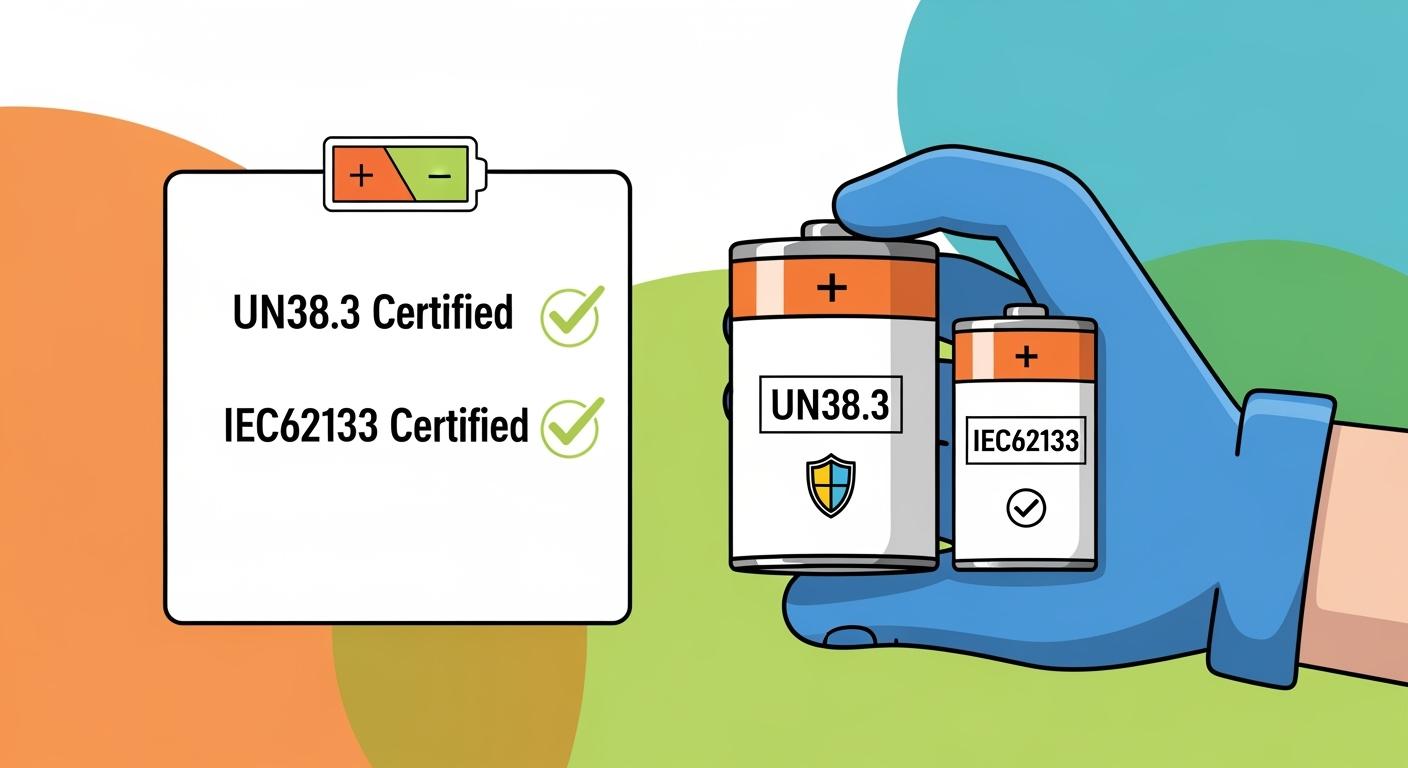
Choosing Batteries with UN38.3 and IEC62133 certifications ensures you meet strict transportation safety standards and safeguard your business from costly shipment delays, legal disputes, and safety hazards. Lithium battery packs fall under international safety standards for transportation as Class 9 Dangerous Goods. Many industries, including consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and energy storage, require rigorous safety and product certification. You face rejection at customs due to improper packaging, incomplete documentation, or non-compliance with safety and environmental standards.
By prioritizing safety testing and global battery testing, you align with the highest product certification benchmarks in transportation and ensure operational safety.
Key Takeaways
Choosing batteries with UN38.3 and IEC62133 certifications ensures safety during transport and use, protecting your business from legal issues and shipment delays.
Always verify certification documents and inspect packaging for authentic marks to avoid counterfeit batteries and ensure compliance with safety standards.
Ask suppliers targeted questions about their testing and quality control processes to confirm their commitment to safety and reliability.
Part1: Lithium Battery Certifications and Standards
1.1 UN38.3 Certification for Batteries
You must understand UN38.3 when selecting lithium battery certifications for your business. This certification sets strict standards for the safe transport of all lithium batteries, including 3.7v lithium battery packs. UN38.3 outlines mandatory certifications that test batteries under extreme conditions. These tests ensure safety during air, sea, and land shipments. The following list shows the main tests required for UN38.3:
Altitude Simulation
Thermal Test
Vibration
Shock
External Short Circuit
Impact
Overcharge
Forced Discharge
UN38.3 compliance requirements protect your shipments from regulatory delays and safety hazards. You must meet these standards to avoid shipment rejection and legal issues.
1.2 IEC62133 Certification Overview
IEC62133 is one of the most recognized lithium battery certifications for portable rechargeable batteries, especially 3.7v lithium battery chemistries. This certification focuses on safety standards for the design and use of lithium-ion and nickel-based cells. IEC62133 addresses electrical, mechanical, and chemical safety. The table below summarizes its scope:
Certification | Definition | Key Tests | Compliance Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
IEC 62133 | International safety standard for portable rechargeable batteries | External short circuit, Overcharge, Forced discharge, Crush, Free fall, BMS and circuit protection | Required for export to EU and many global markets |
You must ensure your 3.7v lithium battery packs pass IEC62133 to meet global regulatory requirements and safety standards.
1.3 Comparing Battery Standards
You need to compare lithium battery certifications to make informed decisions. The table below highlights the differences between UN38.3 and IEC62133:
Feature | IEC 62133-2 | UN38.3 |
|---|---|---|
Focus | Portable electronic devices | Transportation of lithium batteries |
Battery Types Covered | Lithium-ion and lithium polymer | All lithium batteries |
Primary Objective | Ensuring safety during use | Ensuring safety during transport |
UN38.3 and IEC62133 serve complementary roles. UN38.3 covers safety during transport, while IEC62133 ensures safety during use. You must choose batteries that meet both standards to guarantee safety, quality, and compliance with global regulations. Meeting these mandatory certifications supports your business in achieving high energy density, long cycle life, and reliable performance for every 3.7v lithium battery application.
Part2: Choosing Batteries with Verified Certifications

2.1 Checking Battery Certification Documents
When choosing batteries for your business, you must verify certification documents to ensure compliance with safety and transport requirements. Reliable suppliers provide complete documentation for each battery pack, including UN38.3 and IEC62133 certificates. You should request original test reports and certificates for every shipment. These documents must detail the battery chemistry, capacity, and testing procedures. Suppliers must also provide supporting documents for other requirements, such as RoHS, CE, and UL1642. Always check for clear manufacturer information, date stamps, and certifying organization details. Missing or altered marks, incorrect spellings, and inconsistent fonts often indicate fraudulent documents. Many third-party batteries fail to provide valid UN38.3 certificates, which signals a lack of compliance with safety requirements.
Common signs of falsified battery certification documents include:
Labels with incorrect spellings and different fonts.
Missing or altered certification marks.
Counterfeit batteries rebadged with misleading labels.
Homemade batteries lacking safety mechanisms.
Modified logos and missing date stamps.
Falsified certifications and misleading performance claims.
Third-party batteries unable to produce original UN38.3 certificates.
You must avoid these pitfalls by demanding complete documentation and verifying each certificate with the issuing authority.
2.2 Identifying Authentic Certification Marks
Authentic certification marks help you distinguish compliant batteries from unsafe alternatives. UN38.3 certification requires specific packaging and labeling for lithium battery packs classified as Class 9 Dangerous Goods. You should look for the following official marks:
Certification Mark | Description |
|---|---|
Class 9 Lithium Battery Hazard Label | Diamond pattern with 7 vertical stripes, battery pack graphic, and the number ‘9’ underlined. Minimum size: 100x100mm. |
Lithium Battery Mark | Rectangle with red diagonal stripe, battery pack graphic, UNXXXX number, and contact number. Minimum size: 120x110mm or small mark of 105x74mm. |
Cargo Aircraft Only | Black graphic on orange background. Minimum size: 120x110mm. |
IEC62133 compliance is confirmed through a test report that evaluates the battery under various conditions, including overcharging, forced discharge, and vibration resistance. You must check for complete, error-free packaging, clear manufacturer information, and valid certification marks. Misspellings, blurry images, and missing details often signal counterfeit batteries.
2.3 Supplier Questions for Battery Standards
You must ask suppliers targeted questions to confirm compliance with battery standards and requirements. These questions help you assess the supplier’s commitment to safety and quality:
What key safety certifications do your batteries meet?
How do you ensure ongoing compliance with UN38.3 and IEC62133 requirements?
Can you describe your cell sourcing and grading process?
What quality control checks are in place during battery assembly?
How do you manage traceability for each battery pack?
What testing data can you provide on thermal stability and cycle life?
How are your batteries tested for durability and reliability?
What warranty and technical support policies do you offer?
UN38.3 requires manufacturers to pass eight specific tests to ensure safe transport. IEC62133 mandates rigorous testing for electrical, mechanical, and environmental safety. You must confirm that suppliers follow these requirements for every battery pack.
2.4 Comparing Certified and Non-Certified Batteries
Choosing batteries with verified certifications protects your business from safety risks and regulatory issues. Certified lithium battery packs undergo comprehensive testing and meet strict requirements for safety and performance. Non-certified batteries often lack these assurances, exposing you to financial and operational risks.
Feature | Certified Lithium Battery Packs | Non-Certified Lithium Battery Packs |
|---|---|---|
Testing | Rigorous testing for safety and performance | May not have undergone rigorous testing |
Safety Standards | Meet strict requirements (e.g., UL, IEC62133, UN38.3) | Potential safety risks due to lack of certification |
Comprehensive Evaluation | Includes design, BMS, and system-level testing | Lacks comprehensive evaluation |
Quality Assurance | Higher product quality due to strict requirements | Variable quality, no assurance of safety |
Regulatory Compliance | Required for many industries and applications | May not meet industry requirements |
Peace of Mind | Assurance of high safety standards | Uncertainty regarding safety and performance |
Certified batteries undergo thermal, electrical, and mechanical stress testing. Non-certified batteries may fail under real-world conditions, leading to safety incidents and financial liability. Retailers and distributors of non-certified batteries face legal exposure, insurance barriers, and increased return rates. You must choose batteries with both UN38.3 and IEC62133 certifications to ensure compliance and reliability.
2.5 Avoiding Common Battery Pitfalls
You must avoid common pitfalls when choosing batteries for your business. Using lithium-ion batteries without proper certification creates significant safety challenges, including thermal runaway, fires, and explosions. Physical damage, overcharging, and improper storage increase risks. Failing to inspect batteries for damage or leaks, lack of training, and not using personal protective equipment further compromise safety. Manufacturing defects and non-compliance with safety requirements raise the likelihood of incidents.
Financial and legal repercussions include fines, lawsuits, loss of consumer trust, and potential revocation of operating licenses. You must evaluate the total cost of ownership, choose reliable suppliers, and ensure compliance with safety standards. Focus on sustainability, delivery capabilities, and scalability for future energy needs. Always prioritize certified batteries to protect your business and meet global requirements.
Tip: When choosing batteries, always verify certifications, inspect packaging, and demand complete documentation. This approach ensures compliance with safety and transport requirements, reduces operational risks, and supports long-term business success.
You protect your business by choosing batteries with UN38.3 and IEC62133 certifications. Follow these steps for safety and compliance:
Request and verify all certification documents.
Inspect packaging for authentic marks.
Ask suppliers about their testing and quality control.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Safety | Prevents overheating, leaks, and failures |
Legal Assurance | Meets global shipping regulations |
Reliability | Ensures durability and customer trust |
FAQ
What makes UN38.3 and IEC62133 certifications essential for lithium battery packs?
You need these certifications to ensure safe transport and use. They help you meet international regulations and reduce risks for your business.
How can you verify a supplier’s battery certifications?
You should request original UN38.3 and IEC62133 documents. Large Power provides full certification support. Contact our experts for a custom battery consultation.
Which lithium battery chemistries require these certifications?
You must certify lithium-ion, LiFePO4, and lithium-polymer/LiPo battery packs. See more about lithium-ion, LiFePO4, and lithium-polymer/LiPo solutions.




