
Designing Infusion Pump Lithium Batteries for medical devices demands strict compliance with IEC 60601-1 standards. You must prioritize safety and risk management to protect patients and healthcare staff.
Over 56,000 adverse event reports involving infusion pumps occurred in the last five years, including battery failures, serious injuries, and more than 500 deaths.
Robust lithium battery design remains essential for reliability in clinical settings.
Key Takeaways
Follow IEC 60601-1 standards to ensure safety and performance in infusion pump lithium batteries. This helps protect patients and healthcare staff.
Implement advanced battery management systems to monitor voltage, current, and temperature. This reduces risks like overheating and ensures reliable operation.
Design battery enclosures to resist impact and fluid ingress. This protects the battery from physical hazards and extends its lifespan.
Part1: IEC 60601-1 Standards Overview
1.1 Medical Devices and Battery Safety
You face strict expectations when designing battery systems for medical devices. IEC 60601-1 standards set the foundation for patient safety and essential performance. These standards address hazards such as electrical hazards, fire, and mechanical risks. You must consider risk management and hazard analysis at every stage of battery design. By following these requirements, you help prevent incidents that could harm patients or disrupt clinical operations.
1.2 Key IEC 60601-1 Requirements
IEC 60601-1 standards serve as the global benchmark for compliance in medical devices. The International Electrotechnical Commission established these standards to unify safety measures and design requirements worldwide. You must ensure your lithium battery packs meet these requirements for approval and certification. The table below summarizes the scope and purpose:
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Title | Medical electrical equipment – Part 1: General requirements for basic safety and essential performance |
Application | Applies to medical electrical equipment and systems, referred to as ME EQUIPMENT and ME SYSTEMS. |
Purpose | Specifies general requirements and serves as the basis for particular standards. |
“The object of this standard is to specify general requirements and to serve as the basis for particular standards.”
1.3 Impact on Infusion Pump Lithium Batteries
You must integrate IEC 60601-1 requirements into every step of infusion pump lithium batteries design. These standards affect battery selection, custom lithium battery solutions, and the implementation of risk control measures. You need to address hazards such as overheating, leakage, and electrical hazards. Safety testing and hazard analysis become critical for compliance and approval. Your battery design must support essential performance and patient safety. By focusing on robust safety measures, you reduce the risk of failure and ensure reliable operation in demanding medical environments.
Part2: Infusion Pump Lithium Batteries Design Essentials
2.1 Electrical Safety and Protection
You must prioritize electrical safety when designing infusion pump lithium batteries for medical devices. The battery system needs robust protection against hazards such as over-charge, over-discharge, over-current, short circuits, and thermal runaway. These risks can compromise essential performance and patient safety. You should implement advanced battery management systems (BMS) that monitor voltage, current, and temperature in real time.
Tip: Explore more about BMS and PCM here.
A well-designed BMS supports compliance with IEC 60601-1 requirements and enhances reliability. You should select components that meet certification standards and perform thorough testing to verify protection features. Electrical isolation, fusing, and redundant safety circuits further reduce hazards. By integrating these measures, you strengthen risk management and ensure the battery system operates safely in clinical environments.
2.2 Mechanical and Enclosure Design
Mechanical design plays a critical role in protecting lithium battery packs from physical hazards. You must choose enclosure materials that resist impact, vibration, and fluid ingress. The enclosure should shield the battery from accidental drops and exposure to cleaning agents.
You need to design for easy integration into medical devices, considering space constraints and mounting requirements. Secure connectors and locking mechanisms prevent accidental disconnection.
Note: A robust enclosure design supports compliance and extends battery life.
You should also consider custom lithium battery solutions for unique device requirements. By focusing on mechanical protection, you minimize the risk of leakage, swelling, and mechanical failure.
2.3 Performance and Portability
Performance metrics determine the effectiveness of infusion pump lithium batteries in medical devices. You must optimize capacity, cycle life, and energy density to meet clinical demands. The battery should deliver consistent power for extended periods, even during power fluctuations or outages.
In intensive care units, reliable battery operation ensures continuous medication delivery and improves patient stability. You should select lithium chemistries that balance safety, performance, and portability.
Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Enhanced Safety | Protection against over-charge, over-discharge, over-current, short circuits, and thermal runaway. |
Optimized Performance | Precise voltage and current control, cell balancing for maximum capacity and cycle life. |
Data Monitoring & Communication | Real-time monitoring and system integration capabilities. |
Redundant Detection | Real-time monitoring and independent cross-verification. |
Redundant Execution | Physical disconnection mechanisms for added reliability. |
Reduced medication errors
Improved patient stability
You should design the battery for lightweight portability without sacrificing durability. Compact form factors and ergonomic shapes support easy handling and device integration.
2.4 Self-Test and Redundancy
Self-test and redundancy features are essential for compliance and safety in infusion pump lithium batteries. You must implement automated self-test routines that verify battery health and performance at startup and during operation.
Redundant detection systems provide real-time monitoring and independent cross-verification, reducing the risk of undetected faults. Physical disconnection mechanisms add another layer of reliability, ensuring the battery can isolate itself in case of failure.
You should design for continuous data monitoring and communication with the host device. These features support risk management and help meet certification requirements. By integrating self-test and redundancy, you enhance the reliability of battery systems and protect patient safety in critical medical applications.
Part3: IEC 60601-1 Testing and Verification
3.1 Electrical and Functional Tests
You must conduct thorough electrical and functional tests to ensure compliance with IEC 60601-1 requirements for lithium battery packs in medical devices. These tests verify protection against hazards such as over-current, short circuits, and thermal runaway. You need to include Protection Circuit Module (PCM) testing and confirm compliance with IEC 60601-1/A1:2012, which focuses on secondary batteries. The table below outlines key testing requirements:
Testing Requirement | Standard Reference | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Protection Circuit Module (PCM) | IEC 62133-2:2017 | Must be included for safety compliance in battery packs |
Compliance with IEC 60601-1/A1:2012 | Clause 15.4.3.4 | Refers to secondary batteries, not cells |
You should validate essential performance by simulating real-world operating conditions. This process helps you identify potential hazards and supports risk management.
3.2 Environmental and Mechanical Testing
Environmental and mechanical testing ensures your battery systems withstand stress factors found in clinical settings. You must evaluate how temperature and humidity affect lithium battery performance. High temperatures above 40°C can cause permanent capacity loss, while low temperatures may temporarily reduce output. Excess moisture can lead to corrosion in terminals or internal components. The table below summarizes these effects:
Environmental Factor | Effect on Lithium Batteries |
|---|---|
Temperature | High temperatures accelerate chemical reactions, causing permanent capacity loss. Low temperatures reduce immediate output but are generally reversible. |
Humidity | Excess moisture may lead to corrosion in terminals or internal components. |
You should also test for vibration, shock, and drop resistance to meet compliance standards and protect against mechanical hazards.
3.3 EMC and Safety Certification
You must secure certification for lithium battery packs used in medical devices. Certification demonstrates compliance with international safety standards and supports market approval. The table below lists major safety standards and their descriptions:
Safety Standard | Description |
|---|---|
IEC 62133-2:2017 | International safety standard for rechargeable lithium batteries |
UN38.3 | Transportation safety certification |
UL 1642 / UL 2054 | U.S. safety certifications |
ISO 13485 | Medical device quality management system |
IEC 60601 | Compliance for external device batteries ensuring safety standards, leak-proof and short-circuit-proof design |
You should document all testing and certification results to support regulatory submissions and maintain compliance. This process helps you minimize hazards and ensures your battery design meets essential performance requirements for medical devices.
Part4: Integration in Medical Devices
4.1 Form Factor and Space Constraints
You must address strict form factor and space constraints when integrating lithium battery packs into medical devices. Lightweight and slim designs improve portability and usability in diverse healthcare environments. You need to ensure the battery fits within the compact structure of the device. This approach supports essential performance and compliance with industry requirements. Custom lithium battery solutions allow you to tailor the design for unique device geometries, maximizing available space without sacrificing safety or reliability. Careful planning reduces hazards and streamlines certification.
4.2 Thermal Management Solutions
Effective thermal management protects battery systems from overheating and related hazards. You should select solutions that maintain optimal operating temperatures and support compliance with safety standards. The table below outlines recommended thermal management methods for lithium batteries in infusion pumps:
Method | Description |
|---|---|
Air Cooling | Utilizes natural or forced convection to remove heat from batteries. |
Liquid Cooling | Involves direct or indirect cooling methods to efficiently transfer heat away from batteries. |
Phase Change Material (PCM) | Absorbs and releases heat through phase changes, providing passive temperature control. |
Hybrid Cooling | Combines multiple cooling methods for enhanced thermal management performance. |
You must keep lithium battery packs within the optimal temperature range of 25 °C to 40 °C, with a maximum variation of 5 °C. The table below highlights the impact of thermal management on safety and longevity:
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Importance of TM | Effective temperature control is crucial to prevent safety hazards such as thermal runaway. |
Techniques | Active and passive methods, including forced air and liquid cooling, improve reliability. |
Optimal Temperature Range | 25 °C to 40 °C, with a maximum variation of 5 °C. |
Risks of Temperature Fluctuations | High temperatures can cause performance decline and increase the risk of explosion and fire. |
Conclusion | Meticulous thermal management ensures safety, functionality, and longevity of batteries. |
4.3 Durability and Cycle Life
You need to maximize durability and cycle life to meet the rigorous demands of medical devices. Several factors influence the longevity of lithium battery packs:
Battery chemistry
Temperature management
State of charge
Battery management systems
Current levels
Manufacturing quality
Depth of discharge (DoD)
Charging and discharging methods
Temperature
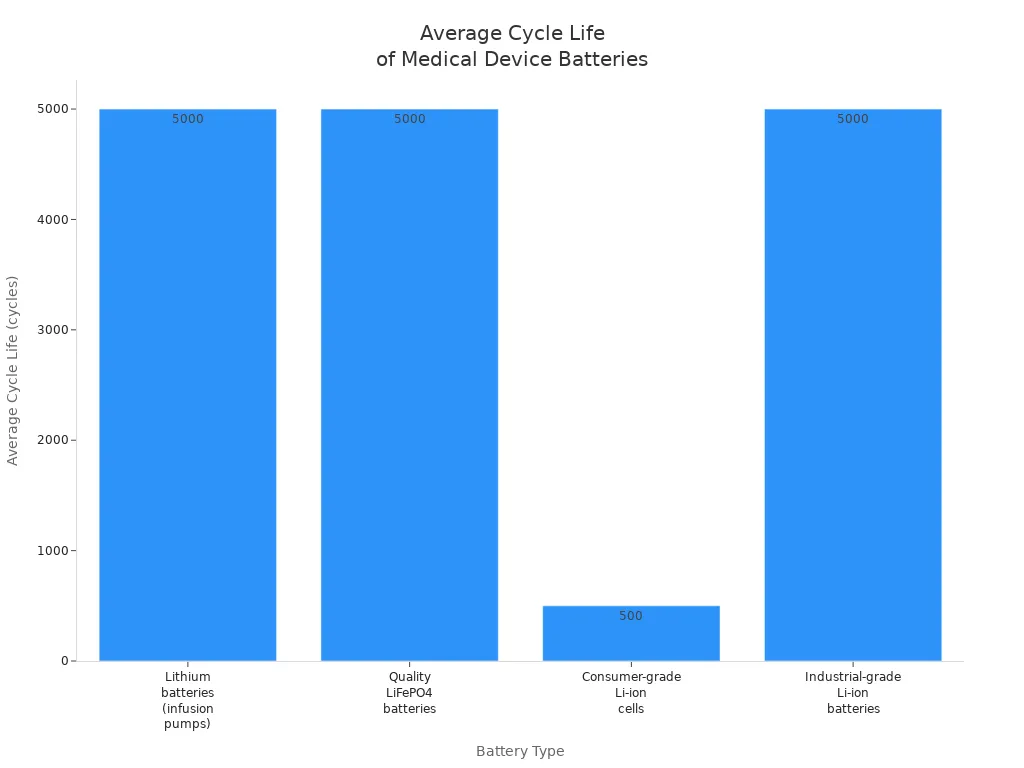
Cycle life varies with depth of discharge. At 100% DoD, you can expect at least 3,000 cycles. At 80% DoD, cycle life increases to 6,000 cycles, and at 50% DoD, it reaches 8,000 cycles. The table below compares average cycle life across battery types used in medical devices:
Battery Type | Average Cycle Life |
|---|---|
Lithium batteries (infusion pumps) | Up to 5,000 cycles |
Quality LiFePO4 batteries | Up to 5,000 cycles |
Consumer-grade Li-ion cells | Around 500 cycles |
Industrial-grade Li-ion batteries | 20-year operational life with similar cycle life |
You should conduct regular testing and risk management to ensure compliance and maintain essential performance throughout the battery’s operational life.
You achieve compliance in medical devices by following these key steps:
Step | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Review component information to ensure compliance with standards. |
2 | Update isolation diagram to reflect the latest design. |
3 | Ensure the test plan is current and comprehensive. |
4 | Verify that marking and labeling meet the required standards. |
5 | Finalize Risk Management Framework (RMF) and essential performance. |
6 | Conduct pre-testing of the device to identify potential issues. |
7 | Prepare necessary documentation and materials for testing. |
8 | Maintain communication with test labs throughout the process. |
You must integrate safety, robust design, and certified components from the start. Compliance documentation and risk management remain essential requirements. For custom battery solutions, consult our experts. Continuous improvement ensures your battery design meets evolving compliance and safety needs.
FAQ
What is the most important safety feature for lithium battery packs in medical devices?
You should prioritize advanced battery management systems. These systems monitor voltage, current, and temperature to prevent hazards and ensure reliable operation.
How does Large Power support custom lithium battery solutions for infusion pumps?
Large Power provides tailored lithium battery packs for medical devices. You can request a custom battery solution here.
How do lithium battery chemistries compare for medical device applications?
Chemistry | Cycle Life | Safety Level | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
Li-ion | 500-5,000 | High | Medical devices |
LiFePO4 | 2,000-5,000 | Very High | Medical devices |




