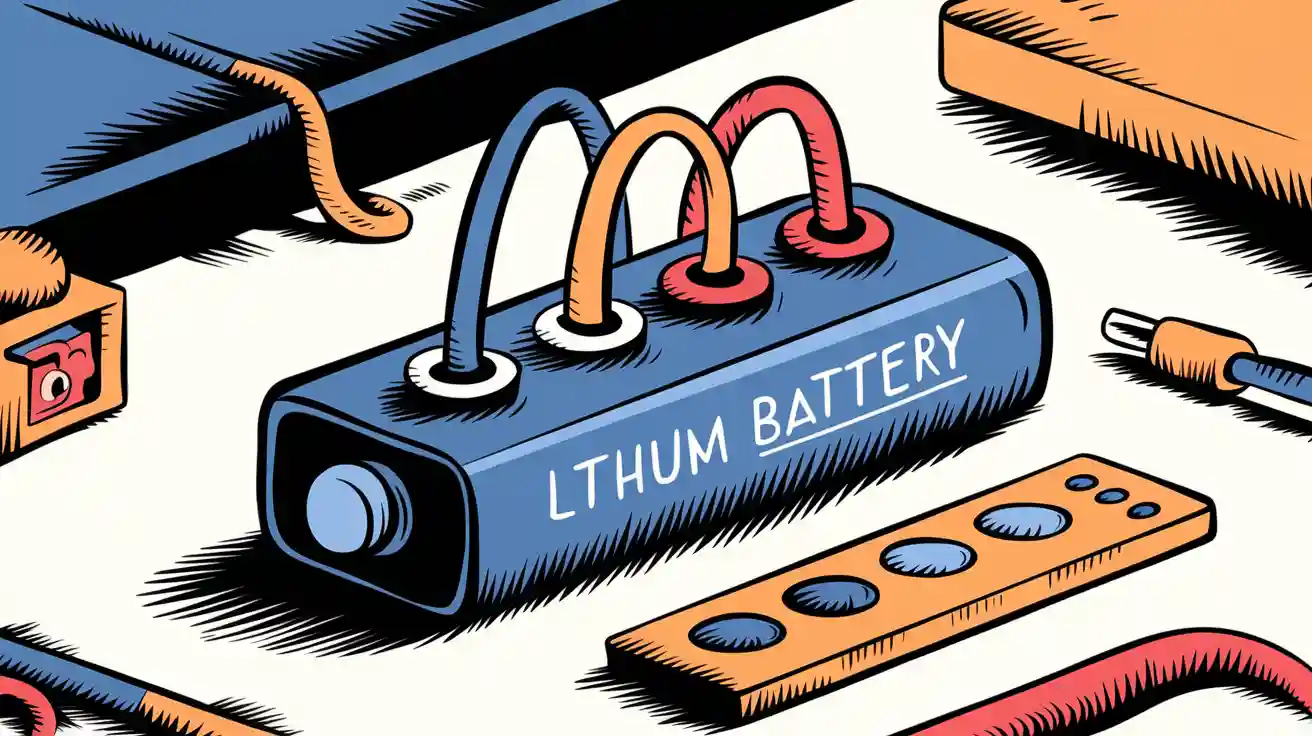
You encounter three wires in lithium battery wiring because you need reliable monitoring and enhanced safety. The first wire carries the positive terminal, the second connects to the negative, and the third enables voltage sensing. With a protection board, you gain automated lithium-ion battery safeguards. Without it, you must manually monitor lithium performance.
Key Takeaways
Lithium batteries use three wires: red for positive, black for negative, and a third wire for monitoring voltage or temperature to keep the battery safe and efficient.
Protection boards or battery management systems actively monitor battery health and prevent dangers like overcharging, short circuits, and overheating.
Correct wiring and regular monitoring are essential to avoid battery damage, improve performance, and ensure long-term safety.
Part 1: Lithium Battery Wiring and Wire Functions

1.1 Wire Roles in Lithium-Ion Battery Packs
When you work with lithium battery wiring, you typically encounter three wires. Each wire serves a distinct electrical role in the battery pack:
The red wire acts as the positive terminal for both charging and discharging.
The black wire connects to the negative terminal.
The third wire, often another color, provides a monitoring or sensing function.
You may find the third wire connected to a temperature sensor (such as a thermistor) for real-time temperature monitoring. In multi-cell packs, this wire can also serve as a voltage balancing line, ensuring that each cell maintains optimal voltage levels. In advanced lithium battery wiring, the third wire may transmit battery status data—such as state of charge or health—to external battery management systems. This configuration supports both battery safety and performance by enabling precise monitoring and control.
Tip: Always verify the function of each wire before connecting a lithium battery pack to your system. Misidentifying wires can compromise battery safety and efficiency.
1.2 Monitoring and Sensing Functions
The monitoring wire in lithium battery wiring plays a critical role in battery safety and efficiency. When you use a protection board (also known as a battery management system or BMS), the monitoring wire connects directly to individual cells. The BMS uses this connection to measure voltage and current parameters in real time. It actively monitors for unsafe conditions, such as overcharge, overdischarge, overcurrent, and short circuits. If the BMS detects a problem, it can disconnect the battery to prevent damage.
Without a protection board, the monitoring wire becomes a passive connection. You must manually monitor cell voltages and temperatures, which increases the risk of missing critical battery safety events. The presence of a BMS transforms the monitoring wire into an essential component for real-time protection and balancing.
Modern lithium battery packs often integrate advanced sensors for voltage and temperature monitoring. These include:
Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) sensors, which offer multiplexing, flexibility, and immunity to electromagnetic interference.
Resistance temperature sensors, valued for precision and stability.
Thermocouples and thermistors, which provide reliable temperature readings.
Integrated microsensors, capable of monitoring multiple parameters—such as temperature, voltage, and current—simultaneously.
These sensors enable you to detect early signs of battery degradation, overcharging, or thermal abuse. Real-time monitoring through battery management systems improves battery safety and extends lifespan by preventing overcharge, reducing parasitic reactions, and optimizing charge cycles. This approach can increase battery runtime by up to 30% and ensures reliable performance in demanding applications such as robotics, medical devices, and industrial systems.
1.3 Identifying Wire Color Codes
Correctly identifying wire color codes is essential for safe and efficient lithium battery wiring. In most lithium-ion battery packs used in professional and industrial settings, you will find:
Wire Color | Typical Function |
|---|---|
Red | Positive terminal (charge/discharge) |
Black | Negative terminal |
White/Blue/Yellow | Monitoring, temperature sensing, or balancing |
Red and black wires follow industry standards to prevent polarity reversal and ensure correct assembly. The third wire may appear in white, blue, or yellow, depending on the manufacturer and the specific function—such as voltage monitoring or temperature sensing.
Note: Always consult the technical documentation for your specific lithium battery pack. Manufacturers may use additional wires for balancing or data communication, especially in packs with advanced battery management features.
By understanding wire roles and color codes, you can assemble and maintain lithium battery packs with greater confidence. This knowledge supports battery safety, maximizes efficiency, and ensures optimal performance in your applications.
Part 2: Battery Safety and Management Systems
2.1 Role of Protection Boards
You rely on protection boards to safeguard lithium battery packs against common battery safety issues. These boards serve as the first line of defense in battery management. They monitor voltage, current, and temperature, disconnecting the circuit when abnormalities occur. Protection boards provide essential functions:
Overcharging prevention: Stops charging when voltage exceeds safe limits.
Over-discharging prevention: Disconnects the load if voltage drops too low.
Short-circuit protection: Interrupts current flow during faults.
Voltage monitoring: Tracks cell and pack voltage for safety.
Current limiting: Restricts current to safe levels.
Thermal protection: Uses sensors to shut down the circuit if overheating occurs.
Protection boards differ from full battery management systems, which offer advanced features like cell balancing and predictive maintenance. In electric vehicles, battery management systems integrate thermal management and active balancing to handle large battery packs. In consumer electronics, systems focus on miniaturization and power efficiency. Both types share core functions, but electric vehicles require more rigorous safety protections and extensive monitoring.
Feature | Protection Board | Battery Management System (BMS) |
|---|---|---|
Overcharge Protection | ✔ | ✔ |
Over-discharge | ✔ | ✔ |
Short-circuit | ✔ | ✔ |
Cell Balancing | ✖ | ✔ |
Thermal Management | Basic | Advanced |
Predictive Maintenance | ✖ | ✔ |
Application | Small packs | Large packs (EV, industry) |
Tip: Always select a protection board or BMS that matches your application’s safety and efficiency requirements.
2.2 Wiring Steps for Battery Safety
You must follow precise wiring steps to maximize battery safety and efficiency. Proper assembly reduces the risk of battery safety accidents and improves BMS efficiency. Use the following procedure for lithium-ion battery packs:
Gather lithium-ion cells, insulated wires, soldering tools, and safety gear.
Identify positive (+) and negative (-) terminals, usually red for positive and black for negative.
Plan the layout and calculate total voltage to ensure compatibility with your device.
Connect cells in series by linking the positive terminal of one cell to the negative terminal of the next.
Secure connections with even soldering or spot welding.
Insulate soldered joints using heat shrink tubing and a heat gun.
Use a multimeter to verify total voltage matches the calculated value.
Install a battery management system according to manufacturer instructions to monitor and balance cells.
Place the battery pack in a secure, well-insulated holder to prevent physical damage.
Test the pack by charging slowly and monitoring for irregularities.
Maintain regular testing and safety checks for long-term reliability.
Note: Always use reputable batteries and protective equipment. Work in a ventilated area and follow manufacturer guidelines for battery management.
2.3 Importance of Correct Wiring
You ensure battery safety and efficiency by wiring lithium battery packs correctly. Accurate wiring prevents battery safety issues such as short circuits, overcharging, and cell imbalance. Regular voltage monitoring is critical. Per-cell voltage monitoring and actionable alarms help you detect problems early, preventing capacity loss and thermal runaway. In electric vehicles, incorrect wiring can lead to catastrophic failures, including fire and loss of vehicle function. You must inspect balance leads and connections before operation. Use detailed checklists and real-time logging to maintain battery safety and improve battery management.
Alert: Incorrect wiring increases the risk of battery safety accidents and reduces efficiency. Always double-check connections and monitor voltage at the cell level.
2.4 Risks of Incorrect Wiring
You face significant risks if you wire lithium battery packs incorrectly. Common causes of battery safety accidents include mechanical abuse, electrical abuse, thermal abuse, and manufacturing defects. Mechanical abuse involves crushing, puncturing, or vibration, which can cause internal shorts and thermal runaway. Electrical abuse includes overcharging, over-discharging, and faulty battery management systems. Thermal abuse results from exposure to high temperatures or poor cooling. Manufacturing defects such as metallic contaminants or poor assembly increase the risk of failure.
You must avoid these risks by following best practices for battery management. Store batteries in cool, dry, ventilated areas. Handle packs carefully to prevent physical damage. Use only approved batteries and chargers. Conduct regular inspections and maintenance to identify and address battery safety issues before they escalate.
Callout: Routine monitoring and maintenance extend battery life and prevent battery safety accidents. Replace batteries approaching end of life and follow product-specific charging instructions.
You benefit from three wires in lithium-ion battery packs because each wire supports power delivery and monitoring. Correct wiring and robust battery management systems help you prevent instability and maintain reliability.
Always follow best practices and industry standards to maximize safety and operational performance.
FAQ
What happens if you connect the three wires incorrectly in a lithium battery pack?
You risk short circuits, inaccurate monitoring, or battery damage. Always verify wire functions before connecting to prevent safety hazards and operational failures.
Can you use a lithium battery pack without a protection board?
You can, but you must manually monitor voltage and temperature. This increases risk and does not address failure mechanisms of lithium-ion batteries.
How do you identify the monitoring wire in a lithium battery pack?
You usually find the monitoring wire in white, blue, or yellow. Check the manufacturer’s documentation to confirm its function before connecting.




