
You face strict demands for safety and reliability in medical lithium battery packs. Advanced BMS Design Strategies help you prevent fire hazards and electrical faults. The right design transforms your battery management system into the central intelligence that safeguards compliance and maximizes performance for every custom solution.
Key Takeaways
Prioritize safety features in your BMS design to prevent fire hazards and ensure patient safety. Implement overcharge protection, thermal sensors, and short-circuit detection.
Use redundant fault detection circuits in your BMS to monitor current, voltage, and temperature. This ensures continuous safety monitoring and enhances reliability in medical applications.
Implement effective cell balancing strategies to maximize battery performance and longevity. Choose between passive and active balancing based on your specific application needs.
Part1: Safety Features in BMS
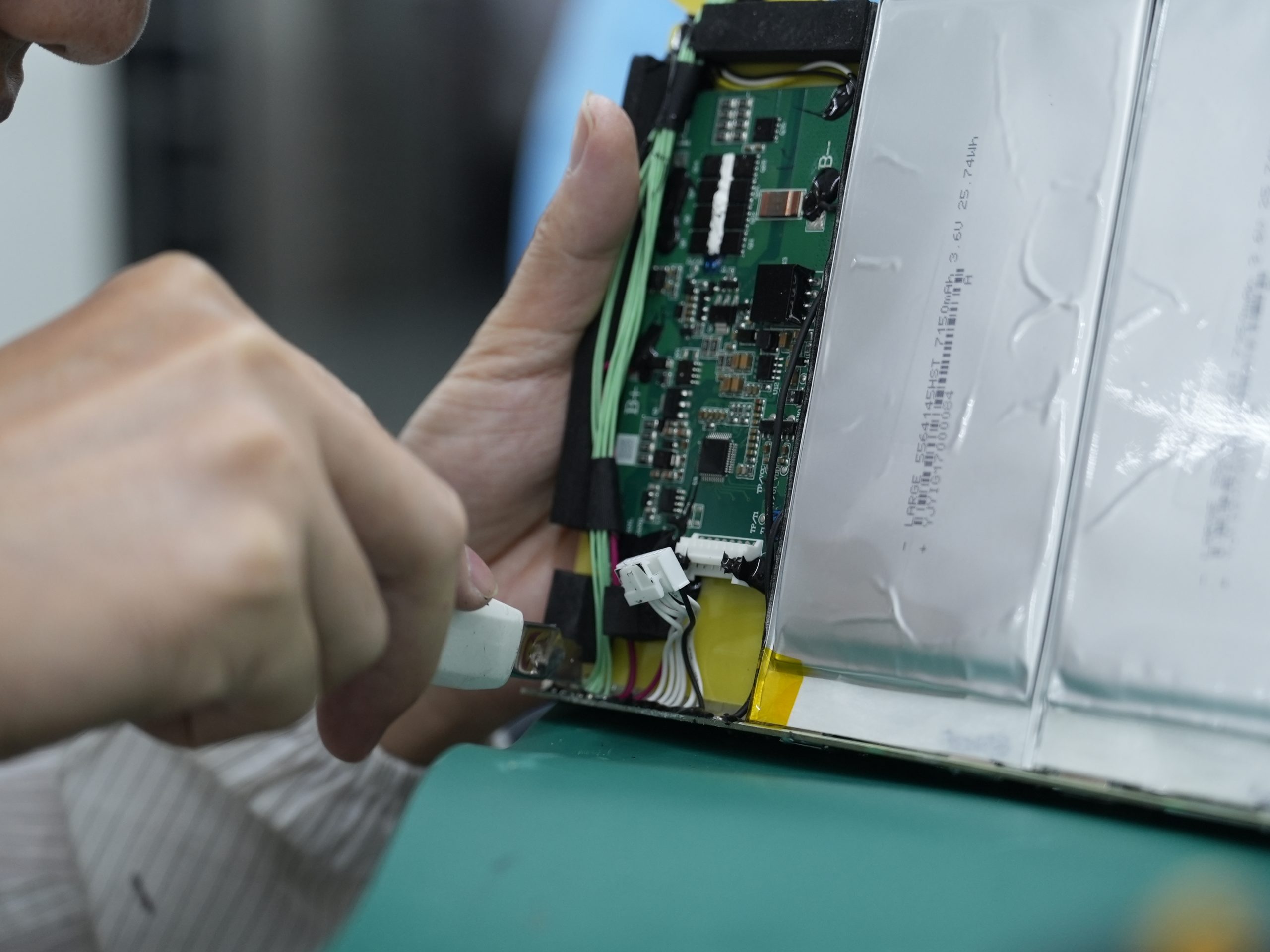

1.1 Cell Protection and Fire Hazard Prevention
You must prioritize safety features when designing battery management systems for medical lithium battery packs. Medical devices demand robust protection features to prevent fire hazards and ensure patient safety. The most common risks include overcharging, overheating, cycling and aging, volatile chemical composition, ejection, risk of reignition, thermal runaway, and signs of physical damage. You can see how these hazards impact medical applications in the table below:
Hazard Type | Description |
|---|---|
Overcharging and overheating | Overcharging can lead to overheating, posing a fire risk. |
Cycling and aging | Degradation over time due to charge/discharge cycles increases risk. |
Chemical composition | Volatile electrolytes can release flammable gases under high temperatures. |
Ejection | Batteries may be ejected during incidents, spreading fire risks. |
Risk of reignition | There is a chance of reignition even after a fire is extinguished. |
Thermal runaway | Uncontrolled heating can lead to fire or explosion due to chain reactions. |
Signs of damage | Mechanical damage, bulging, and visible gases venting indicate risks. |
You need to implement advanced cell protection features in your BMS to address these hazards. Overcharge and over-discharge protection circuits monitor each cell and disconnect the pack if voltage or temperature exceeds safe limits. Short-circuit detection instantly isolates the battery, preventing electrical faults from escalating. You should also use thermal sensors to track temperature changes and trigger shutdowns before overheating occurs.
Fire incidents in medical devices powered by lithium battery packs remain a serious concern. The following chart illustrates the distribution of fire incidents by device type:
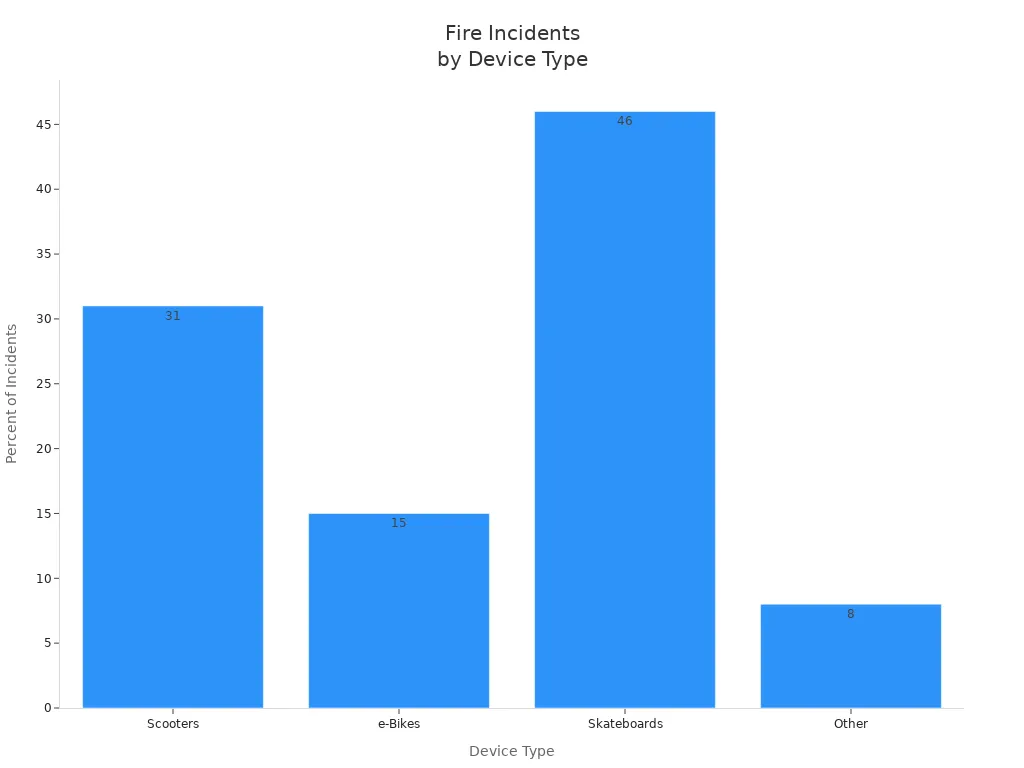
You must recognize that 78% of fires occur inside buildings, and 91% cause property damage. These statistics highlight the importance of integrating comprehensive safety features into your battery management system. By using a BMS with real-time monitoring and protection, you reduce the risk of fire and improve the reliability of your medical devices.
Tip: Always select BMS designs with multi-layer protection features for medical applications. This approach minimizes the risk of thermal runaway and ensures compliance with safety standards.
1.2 Electrical Fault Detection and Redundancy
You must address electrical faults proactively to maintain safety in medical lithium battery packs. Faults such as short circuits, ground faults, and connector failures can compromise device operation and patient safety. Your BMS should include redundant fault detection circuits that continuously monitor current, voltage, and temperature across all cells.
Redundancy in BMS design means you use backup sensors and parallel protection features. If one sensor fails, another takes over, ensuring uninterrupted safety monitoring. You should implement fault-tolerant algorithms that identify abnormal patterns and trigger protective actions before faults escalate. This strategy is essential for medical devices, where reliability cannot be compromised.
You can enhance safety by using self-diagnostic routines in your BMS. These routines check the integrity of sensors and communication lines at startup and during operation. If a fault is detected, the system isolates the affected section and alerts maintenance personnel. You should also consider integrating data logging to track fault events and support traceability for regulatory compliance.
Note: Redundant safety features and fault detection circuits are not optional in medical applications. You must design your BMS to meet the highest standards of reliability and safety.
By focusing on advanced protection features and redundancy, you ensure your medical lithium battery packs deliver consistent performance and meet strict safety requirements. You protect patients, equipment, and facilities from fire hazards and electrical faults.
Part2: Precision Monitoring and Balancing

2.1 Voltage and Temperature Sensing in BMS
You need accurate voltage and temperature sensing to optimize bms design strategies for medical lithium battery packs. Precision sensors monitor each cell, providing real-time data that supports safe operation and compliance with standards. You can use high-resolution analog-to-digital converters to capture voltage fluctuations and temperature changes. This approach helps you detect abnormal conditions early, such as overheating or voltage drift, which can compromise pack density and reliability.
Medical applications require strict adherence to certification requirements. You must select sensors that meet industry standards for accuracy and durability. Reliable sensing ensures your battery pack maintains optimal energy density and extends service life. You can integrate advanced diagnostics to alert you to sensor faults, supporting proactive maintenance and uninterrupted device operation.
Tip: Use sensors with built-in calibration features. This strategy improves measurement accuracy and supports certification for medical devices.
2.2 Cell Balancing Strategies for Custom Battery Pack
You must implement effective cell balancing to maximize the performance and longevity of your medical lithium battery packs. Balancing ensures each cell maintains equal voltage, which reduces degradation and supports consistent density across the pack. You can choose from two main cell balancing techniques:
Passive cell balancing discharges excess energy as heat. This method is cost-effective but can reduce battery runtime and overall density.
Active cell balancing transfers charge between cells. This approach improves efficiency and extends battery life, though it increases system complexity and cost.
Proper cell balancing supports bms design strategies that meet certification requirements and industry standards. You should evaluate your application scenario to select the best technique for your custom battery pack. The following table compares key battery chemistries used in medical devices, highlighting their voltage, energy density, and cycle life:
Chemistry | Nominal Voltage (V) | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|
3.6–3.7 | 150–250 | 500–1500 | |
3.2 | 90–160 | 2000–5000 | |
NMC | 3.7 | 180–220 | 1000–2000 |
LCO | 3.7 | 150–200 | 500–1000 |
LMO | 3.7 | 100–150 | 300–700 |
LTO | 2.4 | 70–110 | 7000–20000 |
You can consult with battery experts to tailor bms design strategies for your specific medical application. This approach ensures compliance with certification requirements and maximizes pack density and reliability.
Part3: BMS Design Strategies for Compliance
3.1 Meeting Medical Standards (IEC, ISO, FDA)
You must design your battery management system to meet strict medical standards. Regulatory bodies such as IEC, ISO, and the FDA set requirements for safety, reliability, and traceability. Your pack must comply with IEC 60601 for medical electrical equipment and ISO 13485 for quality management systems. The FDA also requires robust documentation and risk management for battery-powered medical devices.
To achieve compliance, you should:
Select components with proven reliability for your pack.
Validate your BMS through rigorous testing under real-world conditions.
Document every step of your design and manufacturing process.
You also need to consider sustainability and responsible sourcing. Many medical device manufacturers now require compliance with conflict minerals regulations. For more information, review our approach to sustainability and conflict minerals statement.
Note: Compliance is not a one-time task. You must update your pack design as standards evolve and new risks emerge.
3.2 Data Logging and Traceability in BMS
You need advanced data logging features in your BMS to support traceability and regulatory audits. Your pack should record voltage, temperature, cycle count, and fault events. This data helps you identify trends, optimize maintenance, and prove compliance during inspections.
A robust traceability system allows you to:
Track each pack from production to deployment.
Analyze performance under different power requirements and thermal constraints.
Respond quickly to recalls or field issues.
You can use secure digital storage and encrypted communication to protect sensitive data. For custom consultation on traceability solutions, contact our team.
Tip: Reliable data logging not only supports compliance but also improves the long-term safety and performance of your pack.
Part4: Power Management and Efficiency
4.1 Low-Power BMS Design
You need a low-power BMS design to extend the runtime of your custom battery pack in medical and industrial applications. Efficient power management reduces standby consumption and supports critical devices during long periods of inactivity. You can select microcontrollers with ultra-low quiescent current and optimize firmware for sleep modes. This approach minimizes energy loss and maximizes battery life.
You should focus on monitoring strategies that use event-driven wake-up routines. These routines activate only when voltage or temperature thresholds change, reducing unnecessary power draw. You can implement hardware-based monitoring circuits that operate independently from the main controller, further lowering energy usage. For medical devices, low-power design ensures continuous operation and patient safety, even during emergency situations.
Tip: Consult with battery experts for custom battery pack solutions that balance low-power design and high power density requirements.
4.2 Charge/Discharge Control for Medical Packs
You must implement precise charge/discharge control to protect your custom battery pack and optimize energy density. Advanced monitoring algorithms track cell voltage and current in real time, preventing overcharge and deep discharge events. You can use programmable charge profiles tailored to specific battery chemistries such as LiFePO4 and NMC. The table below compares key parameters for these chemistries:
Chemistry | Nominal Voltage (V) | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|
LiFePO4 | 3.2 | 90–160 | 2000–5000 |
NMC | 3.7 | 180–220 | 1000–2000 |
You should integrate monitoring routines that adjust charge rates based on temperature and load conditions. This strategy supports energy density optimization and extends pack longevity. In medical scenarios, reliable charge/discharge control ensures uninterrupted device operation and compliance with safety standards.
Note: Monitoring is essential for every stage of battery operation. You improve reliability and safety by using real-time data to guide charge and discharge cycles.
Part5: Integration and Scalability in Custom Battery Pack
5.1 Modular BMS for 3S–13S Packs
You need a modular BMS architecture to achieve true scalability and flexibility in your medical lithium battery packs. Modularity lets you tailor each power system to the unique requirements of your application. You can add or remove modules to support different cell counts, such as 3S, 7S, or 13S configurations. This approach helps you address precise electrical load profiles and mechanical constraints, which is critical for medical devices that demand custom solutions.
When you use a modular BMS, you simplify upgrades and maintenance. You can replace or expand modules without redesigning the entire system. This reduces downtime and supports rapid adaptation to new device requirements. Modular designs also support integration in other sectors, including robotics, security, and industrial automation, where you need reliable and adaptable power systems.
Tip: Modular BMS platforms help you future-proof your battery packs, making it easier to meet evolving standards and application needs.
5.2 Communication Protocols (CAN, SMBus)
You must select robust communication protocols to ensure reliable data exchange between your BMS and host devices. In medical lithium battery packs, protocols like CAN and SMBus are widely adopted for their reliability and versatility. The table below compares key protocols used in BMS design:
Protocol | Description | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
CAN | Multi-master, decentralized | Reliable even if one node fails |
RS 485 | Half-duplex transmission | Long-distance, strong noise immunity |
I2C | Synchronous serial | Low power, intra-board communication |
UART | Point-to-point | Simple, low-speed data transfer |
BLE | Wireless | Energy-efficient, remote monitoring for short range |
You should choose a protocol that matches your application’s requirements for speed, distance, and reliability. CAN is ideal for complex medical systems that require robust fault tolerance. SMBus offers compatibility with smart battery standards and is common in portable medical devices. For custom consultation on protocol selection, contact our team.
You improve battery pack safety and reliability by integrating advanced battery management system strategies. Focus on robust fault detection, thermal management, and redundancy to reduce recall risks and extend battery lifespan. Use standards like IEC 62133 and UN 38.3 to guide compliance. Track performance with metrics such as MSE and R². Adapt your battery pack design to evolving medical requirements for optimal performance and longer lifespan.
Mechanism | Benefit for Battery Pack Performance |
|---|---|
Fault Detection | Early issue identification |
Thermal Management | Improved battery lifespan |
Redundancy and Fail-Safe | Continuous battery pack operation |
Predictive Maintenance | Minimized downtime |
Adaptive Control | Optimized battery pack performance |
You enhance battery pack performance in medical, robotics, security, and industrial sectors by leveraging advanced BMS technologies.
FAQ
What makes a 13s bms essential for medical lithium battery packs?
You need a 13s bms to manage series configurations, support precise monitoring, and deliver robust bms protection layers for medical, robotics, and industrial battery system applications.
How do bms protection layers improve safety in custom battery system designs?
You benefit from bms protection layers that detect faults, prevent thermal runaway, and ensure compliance for series packs in medical, security, and infrastructure sectors.
Where can you get custom consultation for advanced bms solutions?
You can contact Large Power for custom battery management system solutions.




