
You can achieve 24+ Hours of Runtime for portable patient monitors by selecting high-capacity lithium battery packs, optimizing device power consumption, and using smart management features. Choose energy-efficient components and update software regularly. Regular maintenance ensures long-term reliability. These strategies support lightweight designs for homecare applications.
Key Takeaways
Select high-capacity lithium batteries to ensure your patient monitor runs for over 24 hours. This choice enhances reliability in both clinical and homecare settings.
Optimize power consumption by using energy-efficient components and software. This practice extends battery life and supports continuous health monitoring.
Implement smart power management features like sleep modes and adaptive brightness. These features significantly reduce battery drain and improve operational efficiency.
Part1: Patient Monitor Lithium Battery Selection
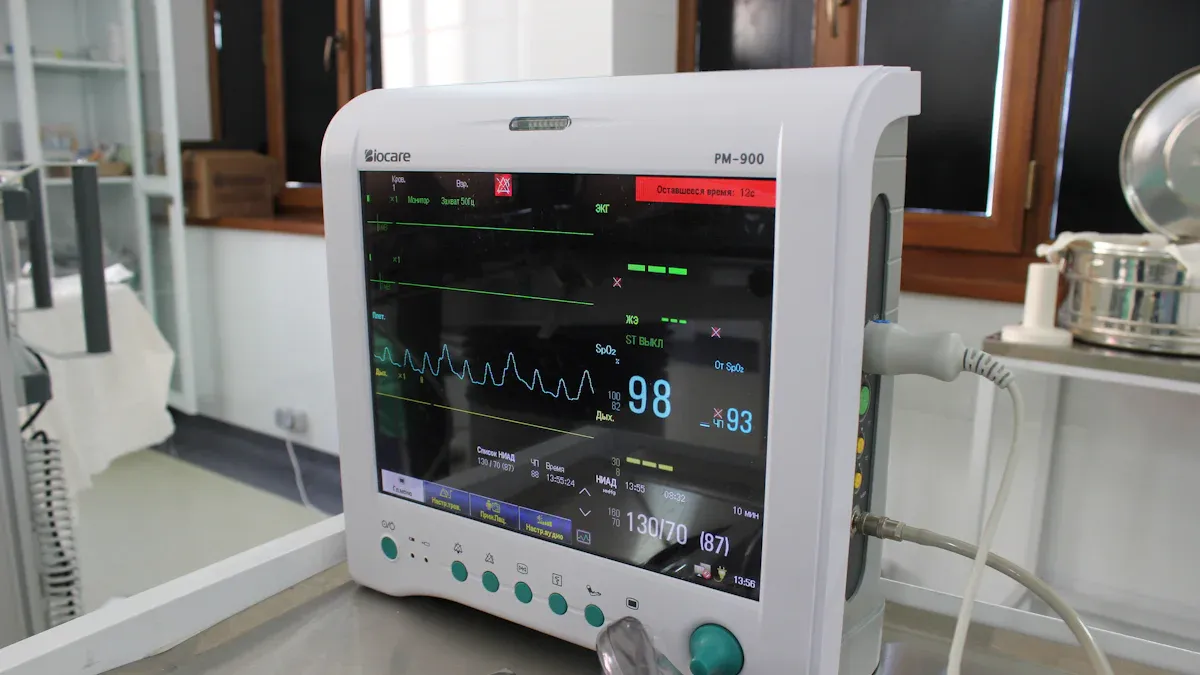
1.1 Lithium-Ion Battery Advantages
When you select a patient monitor lithium battery, you gain significant benefits for medical patient monitor devices. Lithium-ion batteries deliver long-lasting battery life, supporting hundreds of charge cycles while maintaining over 80% capacity after 500 cycles. This durability ensures reliability for continuous health monitoring in both clinical and homecare applications. You experience high energy density, with lithium-ion batteries offering 100–250 Wh/kg, which far exceeds the energy density of older chemistries like NiCad. Fast charging capability allows you to recharge in just 1–2 hours, improving workflow in healthcare and emergency settings. You do not need to schedule cycling or total discharges, which maximizes uptime and flexibility for patient monitoring.
Tip: Lithium-ion rechargeable batteries contain no hazardous metals and feature built-in protection circuits. These features reduce risks of overheating or fire, supporting safe operation in medical environments.
Battery Chemistry Comparison
You should understand the adaptability and flexibility of different lithium battery chemistries for patient monitoring. The table below compares common options for medical patient monitor devices:
Chemistry | Platform Voltage (V) | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) | Safety Features | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Lithium-Ion (NMC, LCO, LMO) | 3.6–3.7 | 100–250 | 500–1000 | Protection Circuit | Medical, robotics, consumer electronics |
3.2 | 90–160 | 2000+ | Thermal Stability | Medical, infrastructure, industrial | |
3.7 | 100–200 | 500–1000 | Flexible Form | Medical, security system, wearables | |
3.7 | 250–500 | 1000+ | Enhanced Safety | Medical, future health monitoring | |
Lithium Metal | 3.0–3.7 | 400+ | 1000+ | Advanced BMS | Medical, industrial, emergency |
LTO | 2.4 | 60–110 | 7000+ | High Safety | Medical, infrastructure, robotics |
You gain flexibility and adaptability by choosing the right chemistry for your patient monitor lithium battery. LiFePO4 batteries offer exceptional cycle life and thermal stability, making them ideal for critical medical and emergency monitoring. Lithium-polymer/LiPo batteries provide flexibility in form factor, supporting lightweight and portable designs for homecare applications. Solid-State Battery technology promises higher energy density and enhanced safety, which will benefit future health monitoring devices.
1.2 Capacity Planning for 24+ Hours of Runtime
You must plan battery capacity to achieve 24+ hours of runtime for patient monitoring. Start by calculating the total energy consumption of your medical patient monitor, including sensors, display, and wireless modules. Select high-capacity lithium batteries that match your device’s power requirements. For example, lithium-ion batteries used in patient monitors typically offer energy densities between 60 and 270 Wh/kg, as shown below:
You should estimate the required battery size based on your device’s average power draw and desired runtime. If your patient monitor consumes 5W per hour, you need a battery with at least 120Wh capacity for 24 hours of continuous monitoring. This approach ensures adaptability for various healthcare scenarios, including emergency and homecare applications.
Note: Always consider the flexibility of battery pack design. Modular battery packs allow you to scale capacity for different patient monitoring needs, supporting adaptability in medical environments.
1.3 Safety and Compliance
You must prioritize safety and compliance when selecting a patient monitor lithium battery. Medical standards require strict adherence to international regulations to ensure patient safety and device reliability. The table below summarizes key safety certifications for lithium batteries in medical patient monitor devices:
Standard | Application |
|---|---|
IEC 60601-1 | Devices with rechargeable batteries |
IEC 62133 | Devices with rechargeable lithium batteries |
IEC 60086-4 | Devices with non-rechargeable lithium batteries |
UL 1642/2054 | Devices sold exclusively in North America |
You ensure compliance with FDA and ISO regulations, which mitigate risks such as overheating, leakage, and battery failure. The FDA provides guidelines for safe design, including ANSI/AAMI ES 60601-1, which you must follow before bringing your medical patient monitor to market. Built-in protection circuits and advanced battery management systems (BMS) further enhance safety, preventing thermal runaway, overcharging, and internal short circuits.
Failure Mode | Description |
|---|---|
Thermal Runaway | Overheating can lead to fires or explosions, often due to overcharging. |
Mechanical Deformation | Stress can compromise battery integrity, causing short circuits or thermal runaway. |
Overcharging/Overdischarging | Leads to battery degradation and safety risks, including irreversible damage to electrodes. |
Internal Short Circuits | Separator failure can cause direct contact between electrodes, risking thermal runaway. |
You maintain adaptability and flexibility by choosing batteries with robust safety features and compliance certifications. This approach supports reliable health monitoring in medical, emergency, and homecare applications.
Part2: Power Optimization for Patient Monitors
2.1 Energy-Efficient Components
You can maximize the runtime of your medical patient monitor by selecting energy-efficient components. The choice of hardware directly impacts the adaptability and flexibility of your device. Low-power microcontrollers and processors allow your patient monitor to operate in low-power states when not processing data, which extends battery life and supports continuous monitoring. You should integrate hardware platforms that use compatible communication protocols to ensure efficient data transmission. This approach is essential for medical, emergency, and homecare applications, where reliability and operational longevity are critical.
The following table highlights how different components contribute to power consumption in portable patient monitors:
Component Type | Contribution to Power Consumption |
|---|---|
Display Technology | LCD panels with LED backlighting consume 60-80% of total system power. |
Touch Technology | Capacitive touchscreens consume less power than resistive types. |
Battery Technology | Lithium-ion batteries enhance efficiency and operational longevity. |
You gain flexibility by choosing capacitive touchscreens, which use less power than resistive types. Lithium-ion batteries, widely used in medical, robotics, security system, infrastructure, consumer electronics, and industrial scenarios, provide longer operational time and stable voltage output. This ensures your patient monitor remains reliable during health monitoring and emergency situations.
Tip: You should always match the battery’s characteristics to the load. This practice improves adaptability and ensures optimal energy use for patient monitoring.
2.2 Display and Sensor Efficiency
You can significantly reduce power consumption by optimizing display and sensor choices in your patient monitor. Display panel technology is a major contributor to overall energy use. LCDs with LED backlighting consume more power, while OLED technology can lower power usage, especially for dark backgrounds. The table below compares the power consumption characteristics of common display technologies:
Display Technology | Power Consumption Characteristics |
|---|---|
OLED | Reduces power for dark content |
LCD | Higher power due to backlighting |
You achieve flexibility and adaptability by selecting the right display for your application. OLED panels offer superior contrast ratios and can reduce power consumption for health monitoring devices that display dark content. LCD panels, especially IPS types, provide excellent color reproduction but tend to use more energy. You should consider the operational environment and monitoring needs when choosing between these technologies.
Sensors play a critical role in medical patient monitors. You should select sensors with low standby current and efficient data acquisition. This approach supports adaptability for continuous monitoring in healthcare and emergency settings. By using sensors that only activate when needed, you conserve battery life and maintain reliability.
Note: The choice of display and sensors directly affects the flexibility of your patient monitor. Efficient components allow you to design lightweight devices for homecare applications.
2.3 Software and Firmware Optimization
You can extend the battery life of your patient monitor by implementing software and firmware optimization techniques. These strategies enhance adaptability and flexibility, allowing your device to operate efficiently in various medical scenarios. You should use low-power microcontrollers and dynamic clock scaling to minimize energy use during idle periods. Firmware can utilize deep sleep modes and direct memory access (DMA) to manage routine tasks while the main processor remains inactive.
The table below summarizes effective software and firmware optimization techniques:
Technique | Description |
|---|---|
Energy Efficiency | Reduces power consumption, critical for portable and wearable medical devices. |
Implement Low-Power Modes | Use sleep and standby modes to conserve energy during idle periods. |
Optimize Clock Speeds | Adjust clock rates dynamically based on processing demands. |
Dynamic Voltage Scaling (DVS) | Lowers voltage dynamically depending on workload, saving power during idle or low-performance operations. |
On-demand Peripherals | Avoid powering up peripherals until they are truly needed. |
You should include battery fuel gauges and capacity monitors to intelligently manage energy resources. This practice improves reliability and ensures your patient monitor can adapt to changing health monitoring requirements. Efficient data compression algorithms for wireless transmission further reduce energy consumption, supporting continuous monitoring in healthcare and emergency environments.
Alert: Low-power design strategies are essential for extending battery life in mobile medical devices. You should prioritize these optimizations to maintain flexibility and adaptability in your patient monitoring solutions.
Part3: Smart Power Management Features
3.1 Sleep Modes and Adaptive Brightness
You can achieve 24+ hours of runtime for your medical patient monitor by using advanced sleep modes and adaptive brightness features. Sleep modes allow your device to minimize battery drain when sensors or displays are not in active use. Adaptive brightness automatically adjusts the display based on ambient light, reducing unnecessary power consumption. The table below shows how these features impact battery performance and runtime:
Feature | Impact on Power Consumption | Runtime Extension |
|---|---|---|
Adaptive Brightness | Reduces by 20% to 30% | 8+ hours per charge |
Sleep Modes | Minimizes power usage | Extends operational time |
Tip: You should select lithium battery packs with robust sleep mode compatibility to maximize operational efficiency in patient monitoring.
3.2 Dynamic Power Scaling
You can further extend battery life by implementing dynamic power scaling in your medical patient monitor. This technique adjusts the power supplied to sensors, displays, and processors based on real-time monitoring needs. You achieve adaptability by scaling down energy use during low-activity periods and ramping up only when patient data requires immediate attention. This approach supports 24+ hours of runtime and enhances flexibility for healthcare professionals in emergency scenarios.
Best practices for sleep mode implementation include:
Integrate multiple power-saving states tailored to hardware capabilities.
Utilize deep sleep and standby modes to reduce current consumption.
Monitor performance impacts during development to ensure proper functionality.
Customize algorithms to leverage sleep functionalities without compromising response times.
Document configurations and results for future scaling decisions.
You should always match lithium battery specifications to your device’s dynamic power requirements. This ensures reliable patient monitoring and supports adaptability in medical environments.
3.3 User Settings for Battery Life
You empower users to extend battery runtime by providing customizable settings in your medical patient monitor. User education plays a critical role in battery management. In one healthcare facility, staff reduced battery replacement costs from $56,000 to $11,000 by using analyzers and proper management practices. You can offer options for display brightness, sensor polling intervals, and sleep mode activation. These settings allow users to optimize battery usage based on patient monitoring needs, supporting flexibility and adaptability in both clinical and homecare applications.
You should educate users on lithium battery care and monitoring best practices. This improves reliability and extends the life of your medical patient monitor, ensuring continuous health monitoring for 24+ hours of runtime.
Part4: Runtime Testing and Validation

4.1 Real-World Testing for 24+ Hours of Runtime
You need to validate your medical patient monitor’s runtime in real-world conditions to ensure adaptability and reliability. Simulate continuous health monitoring by running the device with all sensors, display, and wireless modules active for at least 24 hours. Use lithium battery packs that match your calculated requirements. Test in various environments, including clinical, emergency, and homecare applications, to confirm consistent performance. Real-world testing helps you identify unexpected battery drain and ensures your device meets the demands of healthcare professionals.
Tip: Always document runtime results and compare them to your initial battery capacity planning. This practice supports adaptability and helps you refine your design for future monitoring needs.
4.2 Monitoring Tools and Data Logging
You can use advanced monitoring tools to track battery performance and patient data during runtime tests. Data logging systems record voltage, current, and temperature for each lithium battery pack. These tools help you detect anomalies in sensors or battery behavior. By analyzing this data, you improve adaptability and ensure your medical device maintains reliability in health monitoring. Automated alerts notify you of any deviations, allowing you to address issues before they impact patient safety.
Use battery analyzers to measure charge/discharge cycles.
Review logs regularly to optimize monitoring protocols.
4.3 Medical Standards Compliance
You must ensure your patient monitor meets strict medical standards for battery runtime and safety. Certifications such as IEC 60601-1 and UL 2054 confirm electrical safety and performance. Regulatory frameworks, including FDA and ISO, require you to follow design controls and risk management protocols. The table below summarizes key regulatory requirements:
Regulatory Framework | Description |
|---|---|
FDA & U.S. Regulatory Framework | Medical device manufacturers must adhere to design controls, risk management, and quality system regulations. |
IEC 60601 series | General safety and essential performance standard for medical electrical equipment. |
UL 2054 & UL 1642 | FDA-recognized consensus standards for battery safety in medical devices. |
Certifications: UL60601-1, cUL60601-1, IEC60601-1, EN60601-1, UL60950, FCC class B, CE, Energy Star, RoHS, WEEE.
Electrical safety: IEC 60601-1 protects users from electrical hazards in critical care.
IP65 protection: Ensures resistance to spills and cleaning agents, supporting durability in medical environments.
You maintain adaptability by meeting these standards, which supports safe operation in healthcare, emergency, and homecare applications. For more on medical standards, see medical standards.
You achieve 24+ hours of runtime for medical patient monitors by selecting the right lithium battery, optimizing power, and implementing smart management. Manufacturers face challenges with power consumption, device size, and patient safety. Advancements in lithium battery technology and wireless integration will improve reliability for medical, emergency, and homecare applications.
Choose high-capacity lithium batteries for medical monitoring
Optimize components and software for health monitoring
Use smart management for patient safety and emergency scenarios
FAQ
What factors most impact 24+ hour runtime in medical patient monitors?
You must consider lithium battery capacity, energy-efficient sensors, and optimized health monitoring software. These factors ensure continuous patient monitoring and reliability in healthcare, emergency, and homecare applications.
How do lithium battery packs support health monitoring in homecare applications?
Lithium battery packs provide high energy density and long cycle life. You achieve reliable health monitoring for homecare applications, medical devices, and continuous patient monitoring with minimal maintenance.
Where can you get custom lithium battery solutions for medical monitoring?
You can consult Large Power for custom lithium battery packs.




