects operational safety or mission success. Understanding the technical differences between OEM and aftermarket battery solutions enables engineers to make informed decisions based on application requirements, performance specifications, and total cost of ownership rather than initial purchase price alone.
What OEM Batteries Really Are (Not What You Think)
 Image Source: MANLY Battery
Image Source: MANLY Battery
Common misconceptions persist about OEM battery manufacturing in the electronics industry. OEM batteries represent a specific manufacturing model where battery producers manufacture cells and battery packs according to detailed specifications provided by equipment manufacturers rather than generic replacement components.
Definition of OEM Battery in Engineering Context
Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) refers to companies that produce components based on specifications provided by another company. The OEM relationship involves precise technical partnerships between device manufacturers and battery production facilities. As a custom battery manufacturer, our role centers on receiving comprehensive technical requirements—including voltage parameters, capacity specifications, physical dimensions, thermal management requirements, and safety certifications—then manufacturing battery products that meet those exact parameters. OEM batteries are manufactured according to the precise specifications and requirements established by the brand they are designed for. The manufacturing process includes mandatory testing protocols to verify compliance with quality and safety standards specified by the original brand.
How OEM Batteries Are Manufactured to Spec
OEM battery manufacturing follows established production protocols:
- Specification Receipt– Technical documentation including dimensions, capacity, voltage parameters, and performance requirements from the design entity
- Material Procurement– Sourcing battery cells, protection circuits, and enclosure materials that meet specified parameters
- Production Setup– Configuring dedicated manufacturing lines for the specific battery model
- Quality Control– Implementing testing procedures throughout production to verify performance characteristics
Manufacturing teams work directly from provided design specifications. Each battery undergoes inspection at multiple production stages to confirm performance characteristics match required specifications. This controlled process ensures consistent output that meets the established technical parameters.
Difference Between OEM and ODM Batteries
The distinction between OEM and ODM battery manufacturing lies in design responsibility and development control.
OEM manufacturers focus exclusively on production based on designs provided by another company. ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) operations involve both design and production responsibilities. ODM manufacturers develop the battery design from initial concept through production, while OEM manufacturers produce according to specifications they receive from the design entity.
The technical implications affect project development significantly. ODM projects require extended development timelines for design validation and testing. OEM projects can proceed directly to production once specifications are finalized. OEM batteries typically undergo more comprehensive quality control processes to meet the exact standards established by the associated brand. The choice between OEM and ODM approaches depends on whether the customer has completed their battery design or requires design services as part of the manufacturing engagement.
5 Common Myths About OEM Batteries Debunked
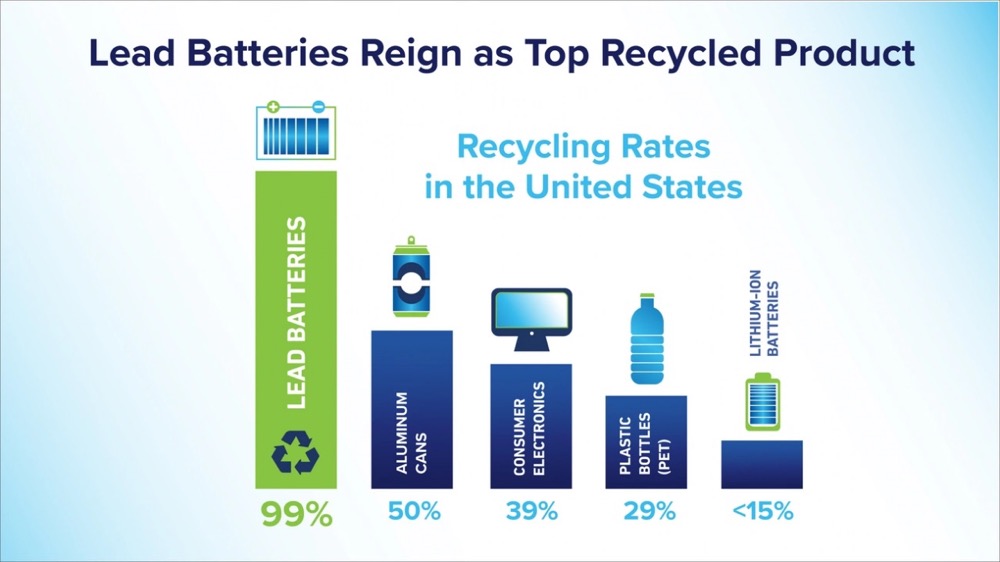 Image Source: Data Center Dynamics
Image Source: Data Center Dynamics
Industry misconceptions about OEM batteries continue to influence engineering decisions despite available performance data and established manufacturing standards. The battery industry faces persistent misinformation that affects procurement strategies across multiple applications.
Myth 1: OEM Batteries Are Just Rebranded Products
OEM batteries undergo specific testing protocols including capacity verification, voltage stability analysis, and thermal performance validation before production release. The manufacturing process requires adherence to design specifications provided by the device manufacturer, including precise voltage tolerances, capacity requirements, and thermal management parameters. Generic alternatives typically lack these manufacturer-specific validation procedures and standardized performance criteria.
Myth 2: OEM Batteries Are Always More Expensive
OEM batteries typically cost more upfront than aftermarket alternatives, yet cost analysis must consider total operational lifetime. Quality aftermarket batteries can reduce initial costs by 20-40% while providing 5-8 years of service under normal usage conditions. Critical applications often justify OEM battery costs through extended operational life, reduced replacement frequency, and lower total cost of ownership.
Myth 3: OEM Batteries Don’t Offer Customization
OEM battery manufacturing operates on a build-to-specification model where customization represents the core service offering. Battery manufacturers routinely modify cell configurations, form factors, discharge rate capabilities, and thermal management systems based on application requirements. OEM services include custom protection systems, battery management software, mechanical design modifications, and branding elements tailored to specific applications.
Myth 4: Aftermarket Batteries Perform the Same
Performance data reveals measurable differences between OEM and aftermarket battery systems. OEM batteries maintain voltage stability throughout discharge cycles and demonstrate superior thermal management under varying load conditions. Comparative testing shows aftermarket batteries exhibit performance variability that can reduce overall system efficiency, particularly in applications with demanding power requirements.
Myth 5: OEM Batteries Are Only for Big Brands
OEM battery manufacturers serve diverse market segments including medical equipment, robotics, security systems, and industrial automation regardless of production volume or company size. The manufacturing approach scales from prototype development through high-volume production, making OEM services accessible to organizations with varying technical requirements and budget constraints.
Why Engineers Trust OEM Batteries in Critical Systems
 Image Source: ATS Industrial Automation
Image Source: ATS Industrial Automation
Critical system applications require power solutions that meet exacting performance specifications under demanding operational conditions. Engineers specify OEM batteries for these applications because the technical advantages extend significantly beyond basic device compatibility.
Precision Fit and Voltage Matching in OEM Design
Voltage compatibility represents a fundamental engineering requirement that cannot be compromised in critical applications. OEM batteries maintain exact voltage specifications established by the device manufacturer, typically within ±0.1V tolerance throughout the discharge cycle. Even minor voltage deviations between the battery pack and system electronics can cause performance degradation or component stress, making precise voltage matching essential. The electrical characteristics of OEM batteries are validated against the specific load profiles and operating conditions of the target device, ensuring optimal power delivery without compromising sensitive electronic components.
OEM Battery Quality Control and Safety Standards
Quality control processes in OEM battery manufacturing focus on identifying and eliminating potential failure modes before deployment. Detection of latent cell defects represents a critical priority, as these defects are responsible for the majority of safety and reliability issues in battery applications. Advanced quality control techniques such as high-throughput CT scanning provide effective methods for identifying potential cell failures during manufacturing, enabling the removal of defective units before they reach critical applications.
Long-Term Reliability in Industrial Applications
Industrial environments demand consistent power performance across extended operational periods and challenging environmental conditions. OEM batteries address these requirements through application-specific designs that incorporate thermal management systems tailored to the operational parameters of the target equipment. These designs often include integrated cooling systems featuring smart fans, heat shielding materials, and thermal monitoring sensors that work together to maintain stable battery operation during continuous duty cycles.
Warranty and Support Advantages of OEM Batteries
Warranty coverage for OEM batteries typically extends from 18 to 48 months depending on the battery chemistry, capacity, and intended application. This extended warranty period reflects manufacturer confidence in the reliability and performance characteristics of their products. The warranty process for OEM batteries can usually be managed directly through the original equipment manufacturer, providing streamlined replacement procedures and technical support throughout the product lifecycle.
OEM Battery vs Aftermarket: What the Data Shows
Performance testing data provides quantitative comparison between OEM and aftermarket battery solutions across multiple operational parameters. Battery performance varies significantly depending on application requirements, environmental conditions, and quality control processes implemented during manufacturing.
Failure Rate Comparison in Field Tests
Independent testing by ARAMARK compared battery-induced failure rates for OEM versus third-party batteries across multiple medical devices. Their data showed no significant difference in failure rates between OEM-supplied batteries and third-party alternatives. The average battery-induced failure rates varied from approximately 4% to 70% per year, with wide variations in standard deviation. However, these results must be interpreted within the context of specific test conditions and equipment types, as longer-term field studies often reveal performance differences that short-term testing may not detect.
Cycle Life and Capacity Retention Differences
Capacity retention—the ratio of discharge capacity to initial capacity after multiple cycles—represents a critical performance metric. Battery cycle life testing demonstrates measurable differences between OEM and aftermarket solutions. OEM EV batteries typically maintain better build quality, requiring less frequent replacement. Aftermarket hybrid batteries can achieve 5-8 years of service with normal driving habits (approximately 12,000 miles annually), though performance consistency varies significantly between manufacturers. The faster you discharge or the lower the temperature, the lower the capacity of any battery, regardless of origin.
OEM Battery Certification and Compliance Standards
Certification standards establish fundamental safety benchmarks for battery performance. Many manufacturers implement digital security codes that restrict aftermarket battery compatibility. For non-critical applications, aftermarket batteries may provide adequate performance, but liability considerations often outweigh potential cost savings. Regulatory compliance becomes particularly important when batteries are used in applications subject to safety standards or transportation requirements.
Case Study: OEM Battery Use in Medical Devices
Medical device testing by ARAMARK evaluated battery performance across defibrillators, infusion pumps, and ventilators. “Infusion Pump A” exhibited significantly higher battery failure rates, ultimately leading to a manufacturer recall. This case demonstrates why healthcare facilities o ften specify custom battery solutions despite higher initial costs—the potential consequences of power system failure in medical applications require the highest reliability standards available.
Contact Large Power, leading lithium battery maker for custom battery/OEM battery requirement.
Conclusion
The technical evidence and comparative data establish clear performance distinctions between OEM and aftermarket battery solutions. While aftermarket alternatives offer initial cost advantages, OEM batteries provide measurable benefits through precise engineering specifications, controlled manufacturing processes, and application-specific design optimization.
Professional engineers specify OEM batteries for critical applications because the manufacturing standards ensure consistent performance characteristics. The quality control protocols implemented during OEM production eliminate many of the variables that can affect long-term reliability in demanding operational environments.
Medical devices, industrial control systems, and mission-critical infrastructure require power sources where performance predictability outweighs initial cost considerations. The comprehensive warranty coverage typically available with OEM batteries provides additional protection against unexpected failures that could compromise system operations.
Field testing data reveals important performance differences over extended operational periods. While some studies indicate comparable short-term failure rates between OEM and aftermarket options, long-term evaluation consistently demonstrates superior capacity retention and cycle life characteristics from properly engineered OEM solutions. These performance advantages become particularly significant in applications where power system failures result in operational disruption or safety concerns.
The selection criteria for OEM versus aftermarket batteries should address specific application requirements including operational environment, reliability expectations, and total cost of ownership calculations. For applications requiring consistent performance over extended service periods, OEM battery solutions from established manufacturers typically provide superior long-term value despite higher initial investment.
Custom lithium ion battery solutions offer the additional advantage of tailored specifications that address unique application requirements. When system reliability requirements exceed standard commercial battery capabilities, the engineering flexibility available through OEM manufacturing processes enables optimization of power system performance for specific operational demands.
Key Takeaways
Understanding the real differences between OEM and aftermarket batteries helps engineers make informed decisions for critical applications where reliability and performance matter most.
- OEM batteries are precision-engineered to exact specifications, not just rebranded products, ensuring optimal compatibility and performance for specific devices.
- While OEM batteries cost more upfront, they deliver superior long-term value through extended lifespans, better capacity retention, and comprehensive warranty coverage.
- Engineers trust OEM batteries in critical systems because they undergo rigorous quality control, maintain precise voltage matching, and offer customization capabilities.
- Data shows OEM batteries excel in cycle life and thermal management, making them essential for medical devices, industrial equipment, and mission-critical applications.
- Custom battery manufacturers provide OEM solutions for companies of all sizes, debunking the myth that these services are only available to major brands.
For applications where failure isn’t an option—from medical devices to industrial systems—the investment in properly engineered OEM batteries pays dividends through consistent performance, reduced maintenance costs, and peace of mind that generic alternatives simply cannot match.
FAQs
Q1. What are the main advantages of using OEM batteries? OEM batteries are designed to meet strict quality standards, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. They undergo rigorous testing, offer precise voltage matching, and provide better long-term reliability compared to aftermarket alternatives.
Q2. Are non-OEM batteries safe to use? While some non-OEM batteries may be safe, they often lack the rigorous safety testing and certification processes that OEM batteries undergo. This can potentially lead to issues like overcharging or overheating, especially in critical applications.
Q3. How do OEM batteries differ from aftermarket options in terms of performance? OEM batteries typically offer superior cycle life, better capacity retention, and more consistent performance over time. They are specifically engineered to meet the exact specifications of the devices they power, ensuring optimal compatibility and efficiency.
Q4. Are OEM batteries worth the higher cost? While OEM batteries often have a higher upfront cost, they generally provide better value in the long run. Their extended lifespan, reduced replacement frequency, and comprehensive warranty coverage often offset the initial price difference, especially in critical or industrial applications.
Q5. Can small companies or projects benefit from OEM battery solutions? Absolutely. Many custom battery manufacturers cater to diverse industries and organizations of various sizes. OEM battery solutions are available for a wide range of applications, from medical equipment and robotics to security systems and industrial devices, regardless of company scale.




