You face strict bms requirements when designing lithium battery packs for infusion pumps. The battery management system must deliver safety, reliability, and compliance with safety standards and certifications. You need robust fuse and safety switches, along with advanced monitoring. The following table highlights essential standards and protection features:
Standard/Feature | Description |
|---|---|
ISO 13485 | Ensures rigorous processes for medical safety and reliability in battery manufacturing. |
CE | Indicates compliance with safety standards in the EU market. |
UL | Certifies that the battery meets specific safety standards. |
IEC | Ensures international safety and performance compliance. |
Overcharging Protection | Safeguards against excessive charging, preventing battery damage. |
Short-Circuit Protection | Prevents damage from unintended electrical connections. |
Thermal Regulation | Manages temperature to avoid overheating and potential hazards. |
Key Takeaways
Prioritize electrical safety in lithium battery packs for infusion pumps. Implement robust monitoring to prevent overheating and electrical shorts.
Ensure compliance with IEC and FDA standards. Document all battery management system features to maintain safety and performance.
Integrate advanced protection circuits like PCM and ASIC. These enhance safety, improve battery performance, and reduce maintenance needs.
Part1: BMS Requirements and Safety in Medical Devices
1.1 Electrical Safety for Infusion Pump Battery Packs
You must prioritize electrical safety when designing lithium battery packs for infusion pumps. The battery management system plays a critical role in protecting both patients and healthcare staff. Lithium batteries present several risks that you need to address:
Lithium-ion batteries can experience thermal runaway, which may lead to fire or explosion, especially under pressure.
In environments like hyperbaric chambers, increased oxygen levels make materials more flammable, raising the risk of ignition.
Devices must use oxygen-compatible materials to minimize fire hazards.
Battery failures can result in chemical hazards, threatening patient health and staff safety.
You need to implement robust battery management strategies to prevent these incidents. The battery management system should continuously monitor temperature, current, and voltage across each lithium cell. This monitoring helps you detect abnormal charging or discharging events, which can cause overheating or electrical shorts. You must also ensure that the battery management system includes protection features such as overcharge, overdischarge, and short-circuit prevention.
Note: Most recalls of infusion pumps stem from battery failures. These failures often result from design flaws or manufacturing defects, causing batteries to overheat and devices to shut down unexpectedly. If the low-battery alarm does not function properly, the risk to patient health increases.
You should review documented incidents to understand the consequences of inadequate electrical safety:
Incident Type | Description |
|---|---|
Power Failure | Device ceases operation without warning, leading to loss of therapy and data. |
Battery Discharge | Excessive discharge can damage batteries, interrupting therapy. |
Component Failure | Sensor failure, pump door breakdown, and flow restrictor failure, leading to operational issues. |
You must inspect battery packs for damage, fluid, or debris. Damaged lithium cells may trigger alarms, and overheating can melt components or cause electrical shorts. You should avoid using batteries with corroded terminals and replace any damaged components immediately.
1.2 Regulatory Compliance: IEC and FDA Standards
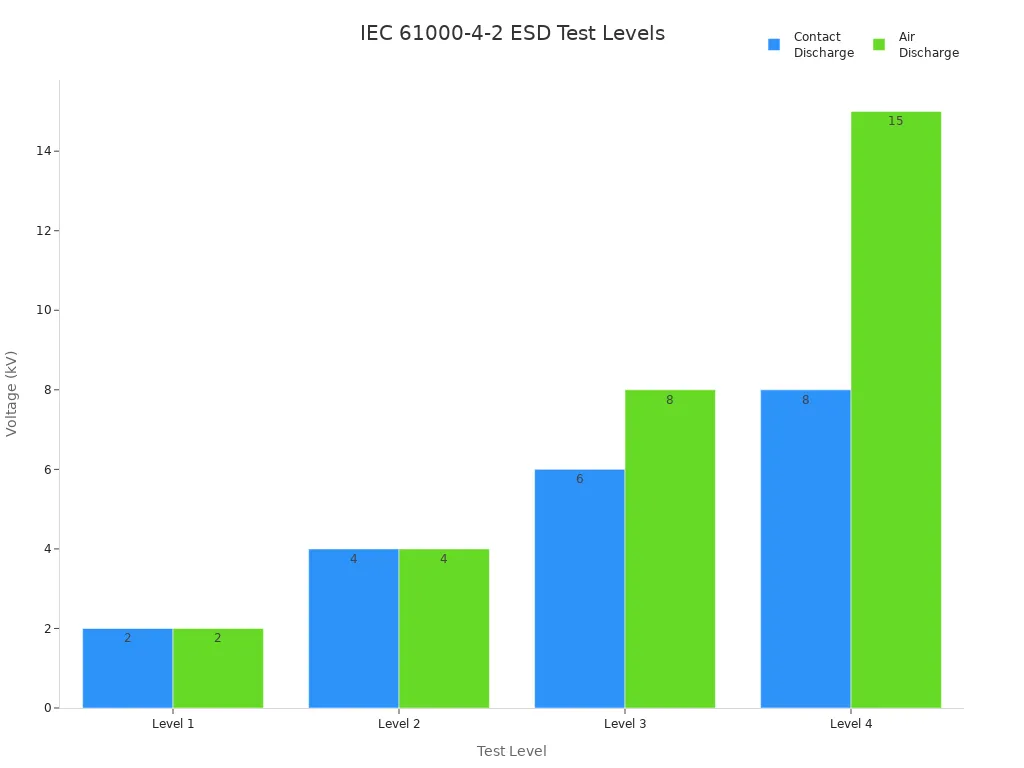
You must meet strict regulatory standards when designing battery management systems for medical devices. The IEC 61000-4-2 standard outlines immunity requirements and testing methods for electrostatic discharge (ESD). This standard ensures that your battery packs can withstand discharges from operators and nearby personnel, maintaining device performance and patient safety.
IEC 61000-4-2 specifies test levels for both contact and air discharge voltages:
Level (Contact) | Voltage (Contact) | Level (Air) | Voltage (Air) |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | 2kV | 1 | 2kV |
2 | 4kV | 2 | 4kV |
3 | 6kV | 3 | 8kV |
4 | 8kV | 4 | 15kV |
You must follow detailed procedures for testing, calibration, and measurement uncertainty. The battery management system should demonstrate immunity to ESD events, ensuring reliable operation in clinical environments.
The FDA also requires you to comply with safety and performance standards for medical devices. You must document all battery management system features, including protection features and monitoring capabilities. You should maintain compatibility with other pump electronics and ensure communication between the battery monitoring unit and the main controller.
You must address the most frequently cited causes of battery-related recalls:
Damaged batteries may trigger alarms.
Users should check for fluid or debris in the battery compartment.
Overheating and melting of components can result from internal circuit board damage.
Electrical shorts may occur due to battery separator damage or foreign material.
Battery damage can lead to ‘Low Battery’ or ‘Depleted Battery’ alarms.
You must design the battery management system to maximize energy efficiency, maintain optimal temperature, and ensure safe charging and discharging cycles. You should implement advanced monitoring and communication protocols to support health data integrity and device reliability.
By meeting bms requirements and regulatory standards, you ensure the safety, performance, and health of patients using infusion pumps. You must integrate robust protection features and maintain strict management of lithium cell parameters to achieve compliance and reliability in medical devices.
Part2: Protection Design for 3S–5S Battery Packs

2.1 Core BMS Protection Features: Overcharge, Overdischarge, Overcurrent, Short-Circuit
You must implement robust protection features in every battery management system for 3S–5S lithium battery packs used in infusion pumps. These features protect patient health and device reliability. The most critical protection functions include overcharge, overdischarge, overcurrent, and short-circuit protection. You need to monitor voltage, current, and temperature for each lithium cell to prevent hazardous events.
You should follow industry best practices for protection design:
Charging over voltage protection
Charging over current protection
Charging/discharging over temperature protection
Reverse polarity protection
Short circuit protection
Over voltage and deep discharge protection
You must set precise thresholds for each parameter. The table below summarizes the typical values for lithium battery chemistries, such as lithium-ion, LiFePO4, and others:
Parameter | Definition | Design Basis | Typical Values |
|---|---|---|---|
Overcharge Voltage (VC) | Max safe charging voltage | Battery chemistry (LCO ≤4.25V) | 4.25V ± 0.05V |
Over-discharge Voltage (VD) | Min safe discharge voltage | Prevents copper dissolution (LFP ≥2.5V) | 2.50V ± 0.08V |
Overcurrent (OC) | Safe discharge current threshold | Internal resistance + heat limits | Power tools: 30A; Earbuds: 3A |
Short-Circuit Response Time | Delay before circuit cutoff | Balances safety and false triggers | 200μs–1ms |
You must design the battery pack with physical and mechanical barriers to prevent cell-to-cell and cell-to-case short circuits. This approach reduces the risk of catastrophic failure. You should also use a charge/discharge control circuit to manage current flow and maintain safety.
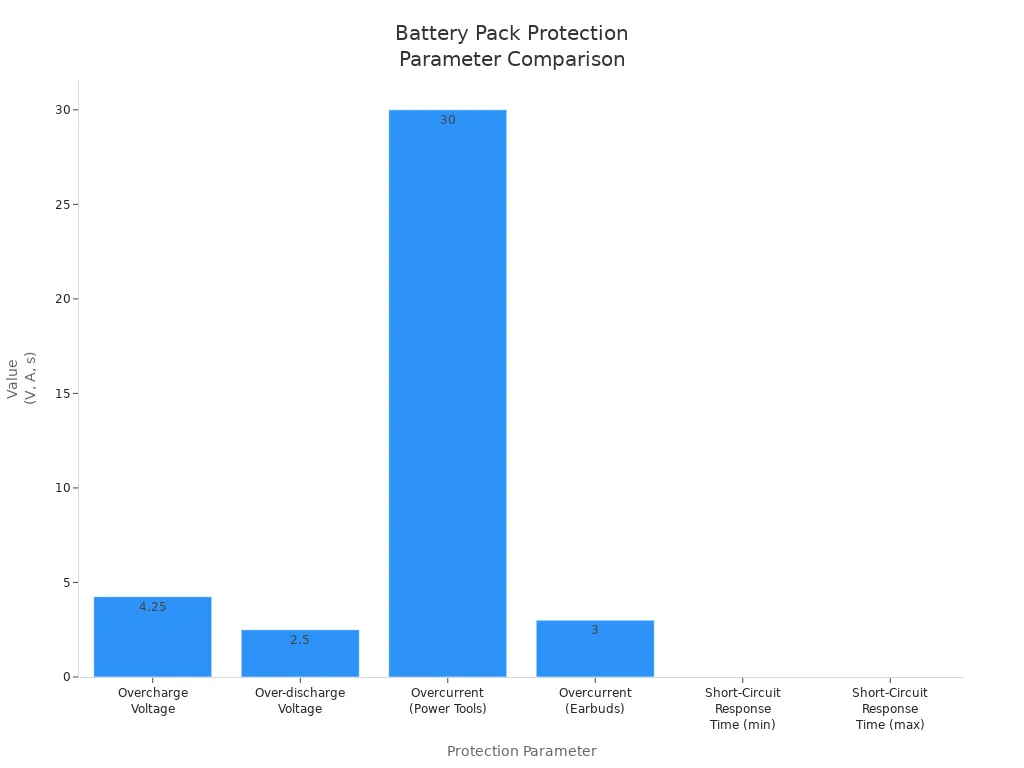
You must set overcharge protection for each cell at 4.25V, so a 5S pack should not exceed 21.25V. Over-discharge protection should trigger at 2.8V per cell, or 14.0V for a 5S pack. You should limit the maximum pulse current to 30A for safety. These thresholds ensure the battery management system prevents damage from abnormal charging or discharging events.
Tip: Always verify that your BMS requirements align with the latest regulatory standards and manufacturer specifications for lithium cell safety.
2.2 Advanced Protection Circuits: PCM and ASIC Integration
You can enhance the safety and reliability of your battery management system by integrating a protection circuit module (PCM) and application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). These components add advanced monitoring and control capabilities to your lithium battery pack.
The table below highlights the main advantages of PCM and ASIC integration:
Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
Overcharge Protection | Prevents battery instability and potential hazards like overheating or explosion due to overcharging. |
Over-discharge Protection | Protects the battery from excessive stress, prolonging its lifecycle by preventing deep discharge. |
Additional Safety Features | Includes short circuit protection, temperature protection, and electrostatic discharge protection. |
You gain several benefits from PCM and ASIC integration:
Advanced safety measures such as thermal management and fault diagnostics
Enhanced battery performance through cell balancing and precise state of charge estimation
You improve reliability by using a PCM 5S BMS, which ensures dependable performance in critical medical devices. Integrated protective functions include overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, and thermal protection. These features stabilize the battery pack and extend its service life.
The integration of PCM and ASIC also reduces maintenance requirements. You benefit from self-regulation and automated alerts for anomalies, which lowers the need for frequent manual checks. This approach supports health data integrity and continuous device operation.
2.3 Design Considerations: Cell Balancing, Thermal Management, Compact Form Factor
You must address several design challenges when developing a battery management system for 3S–5S lithium battery packs in infusion pumps. These challenges include cell balancing, thermal management, and compact integration with pump electronics.
Cell Balancing Techniques
You can choose from three main cell balancing methods:
Passive balancing: Uses resistors to discharge higher state-of-charge cells, matching them to the lowest cell. This method is simple and cost-effective but wastes energy as heat.
Active balancing: Transfers charge between cells using specialized circuitry. This method conserves energy but increases cost and complexity.
Hybrid balancing: Combines passive and active methods to optimize cell balance and energy efficiency.
Thermal Management and Temperature Control
You must implement a thermal management system to maintain safe operating temperatures for all lithium cells. Continuous temperature monitoring helps you detect overheating and prevent thermal runaway. You should use temperature sensors and control circuits to adjust charging and discharging rates as needed.
Compact Form Factor and Integration
You face strict space and weight constraints in portable infusion pumps. The table below compares two leading infusion pump systems:
Specification | B Braun Infusomat Space Infusion System | Sigma Spectrum 6.05.14 Wireless B/G |
|---|---|---|
Height | 4.9 in | 5.8 in |
Length | 2.7 in | 4.2 in |
Width | 8.4 in | 2.5 in |
Weight | 3 lbs | 25 oz ± 1 oz (708 grams ± 28 grams) |
With IV Pole Clamp Weight | N/A | 33.5 oz ± 1 oz (950 grams ± 28 grams) |
You must design the battery management system to fit within these compact dimensions while maintaining high performance and safety. You should prioritize mobility and patient comfort. Efficient lithium battery technology supports long-lasting operation and reduces the need for frequent charging.
Note: Battery life is a key differentiator in the competitive market for medical devices. Smaller batteries with longer charge retention improve device performance and user satisfaction.
You must ensure compatibility with pump electronics and maintain robust communication and monitoring capabilities. Custom battery solutions can further enhance performance in compact systems.
By focusing on advanced protection circuits, precise monitoring, and efficient design, you meet the strict bms requirements for infusion pumps. You ensure patient health, device safety, and regulatory compliance in every application.
You strengthen infusion pump safety and reliability by meeting robust BMS requirements for 3S–5S lithium battery packs. Advanced protection circuits help you prevent electrical faults and comply with IEC and FDA standards.
FAQ
What are the main differences between Li-ion and LiFePO4 battery packs for infusion pumps?
Chemistry | Platform Voltage | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|
Li-ion | 3.7 V | 180–250 | 500–2,000 |
LiFePO4 | 3.2 V | 100–180 | 2,000–5,000 |
How does Large Power support custom BMS solutions for medical device manufacturers?
You can request a tailored lithium battery pack design with advanced BMS features. Visit Large Power Custom Consultation for expert guidance.
Why do you need cell balancing in 3S–5S lithium battery packs?
You ensure each cell charges and discharges evenly. This maximizes battery life, maintains safety, and prevents capacity loss in critical medical applications.




