You depend on portable lab scales for accurate results wherever your work takes you. Lithium batteries make this possible, giving you both mobility and reliability. The demand for portable lab equipment keeps rising, fueled by advances in technology, increased healthcare spending, and more chronic diseases.
The market is set to grow from USD 2,967.54 million in 2020 to USD 3,587.54 million by 2028.
Professionals like you choose lithium batteries because they provide consistent power, long cycle life, and safety through strict testing.
Key Takeaways
Lithium batteries provide portable lab scales with the mobility needed for accurate measurements in various settings, from healthcare to environmental testing.
Choosing lithium batteries with high energy density ensures longer usage times and reduces the need for frequent recharging, enhancing efficiency in the field.
Safety features in lithium batteries, such as pressure-relief devices, help prevent overheating and ensure reliable operation in demanding environments.
Proper disposal and recycling of lithium batteries protect the environment and prevent hazardous materials from contaminating ecosystems.
Regularly check battery specifications and certifications to ensure safety and performance, matching the right chemistry to your specific application needs.
Part 1: Mobility with Lithium Batteries

1.1 Portable Lab Scales in Action
You know how important it is to get accurate measurements wherever your work takes you. Portable lab scales powered by lithium batteries let you do just that. You can bring these devices into the field, set them up in remote clinics, or use them in temporary labs. Their lightweight and compact design means you can carry them easily, even when you need to move quickly between locations.
You see portable lab scales making a difference in many real-world situations. Here are some of the most common ways professionals like you use them:
Improving turnaround time for public health microbiological testing
Environmental testing in the field
Point of care testing at patient bedsides
Food safety monitoring in processing plants or markets
Outbreak management in low-resource settings
You might work in healthcare, environmental science, or food safety. In each of these areas, you need reliable, portable power solutions to keep your equipment running. Lithium batteries help you meet tight deadlines and deliver results on-site, not just in the lab.
1.2 Powering Mobility
You want your portable lab scales to work as hard as you do. That means you need batteries that last, weigh little, and fit into small spaces. Lithium batteries stand out because they offer the highest energy density among all common battery types. You get more power in a smaller, lighter package. This is a game-changer for portable devices, where every ounce and inch counts.
When you choose lithium batteries, you unlock true mobility. You can run your portable lab scales for hours without worrying about frequent recharging or swapping out heavy batteries. This makes a big difference in field research, emergency response, and mobile clinics. You can trust your equipment to keep working, even when you are far from a power outlet.
Many portable power solutions now use advanced lithium chemistries like LiFePO4, NMC, and LCO. These options give you a balance of high platform voltage, long cycle life, and excellent energy density. You get reliable performance, whether you are testing water quality in the field or weighing samples in a mobile medical unit.
Tip: Always check the battery specs for your portable lab scales. Look for lithium batteries with proven safety features and certifications. This helps you avoid downtime and keeps your team safe.
You rely on portable power solutions to keep your work moving. With lithium batteries, you get the freedom to go wherever your job takes you, without sacrificing accuracy or reliability.
Part 2: Reliability of Lithium-Ion Batteries
2.1 Consistent Performance
You need portable lab scales that deliver stable results every time. That’s why you rely on lithium batteries. These batteries provide consistent power, so your measurements stay accurate whether you’re working in a hospital, a robotics lab, or an industrial facility. You don’t want to worry about sudden drops in voltage or unexpected shutdowns. With lithium-ion batteries, you get steady performance that keeps your equipment running smoothly.
Let’s look at the technical specifications that make lithium batteries so reliable for portable lab scales:
Specification | Description |
|---|---|
Energy Density | High specific energy enables longer usage times without frequent recharging. |
Lightweight Design | Reduces overall weight of portable lab scales, enhancing portability. |
Long Cycle Life | Ensures longevity and reliability in performance over time. |
Low Self-Discharge Rate | Maintains charge for longer periods, ensuring readiness for use. |
You see these benefits in action across different sectors. In medical labs, lithium batteries keep diagnostic equipment running during long shifts. In robotics, you get precise control and stable power for sensors and actuators. Security teams use portable scales for evidence handling, and infrastructure crews rely on them for field testing. Industrial teams need batteries that last through demanding workdays.
Power stability matters. Here’s how lithium-ion batteries deliver:
Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
High Energy Density | Cobalt-based lithium-ion batteries provide long run-time, making them suitable for portable devices. |
Low Internal Resistance | High ion flow reduces internal resistance, enhancing loading capability and power stability. |
Thermal Stability | Spinel structure in lithium manganese oxide batteries offers high thermal stability, reducing safety risks. |
You want batteries that work in tough environments. Temperature swings can affect reliability. At high temperatures, batteries may discharge faster and risk thermal runaway. At low temperatures, you might see a drop in capacity—sometimes up to 20% at 0°C and over 40% at -20°C. The electrolyte thickens, slowing ion movement and reducing performance. If you leave batteries in cold storage for 24 hours, you’ll notice faster capacity degradation, especially with frequent use.
Tip: Store your batteries at room temperature and avoid exposing them to extreme heat or cold. This helps maintain reliability and extends battery life.
2.2 Long-Term Use
You want your portable lab scales to last. That means choosing batteries with a long cycle life and robust construction. Most lithium-ion batteries offer around 500 cycles, but advanced models like the EcoFlow DELTA 2 Max can reach 3,000 cycles before dropping to 80% capacity. Chemistries like NMC and NCA typically deliver between 500 and 1,500 cycles, making them ideal for frequent use in industrial and medical settings.
Here’s a technical comparison of common lithium battery chemistries used in portable lab scales and other sectors:
Chemistry | Platform Voltage (V) | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|
LCO | 3.7 | 150-200 | 500-1,000 | Consumer electronics, medical devices |
NMC | 3.7 | 180-220 | 1,000-2,000 | Industrial, robotics, infrastructure |
LiFePO4 | 3.2 | 90-160 | 2,000-5,000 | Medical, security, industrial |
LMO | 3.7 | 100-150 | 700-1,500 | Consumer electronics, infrastructure |
LTO | 2.4 | 70-110 | 5,000-10,000 | Industrial, robotics, security |
Solid-State | 3.7 | 250-350 | 2,000-10,000 | Medical, robotics, infrastructure |
Lithium Metal | 3.7 | 350-500 | 1,000-2,000 | Advanced medical, industrial |
You see solid-state batteries and lithium metal batteries emerging in high-demand sectors. These chemistries offer better efficiency, durability, and safety. Silicon anodes and carbon nanotube technology boost energy storage and stability, which is great for long-term use. Lithium-sulfur and magnesium-ion batteries also promise longer cycle life and improved safety.
Battery management systems (BMS) play a key role in reliability. They monitor voltage, temperature, and charge cycles to prevent failures like thermal runaway, swelling, leakage, and over-discharge.
Here are the most common failure modes you should watch for:
Failure Mode | Description |
|---|---|
Thermal Runaway | Excessive heat buildup due to overcharging, punctures, or internal shorts can lead to fires. |
Swelling | Indicates battery degradation; swollen batteries should be replaced immediately. |
Leakage | Can cause significant safety hazards; requires careful handling and disposal. |
Over-Discharge | Reduced performance and potential permanent damage if ignored. |
Charger Mismatch | Using incorrect chargers can lead to overvoltage and battery damage. |
Environmental Stress | Punctures, moisture, or extreme temperatures can compromise battery safety and performance. |
Note: Always use certified chargers and inspect batteries regularly. Replace any battery that shows signs of swelling or leakage.
Recent advancements make lithium batteries even more reliable for portable lab scales. Solid-state batteries use solid electrodes for better durability. Silicon anodes and carbon nanotube technology increase energy storage and efficiency. Lithium-sulfur and magnesium-ion batteries offer longer cycle life and improved safety. Battery management systems optimize performance and longevity, while wireless charging technology adds convenience for busy professionals.
You depend on lithium batteries to keep your portable lab scales working day after day. By choosing the right chemistry and following best practices, you get the reliability and long-term use you need for demanding applications in medical, robotics, security, infrastructure, consumer electronics, and industrial sectors.
Part 3: Safety and Environmental Impact

3.1 Safe Operation
You want your lithium batteries to work safely in every lab setting. Manufacturers design these batteries with safety features that protect you and your equipment. You often see pressure-relief devices and positive temperature coefficient (PTC) resistors built into lithium battery packs. These features help prevent overheating and short circuits, which keeps your portable lab scales running smoothly.
You can boost safety by following best practices for handling and storing batteries:
Store lithium-ion batteries in a temperature-controlled environment, ideally at 15°C (59°F).
Keep the state of charge around 40% to reduce instability.
Use fire suppression systems, such as dry chemical storage or water sprinklers.
Choose fire-rated storage buildings that meet EPA, OSHA, and NFPA standards.
Isolate high-capacity batteries in multi-room storage areas.
You work in medical, robotics, or industrial labs. You know that a safe battery means fewer interruptions and better results. Always inspect batteries for damage before use. Replace any battery that shows swelling or leakage. You can read more about sustainability and safe battery practices here.
Tip: Never mix different lithium battery chemistries like LiFePO4, NMC, or LCO in the same device. This helps you avoid compatibility issues and keeps your equipment safe.
3.2 Responsible Disposal
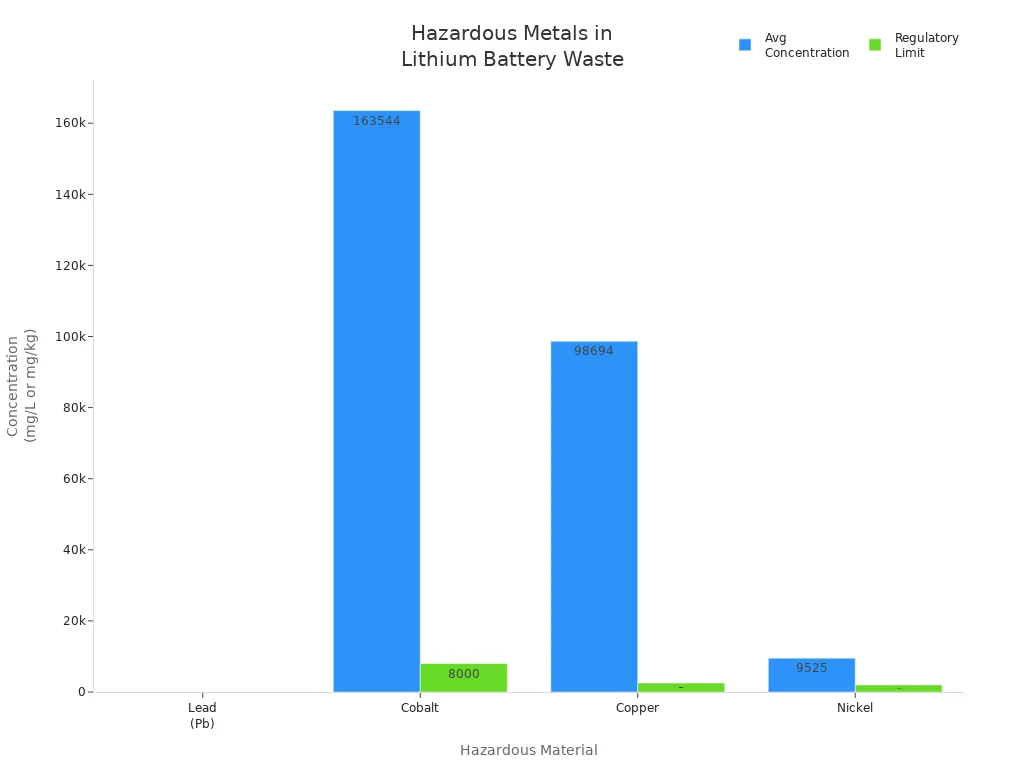
You care about the environment and want your batteries to have a longer lifespan. When a battery reaches the end of its lifespan, you need to dispose of it responsibly. Improper disposal can release hazardous materials into soil, water, and air. Toxic metals like lead, cobalt, copper, and nickel can harm ecosystems and enter the food chain.
Hazardous Material | Average Concentration (mg/L or mg/kg) | Regulatory Limit |
|---|---|---|
Lead (Pb) | 6.29 mg/L | 5 |
Cobalt | 163,544 mg/kg | 8,000 |
Copper | 98,694 mg/kg | 2,500 |
Nickel | 9,525 mg/kg | 2,000 |
Chromium | Exceeded California limits | N/A |
Thallium | Exceeded California limits | N/A |
Silver | N/A | N/A |
You see risks like contamination, fire hazards, and explosions from damaged batteries. You can help by using effective recycling methods:
Hydrometallurgical processes recover metals like cobalt, nickel, and lithium.
Pyrometallurgy uses high temperatures to separate metals.
Mechanical recycling breaks down components with gravity and magnets.
Solvent extraction dissolves and recovers metals.
You support responsible sourcing by choosing battery packs that avoid conflict minerals. Learn more about conflict minerals here. By recycling and disposing of batteries properly, you protect the environment and extend the longer lifespan of your lab equipment.
Part 4: Choosing Lithium Batteries for Portable Lab Scales
4.1 Assessing Needs
You want your portable lab scales to perform reliably in every setting. Start by looking at your power requirements. Think about how long you need your batteries to last and how much power your equipment uses. You should check the internal resistance of each battery. Lower resistance means better energy conversion and stronger power output. Cycle life matters too. You want batteries that can handle many charge and discharge cycles without losing performance.
Temperature can affect battery safety and performance. Test how your batteries behave in hot and cold conditions. Safety testing is also important. Make sure your batteries can handle overcharging, short circuits, and extreme temperatures. You need batteries that meet strict safety standards.
Here’s a quick checklist to help you assess your needs:
Internal resistance testing for energy efficiency
Cycle life testing for long-term reliability
Temperature testing for safe operation in different environments
Safety testing for compliance with lab standards
Tip: Always match your battery choice to your lab’s specific use case. Medical, robotics, and industrial sectors may need different chemistries and technical specs.
4.2 Battery Selection Tips
When you compare batteries for portable lab scales, look at technical data and certifications. You want batteries that meet international safety standards. Here are the most important certifications to check:
UN 38.3 – Safe transportation of lithium batteries
IEC 62133 – Safety for portable lithium batteries
UL 1642 and UL 2054 – Safety for cells and battery packs
CE Marking – EU safety and environmental compliance
RoHS – Restricts hazardous materials
You should also compare battery chemistries and technical specs. Use this table to guide your selection:
Chemistry | Platform Voltage (V) | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|
LiFePO4 | 3.2 | 90-160 | 2,000-5,000 | Medical, security, industrial |
NMC | 3.7 | 180-220 | 1,000-2,000 | Industrial, robotics, infrastructure |
LCO | 3.7 | 150-200 | 500-1,000 | Consumer electronics, medical devices |
LMO | 3.7 | 100-150 | 700-1,500 | Consumer electronics, infrastructure |
LTO | 2.4 | 70-110 | 5,000-10,000 | Industrial, robotics, security |
Solid-State | 3.7 | 250-350 | 2,000-10,000 | Medical, robotics, infrastructure |
Lithium Metal | 3.7 | 350-500 | 1,000-2,000 | Advanced medical, industrial |
When you evaluate manufacturers, look at cycle life, energy density, production costs, thermal safety, voltage requirements, and temperature tolerance. You want a battery pack with consistent performance and robust structural design. Thermal management is key for safety and longevity.
Note: Choose manufacturers with strong support and proven track records in your sector. Reliable batteries keep your portable lab scales running and your results accurate.
Lithium batteries give your portable lab scales the edge in mobility and reliability. Their lightweight design, high energy density, and long lifespan mean you spend less time on battery changes and more time on accurate results. You help the environment by choosing batteries that last longer and reduce waste.
Faster charging and consistent power keep your devices ready for action in medical, robotics, and industrial settings.
Built-in safety features and responsible disposal protect your team and the planet.
Stay informed about new battery technologies—like AI-driven BMS and real-time monitoring—to keep your lab running at its best.
FAQ
What makes lithium batteries ideal for portable lab scales?
Lithium batteries like LiFePO4, NMC, and LCO offer high energy density and long cycle life. You get lightweight power packs that keep your lab scales running in medical, robotics, and industrial settings. These batteries help you work anywhere without frequent charging.
How do I choose the right lithium battery chemistry for my application?
Check your sector’s needs. For medical and industrial labs, LiFePO4 gives you up to 5,000 cycles. NMC works well in robotics and infrastructure with 1,000–2,000 cycles. Use LCO for consumer electronics. Always match platform voltage and energy density to your equipment.
What safety features should I look for in lithium battery packs?
You want packs with pressure-relief devices, PTC resistors, and certified Battery Management Systems (BMS). Look for certifications like UN 38.3, IEC 62133, and UL 1642. These features protect your team and equipment from overheating, short circuits, and other risks.
How do I dispose of lithium batteries responsibly?
Recycle batteries using approved methods like hydrometallurgy or mechanical separation. You help prevent hazardous metals like cobalt and nickel from polluting the environment. Always follow local regulations and choose recycling partners with strong compliance records.
Can lithium batteries handle extreme temperatures in field operations?
Most lithium chemistries work best at room temperature. LiFePO4 and NMC offer good stability, but you should avoid exposing batteries to heat or freezing conditions. Store batteries in climate-controlled areas to maintain performance and safety.




