You design battery packs for handheld ultrasound and ECG monitors with a focus on custom lithium-ion solutions. Medical equipment demands lithium-ion batteries that deliver high energy density and compact size. You face challenges with miniaturization, energy density, device integration, biocompatibility, and regulatory compliance. The table below highlights the most common issues:
Design Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Miniaturization | Batteries need to be compact enough for portable medical devices. |
Energy Density | Batteries must provide sufficient energy in a small package for device performance. |
Device Integration | Batteries should integrate seamlessly with medical devices. |
Biocompatibility | Batteries must be safe for use, especially when in contact with skin. |
Regulatory Compliance | Batteries must adhere to strict regulations for safety and efficacy. |
You balance battery life, lithium-ion battery performance, and medical-grade safety from the start. Your process integrates lithium-ion battery packs with medical devices, ensuring reliable operation.
Key Takeaways
Designing battery packs for medical devices requires a focus on high energy density and compact size to ensure portability and performance.
Integrate advanced battery management systems to monitor battery health and enhance safety, preventing issues like overcharging and overheating.
Ensure compliance with strict regulatory standards to guarantee safety and reliability in medical battery applications.
Part 1: Custom Lithium-Ion Battery Packs for Medical Devices

1.1 Design Requirements for Battery Packs
You must address several critical factors when designing battery packs for handheld ultrasound machines and ECG monitors. Medical battery packs require high energy density, compact size, and robust safety features to meet the demands of portable medical devices. You need to select battery chemistry that ensures performance and safety. Discharge rates play a vital role in predicting runtime and maintaining device reliability. Protection mechanisms prevent overcharging and overdischarging, which can lead to battery failure. Mechanical design must balance protection and functionality while complying with healthcare standards. Effective thermal management helps prevent overheating and extends battery life.
Tip: Always validate every batch of certified batteries to prevent failures that could risk patient safety.
Medical device standards strongly influence your design requirements. The table below summarizes key regulatory and quality considerations:
Requirement Type | Description |
|---|---|
Regulatory Compliance | Varies by device class; Class III devices require pre-market approval and oversight. |
Safety Standards | Batteries must be free from contaminants and safe for patient use. |
Quality Assurance | Certification processes like ISO 13485 and ISO 9001 ensure quality and reliability. |
Validation | Every batch of batteries must be validated to prevent failures that could risk patient safety. |
You must ensure that your battery packs meet all safety standards and certifications to guarantee reliable operation in medical equipment.
1.2 Selecting High-Performance Lithium-Ion Batteries
Selecting high-performance lithium-ion batteries is essential for medical devices such as portable ultrasound scanners and ECG monitors. You should consider lithium-ion batteries for their high energy density, long cycle life, and low self-discharge rates. These characteristics make lithium-ion batteries ideal for medical battery applications, including heart pumps and other critical devices.
You may also evaluate lithium thionyl chloride batteries for high-reliability applications, such as implantable medical devices, due to their stability and long shelf life. Custom lithium-ion battery packs allow you to optimize capacity based on device needs, maintain low self-discharge rates for reliable performance, and provide precise voltage control for stable power delivery.
The table below compares common lithium-ion chemistries used in medical battery packs:
Chemistry Type | Platform Voltage | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) | Application Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|---|
NMC | 3.7 V | 180-220 | 1000-2000 | Medical, robotics, consumer electronics |
LCO | 3.6 V | 150-200 | 500-1000 | Medical, industrial, security |
LMO | 3.7 V | 100-150 | 300-700 | Medical, infrastructure |
LTO | 2.4 V | 70-110 | 3000-7000 | Medical, industrial |
LiFePO4 | 3.2 V | 90-160 | 2000-5000 | Medical, infrastructure, robotics |
Solid-State Battery | 3.7 V | 500-700 | 2000-5000 | Medical, industrial |
You should conduct performance testing, capacity testing, safety testing, and environmental testing to evaluate high-performance lithium-ion batteries for medical battery applications. Manufacturing quality control ensures consistent quality and reliability.
Note: Robust battery management systems (BMS) are essential for monitoring battery conditions and ensuring battery safety in medical devices.
1.3 Optimizing Battery Life and Size
You must optimize battery life and size to meet the demands of portable medical devices. Advanced materials and nanotechnology help you enhance battery performance and reduce size. High energy density solutions allow you to achieve longer runtimes without increasing weight. Effective power management schemes, such as low-power microcontrollers, extend operational time for medical battery packs.
You should carefully select battery chemistry to balance energy density with safety and reliability. Custom battery packs provide optimized capacity and precise voltage control, which improves performance and reliability. For example, a leading hospital in Germany switched to custom 7.4V 20Ah lithium-ion battery packs for patient monitoring devices, resulting in a 35% longer runtime per charge and a 50% reduction in battery replacements over two years.
The average lifespan of lithium-ion battery packs in handheld medical devices is approximately 300 cycles, translating to about 3-5 years under normal usage conditions. You must implement advanced cooling systems and robust battery management systems to prevent overheating and ensure safe operation. Regular maintenance further reduces the risk of battery failure.
Cost implications for designing custom lithium-ion battery packs include battery cell chemistry, configuration, battery management system features, mechanical and structural design, thermal management, certifications, system integration, and engineering time. You must balance these factors to achieve optimal performance, safety, and compliance for medical battery packs.
If you need a custom solution for your medical devices, click here for custom consultation.
Part 2: Safety, Compliance, and Integration of Medical Battery Packs
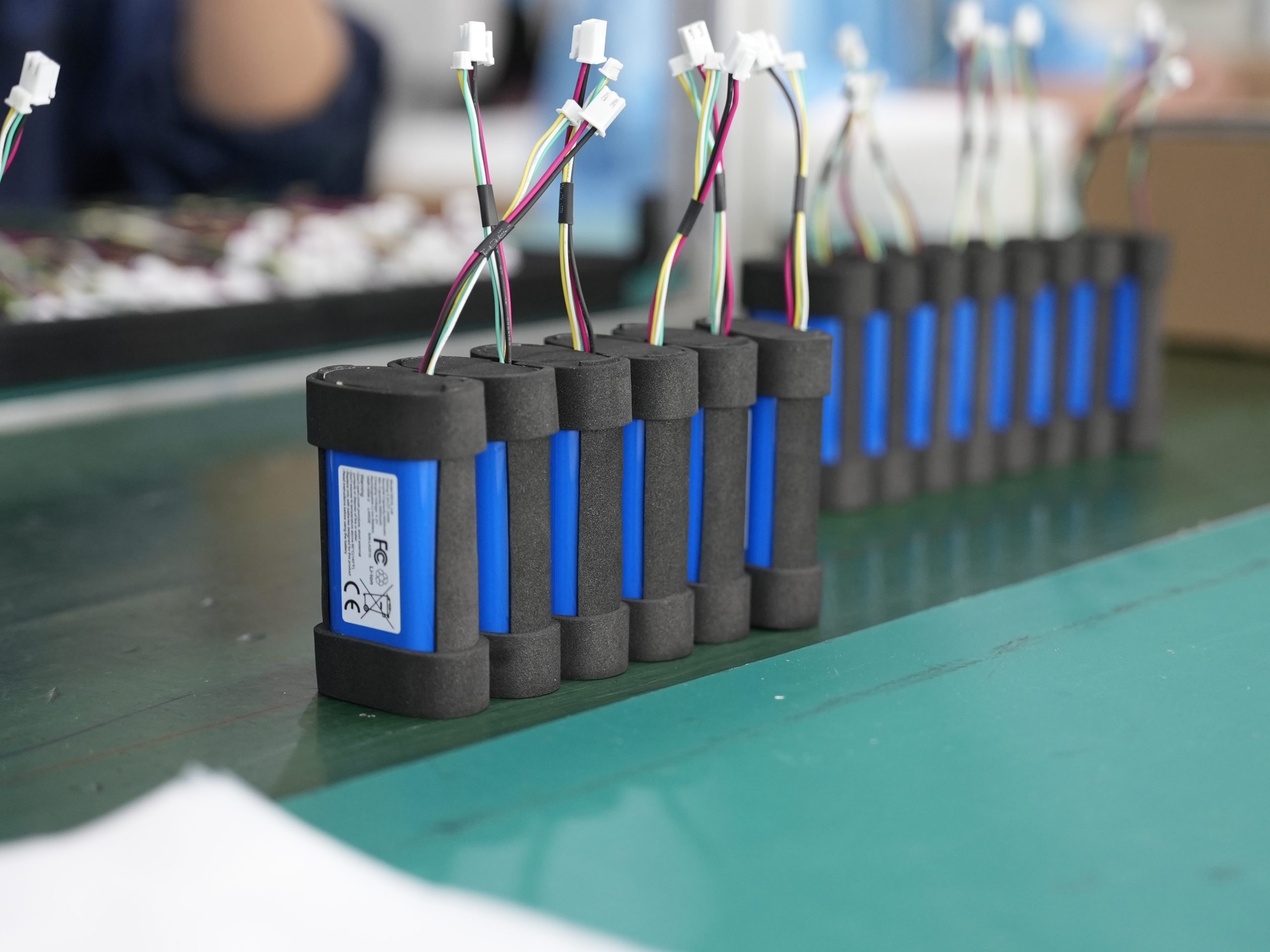
2.1 Battery Management Systems and Safety Features
You must integrate advanced battery management systems (BMS) into medical battery packs to ensure reliable operation and safety. These systems monitor lithium-ion batteries in real time, protecting medical devices from risks such as overcharging, overheating, and electrical faults. You can see the main safety features in the table below:
Safety Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Alarm and Safety Features | Notify users of potential battery issues, reducing accident risks and enhancing battery life. |
Battery Balancer | Ensures balanced charging and discharging, preventing damage and extending battery lifespan. |
Electrical Management Protection: Current | Monitors current and cell voltages, preventing unsafe operation and responding to load changes. |
Electrical Management Protection: Voltage | Maintains operation within safe voltage ranges, adjusting charging current as needed. |
Thermal Management Protection: Temperature | Manages temperatures to ensure optimal performance and prevent overheating. |
You benefit from features such as overcharge protection, over-discharge protection, temperature monitoring, and short-circuit protection. These functions help maintain battery health and device performance, especially in critical medical equipment. Compliance with UL 2054 and thermal runaway suppression further enhance safety.
2.2 Regulatory Compliance for Medical Battery Packs
You must comply with strict global standards when designing medical battery packs. The table below highlights key regulatory standards:
Standard | Purpose | Impact on Future Regulations |
|---|---|---|
Battery safety requirements | Sets benchmarks for future safety | |
UN38.3 | Transport safety for lithium batteries | Ensures safe shipping of medical devices |
You need to pass tests such as altitude simulation, thermal test, vibration, shock, short circuit, impact, overcharge, and forced discharge. The certification process involves submitting requests, identifying system components, selecting accredited labs, completing testing, preparing documentation, and paying fees. You receive official certification after meeting all requirements. Manufacturers must monitor products and ensure compliance with Articles 6-20, including market surveillance and removable batteries by 2027 for most devices.
2.3 Charging Solutions for Medical Devices
You should select charging solutions that maintain battery health and support medical device performance. Wireless charging, especially inductive coupling, eliminates physical connections and reduces wear on lithium-ion batteries. This method enhances longevity and reliability for medical battery packs. You must design wireless power transfer systems to address challenges posed by the human body and ensure efficient energy transfer.
When integrating custom lithium-ion battery packs, you should use standardized interfaces for compatibility, match voltage and capacity to device requirements, and schedule routine assessments. Ergonomic considerations include flexible battery shapes for comfort and durability, especially in wearable medical equipment. High power capacity, small size, and reliability remain essential for both handheld and wearable devices.
If you need a custom solution for your medical devices, request a custom consultation.
You achieve success in designing custom lithium-ion battery packs for medical devices by focusing on safety, compliance, and integration. Choose suppliers with proven experience and certifications. Follow these best practices for medical battery management systems:
Prioritize overcharge protection and thermal monitoring.
Maintain regular BMS inspections.
Use robust hardware and software.
Quality Assurance Standard | Impact on Safety and Compliance |
|---|---|
ISO 13485 | Ensures safe integration into medical devices |
ISO 14001 | Addresses environmental compliance and safety |
RoHS | Mitigates risks from toxic materials |
REACH | Ensures safe chemical use in battery production |
Dispose of lithium-ion batteries responsibly to protect health and the environment.
FAQ
What factors should you consider when selecting lithium-ion battery packs for medical devices?
You should evaluate energy density, cycle life, platform voltage, and safety certifications. Large Power offers custom battery solutions.
How do lithium-ion chemistries compare for handheld medical devices?
Chemistry | Platform Voltage | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|
NMC | 3.7 V | 180-220 | 1000-2000 |
LCO | 3.6 V | 150-200 | 500-1000 |
LiFePO4 | 3.2 V | 90-160 | 2000-5000 |
Solid-State | 3.7 V | 500-700 | 2000-5000 |
Why should you choose Large Power for custom lithium battery pack solutions?
You gain access to certified engineering, robust battery management systems, and tailored integration.




