When you choose batteries for GPS and field monitoring tools, focus on device compatibility, battery type, energy demands, and the surrounding environment. Lithium options often deliver the best balance of power, weight, and lifespan. To make an informed decision, review your device’s voltage and capacity needs. Consider how often you use the equipment and the conditions it faces. The table below shows the most common battery types for these tools:
Battery Type | Description |
|---|---|
Lithium Thionyl Chloride (Li-SOCl2) | High energy density, long shelf life, ideal for long-term field use. |
High energy output and long life, fits a wide range of GPS applications. | |
Lightweight, flexible shape, offers good battery life for GPS devices. |
Matching battery chemistry to your application ensures you get reliable performance and control costs.
Key Takeaways
Understand your device’s power needs by checking voltage and current specifications. This ensures you select a battery that can reliably power your equipment.
Choose lithium batteries for their high energy density and long lifespan. They perform well in extreme temperatures, making them ideal for field use.
Consider your usage patterns. For frequent use, rechargeable batteries like NiMH are cost-effective. For occasional use, non-rechargeable alkaline batteries may be more practical.
Match the battery type to environmental conditions. Lithium batteries excel in harsh environments, while other types may not perform as well.
Always prioritize safety and compliance. Use certified batteries and monitor them with battery management systems to prevent risks.
Part1: Choose Batteries for GPS and Field Tools
1.1 Device Power Needs
When you choose batteries for GPS and field monitoring tools, you need to understand your device’s power requirements. Start by checking the voltage and current specifications listed in your device’s manual. These numbers tell you how much energy your equipment needs to operate reliably.
To measure power needs accurately, you can use several tools:
Data loggers record voltage and current directly from your device.
Transducers convert voltage to a range that matches your data logger, making measurements more precise.
Signal conditioners amplify and isolate signals, which helps when you monitor multiple devices at once.
Current shunts measure current by detecting voltage drops across a known resistance.
Current transducers use Hall Effect sensors for non-contact current measurement, which works well for higher currents.
You can estimate total power consumption by adding up the current draw for each component. The table below shows typical values for popular GPS and field monitoring devices:
Component | Current Draw (mA) |
|---|---|
Ublox GPS module | 40 |
Adafruit Fona GSM | 50 (average) |
Arduino Nano | 20 |
Total Estimate | 110 |
If your device uses multiple modules, add their current draws together. This helps you choose batteries with enough capacity to last through your field session. Lithium battery packs often provide the best balance of energy density and reliability for these needs.
1.2 Usage and Environment
How you use your GPS and field monitoring tools affects battery choice. If you run your equipment continuously, you need batteries with higher capacity. If you use your tools only for short periods, you can select smaller batteries.
Environmental conditions play a big role in battery performance. Temperature extremes, humidity, and exposure to the elements can shorten battery life. Batteries work best between 50°F and 85°F, with optimal performance around 77°F. Cold temperatures increase internal resistance, which reduces charge acceptance and capacity. Freezing can cause permanent damage. High temperatures speed up corrosion and cause battery fluid to evaporate, cutting battery lifespan in half for every 10°C increase above normal. Humidity can lead to corrosion and electrolyte loss.
You should also consider how often you track data, the strength of the signal needed, and the number of active features. These factors increase power demand and affect how long your battery lasts in the field. Many lithium battery packs are designed to operate in wide temperature ranges, from -40°C to 85°C, making them suitable for harsh outdoor environments.
Tip: Always match your battery type to your device and field conditions. Lithium battery packs offer high energy density, long shelf life, and reliable performance in extreme temperatures. When you choose batteries, think about both your power needs and the environment where you will use your equipment.
Part2: Battery Types Overview

2.1 Lithium Batteries
Lithium batteries stand out as the top choice for most GPS and field monitoring tools. You get high energy density, long cycle life, and reliable performance in tough environments. These batteries come in several chemistries, such as lithium-ion (Li-ion) and lithium-polymer (Li-Po). Both types deliver strong power output and work well in compact devices.
Here is a quick look at energy density for common battery types:
Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) |
|---|---|
Lithium-ion | 150-250 |
Lithium-polymer | N/A |
NiMH | 60-120 |
Alkaline | N/A |
You benefit from lithium batteries because they last longer and weigh less than other options. They also offer excellent thermal stability and do not overheat easily. You can store them safely in confined spaces without worrying about explosion risks.
High energy density for longer operation
Long cycle life, reducing replacement needs
Safe for use in many environments
Low maintenance requirements
No dangerous gas emissions
Tolerate partial charging without damage
However, you should know about possible failure modes. Short circuits, punctures, swelling, and using the wrong charger can cause problems. Always follow manufacturer guidelines to keep your devices safe.
Failure Mode | Description |
|---|---|
Short Circuits | Metallic particles can cause internal contact, leading to thermal runaway. |
Puncture and Leakage | Mechanical stress or sharp objects may cause electrolyte leakage. |
Battery Pack Swelling | Moisture, overcharging, or aging can cause swelling and higher temperatures. |
Incorrect Charger Use | Using the wrong charger may lead to overcharging and swelling. |
2.2 NiMH and Alkaline
You may also consider nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) and alkaline batteries for your field tools. NiMH batteries are rechargeable and provide steady power, making them a good fit for high-drain devices like GPS units. Alkaline batteries are non-rechargeable and work best for low-drain applications.
Rechargeable AA batteries using nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) chemistry provide an eco-friendly and economical alternative to single-use batteries.
When you compare cost-effectiveness, NiMH batteries save money over time if you use your devices often. Alkaline batteries cost less up front and suit devices that do not need much power.
Battery Type | Best Use Scenario |
|---|---|
Alkaline | Low-drain devices |
NiMH | High-drain devices (frequent use) |
You should choose batteries based on how often you use your equipment and how much power it needs. For frequent, high-energy use, NiMH batteries work best. For occasional, low-energy use, alkaline batteries are more practical.
Part3: Battery Chemistry Comparison

3.1 Energy Density
Energy density tells you how much power a battery stores for its weight. This factor matters when you need lightweight equipment that runs for long periods. Lithium-ion batteries stand out for their high energy density, which makes them a top choice for GPS and field monitoring tools. You can see how different battery types compare in the table below:
Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) |
|---|---|
Lithium-ion | 50-260 |
Nickel-metal hydride | 60-120 |
Alkaline | Not directly referenced |
High energy density means your devices last longer between charges. Lithium-ion batteries also hold their charge well and have a low self-discharge rate. This feature lets you use your GPS devices for extended periods without frequent battery changes.
Lithium-ion batteries help you maximize operational time in the field. You get longer usage, fewer replacements, and reliable performance for demanding applications.
3.2 Lifespan and Cost
When you choose batteries, you should look at both lifespan and cost. Lithium batteries last much longer than NiMH or alkaline batteries. The table below shows the average number of charge cycles for each type:
Battery Type | Average Lifespan (Charge Cycles) |
|---|---|
Lithium | 1000-5000 |
NiMH | 300-1000 |
Alkaline | N/A |
NiMH batteries cost less at first, which can help if you have a tight budget. However, lithium-ion batteries give you better value over time. They last longer, work more efficiently, and need less maintenance. This makes them a smart investment for field monitoring projects that require reliability and long-term use.
3.3 Performance Factors
Performance factors like self-discharge rate and temperature tolerance affect how well your batteries work in real-world conditions. The table below compares these features:
Battery Type | Self-Discharge Rate Characteristics |
|---|---|
Lithium | Excellent retention, steady self-discharge throughout service life |
Alkaline | Good retention, but not as effective as lithium |
Nickel-based | Higher self-discharge, needs recharging after a few days |
Lithium batteries support a wide temperature range, so you can use them in extreme heat or cold.
These batteries deliver consistent power, even in harsh environments.
You can expect a long operating life—often 5 to 10 years—without maintenance.
You will find lithium battery packs in many industries, including medical devices, robotics, security systems, infrastructure monitoring, consumer electronics, and industrial automation. Their high energy density, long lifespan, and strong performance make them the preferred choice for mission-critical field applications.
Part4: Selection Tips and Best Practices
4.1 Battery Life
Maximizing battery life is essential for reliable GPS and field monitoring operations. You can extend operational time by selecting the right tracking method and optimizing device settings. The table below compares average battery consumption for common tracking methods:
Tracking Method | Average Battery Consumption (%) | Recommended Use Case |
|---|---|---|
Continuous GPS | 30-50 | High accuracy required |
Geofencing | 5-10 | Zone-based actions |
Wi-Fi Positioning | 10-20 | Urban settings |
Bluetooth Beacons | 15-25 | Indoor navigation |
Activity-based Tracking | 5-15 | Dynamic movement |
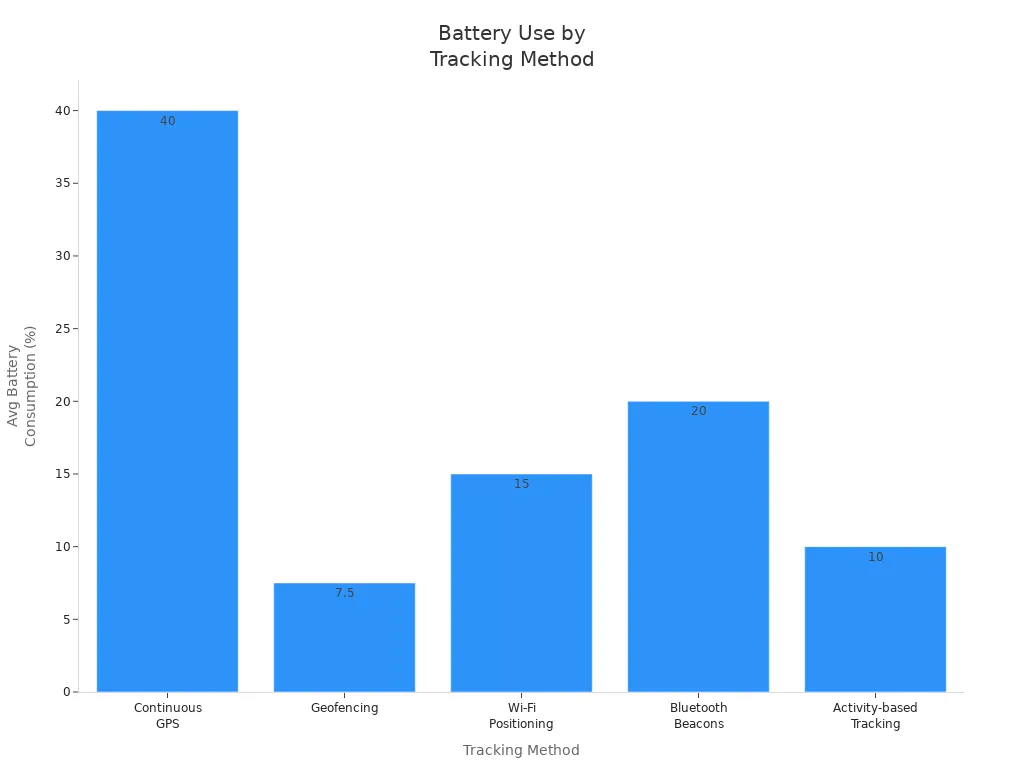
You can save up to 80% of power by using geofencing instead of continuous tracking. Adjusting update frequency and lowering precision in urban areas can also reduce energy use by 40%-60%. For B2B clients, these strategies help lower maintenance costs and improve device uptime.
Tip: Implement dynamic update intervals and choose the most efficient tracking mode for your application.
4.2 Rechargeability
Choosing between rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries depends on your usage pattern. The table below highlights key differences:
Feature | Rechargeable Batteries | Non-Rechargeable Batteries |
|---|---|---|
Battery Life | Shorter due to self-discharge | Longer shelf life, minimal self-discharge |
Usage Frequency | Ideal for frequent use | Best for low-power, occasional use |
Environmental Suitability | May struggle in extreme conditions | Performs well in wide temperature ranges |
Economic Considerations | Cost-effective over time | Higher initial cost, no need for replacement |
Self-Discharge Rate | Higher, but improving | Lower, suitable for long-term storage |
Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries offer environmental and cost benefits. You can reuse them many times, which supports your company’s sustainability goals. However, they may have lower voltage and higher upfront costs. For frequent field use, rechargeable packs are the best choice. For long-term storage or rare use, non-rechargeable options may suit your needs.
4.3 Size and Weight
Battery size and weight affect portability and deployment flexibility. Lightweight lithium battery packs make your devices easier to carry and install. Many GPS trackers weigh less than 2 ounces and measure under 2 inches, so you can attach them to assets, equipment, or shipments without adding bulk.
Small, lightweight batteries improve user comfort and reduce shipping costs.
Compact designs allow discreet placement for security and asset tracking.
For B2B clients, choosing the right battery size ensures efficient logistics and better field performance.
4.4 Safety and Compliance
Safety and regulatory compliance are critical for field deployments. You must select batteries that meet industry standards and certifications. The table below lists common certifications for GPS and field monitoring batteries:
Certification | Description | Common Use Environments |
|---|---|---|
ATEX Zone 1/2 | For explosive gas atmospheres in Europe | Refineries, chemical plants |
IECEx | International equivalent of ATEX | Global energy & process sites |
Class I Division 1/2 | Required in North America | Oil rigs, mining, distilleries |
IP Ratings (e.g., IP68) | Dust and water ingress protection | Outdoor, industrial fieldwork |
Lithium batteries can present risks such as leakage, fire, or explosion, especially during storage or transport. You should always use certified battery packs and advanced battery management systems (BMS) to monitor safety and performance. For responsible sourcing, review your supplier’s conflict minerals statement.
Note: B2B clients should require documentation for all safety certifications and request regular compliance updates from suppliers.
To choose the right battery for your GPS or field monitoring tools, follow these key steps:
Assess how long your device needs to run.
Match the battery to your device type and size.
Consider the environment and temperature range.
Decide between rechargeable and single-use options.
Check that the battery fits and meets your power needs.
Lithium battery packs deliver strong performance, long life, and reliability for most applications. When you apply best practices and maintain your batteries, you reduce costs and avoid downtime. 🚀
FAQ
What makes custom lithium battery packs the best choice for GPS and field monitoring tools?
Custom lithium battery packs offer high energy density, long lifespan, and reliable performance in harsh environments. You get more power in a smaller, lighter package. These features make them ideal for demanding applications.
How do I calculate the right battery capacity for my device?
Check your device’s current draw (in milliamps) and expected runtime (in hours). Multiply these numbers to find the required battery capacity (mAh). For example:
Current (mA) | Runtime (h) | Capacity Needed (mAh) |
|---|---|---|
100 | 10 | 1,000 |
Can lithium battery packs handle extreme temperatures?
Yes. Most lithium battery packs operate from -20°C to 60°C. Special purpose lithium batteries can be used in both hot and cold environments. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications for exact temperature ranges.
Are lithium battery packs safe for field deployment?
You get strong safety features with certified lithium battery packs. Built-in battery management systems (BMS) help prevent overcharging, overheating, and short circuits. Always choose packs with proper certifications for your industry.
How often should I replace lithium battery packs in field devices?
Most lithium battery packs last 1,000 to 5,000 charge cycles. You should monitor battery health regularly. Replace packs when you notice reduced runtime or if the battery fails safety checks.




