You need a custom lithium battery pack to meet the strict demands of medical technology. Safety, reliability, and compliance with standards drive every design decision, especially for Disposable Surgical Tools. Review common regulatory requirements below:
Regulatory Standard | Description |
|---|---|
UL2054 | Certification for battery packs, depending on the type of medical device and market. |
CE Mark | Required in Europe for safety and EMC compliance. |
UN38.3 | Safety standard for lithium batteries during transport. |
UL1642 | Safety standard for lithium cells. |
IEC62133 | International standard for safety requirements for batteries used in portable applications. |
Key Takeaways
Custom lithium battery packs are essential for medical devices to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with strict regulations.
Choosing the right configuration of cells in series or parallel optimizes voltage and capacity, enhancing device performance and safety.
A robust Battery Management System (BMS) is crucial for monitoring, protecting, and optimizing battery performance in medical applications.
Part1: Why Custom Lithium Battery Pack Design Matters
1.1 Medical Device Requirements
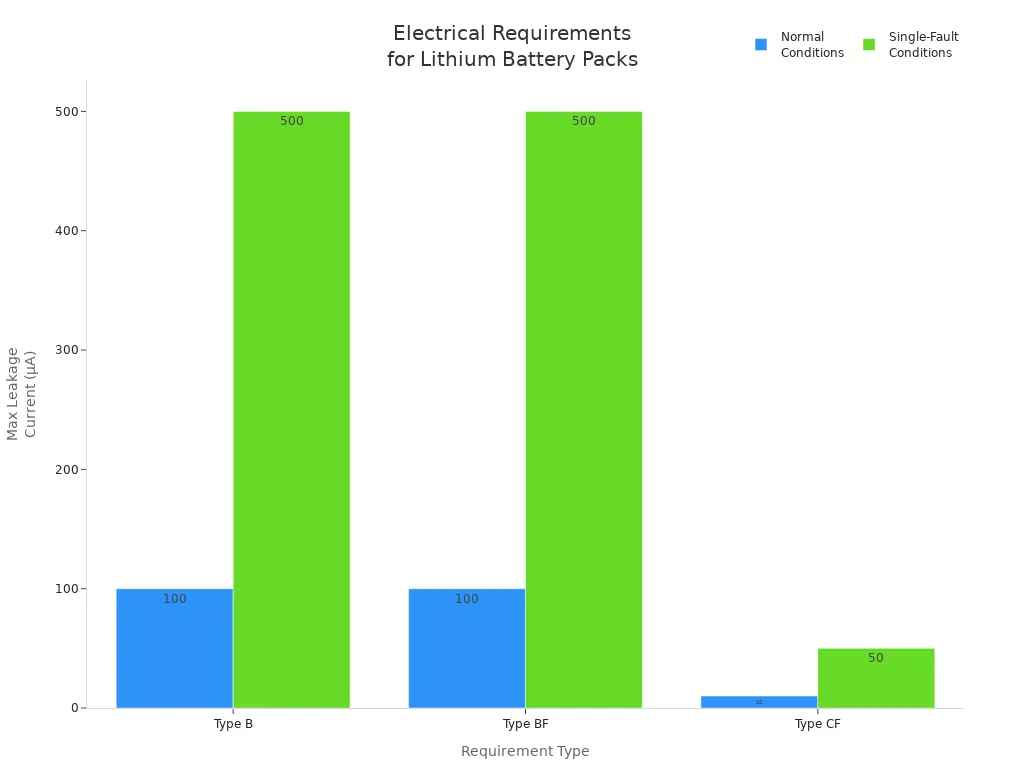
You face strict requirements when designing lithium battery packs for medical devices. Electrical and mechanical safety standards protect both patients and equipment. For example, you must control leakage current and ensure proper insulation. The table below summarizes key electrical requirements for different device types:
Requirement Type | Normal Conditions | Single-Fault Conditions |
|---|---|---|
Type B | 100µA | 500µA |
Type BF | 100µA | 500µA |
Type CF | 10µA | 50µA |
You also need to meet mechanical standards. The following table outlines insulation and isolation needs:
Equipment Type | Isolation Voltage | Creepage Distance | Insulation Type |
|---|---|---|---|
Type B | 1500 Vac | 2.5 mm | Basic Insulation |
Type BF | 3000 Vac | 5 mm | Double Insulation |
Type CF | 4000 Vac | 8 mm | Double Insulation |
You must verify insulation, test for shock protection, and ensure compliance with IEC 60601-1 before deploying disposable surgical tools. Regulatory standards such as IEC 62133, UL 2054, and ISO 13485 guide your battery pack configuration and design choices. Customization allows you to optimize configuration for unique device shapes, maximize runtime, and integrate advanced safety features. This approach ensures disposable surgical tools meet the highest safety and reliability standards.
1.2 Risks of Off-the-Shelf Packs
Using off-the-shelf lithium battery packs in disposable surgical tools introduces significant risks. These packs may not match your device’s configuration or safety needs. Common hazards include:
Thermal runaway, which can cause fire, toxic gas release, or explosion.
Overheating and fire due to overcharging, overloading, or mechanical stress.
Catastrophic failures from internal short circuits or physical damage.
Non-compliance with IEC 62133, leading to regulatory issues.
Off-the-shelf packs often lack the advanced safety features found in custom solutions. You may face higher long-term costs due to frequent maintenance or replacement. Custom battery pack configuration for disposable surgical tools provides tailored protection, advanced monitoring, and compliance with global standards. This approach reduces risk and ensures reliable operation in critical medical environments.
Part2: Battery Pack Configuration for Medical Devices

2.1 Series vs. Parallel Basics
When you design a lithium battery pack for medical devices, you must decide how to connect the cells. The two main options are cells in series and cells in parallel. Each configuration changes the electrical properties of your battery pack and affects its performance in different ways.
Configuration | Voltage | Capacity | Applications | Safety Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Series | Increases voltage | Same capacity as one cell | High-power medical and industrial devices | Risk of electric shock; requires protective gear |
Parallel | Same voltage as one cell | Increases capacity | Low-voltage systems, backup power | High current risk; requires caution |
Cells in series increase the total voltage of your battery pack. For example, if you connect four 3.7V cells in series, you get a total voltage of 14.8V. The capacity remains the same as a single cell. This configuration works well for devices that need higher voltage to drive motors or advanced electronics, such as surgical drills or robotic medical tools.
Cells in parallel keep the voltage the same as a single cell but increase the total capacity. If you connect four 2,000mAh cells in parallel, you get a total capacity of 8,000mAh. This setup extends runtime and supports devices that require long operation at lower voltages, such as portable monitors or infusion pumps.
You may also combine both methods, creating a series-parallel configuration. This approach lets you achieve both the voltage and capacity targets for your application. The choice between series vs parallel depends on your device’s power needs, size constraints, and safety requirements.
⚡ Tip: Modern medical batteries use smart protection systems with both electrical and physical safety features. These include special parts that physically break circuits if something goes wrong, improving safety for both patients and operators.
2.2 Optimizing Voltage and Capacity
Optimizing your battery pack configuration improves efficiency and performance. The right balance between cells in series and cells in parallel ensures your device meets demanding medical standards and delivers reliable results.
Configuration Type | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
Series | Higher voltages, less current, thinner wires, reduced voltage drop | One failed cell can stop the whole pack |
Parallel | Backup power, longer runtime at lower voltages, balanced charging | Requires more space for additional cells |
Series-Parallel | Combines benefits of both, achieving target voltage and capacity | More complex design and management |
When you use cells in series, you can reduce the current needed for the same power output. This allows you to use thinner wires and minimize voltage drop, which is critical for high-performance medical equipment. However, if one cell fails, the entire pack may stop working. You must include monitoring and balancing systems to prevent this risk.
Cells in parallel provide backup power and longer runtime. This configuration supports balanced charging and discharging, which extends battery life. However, it requires more space, which can be a challenge in compact medical devices.
A series-parallel configuration combines the strengths of both. You can achieve the voltage and capacity your device needs, but the design becomes more complex. You must manage cell balancing, thermal management, and safety features carefully.
CCCV (Constant Current, Constant Voltage) charging extends battery life by up to three times compared to older charging methods.
This method reduces charging time by nearly 24%.
It balances quick charging with longer battery life, which is crucial for medical applications where downtime is not acceptable.
For disposable surgical tools, configuration choices have a direct impact on performance and ergonomics. For example:
BioAccess, Inc. upgraded their surgical drill from alkaline batteries to lithium metal oxide batteries. This change led to a 36% weight reduction and a 40% volume reduction.
The new battery configuration allowed for faster drilling speeds and more active drill time, improving efficiency and reducing operator fatigue.
Lithium metal oxide batteries deliver high continuous power and high pulse amplitude, making them ideal for surgical applications.
The right battery selection can significantly reduce the size and weight of surgical tools without sacrificing performance.
The adoption of Lithium Ferro Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries is increasing due to their advantages in portability and efficiency for surgical tools.
These tools must meet strict ergonomic and sterilization requirements, so battery selection and configuration play a key role in the design process.
When you optimize the arrangement of cells in series and cells in parallel, you improve device performance, safety, and reliability. You also ensure compliance with medical standards and extend the operational life of your products.
Part3: Cell Selection for Lithium-Ion Battery Packs
3.1 Choosing Lithium Chemistry
Selecting the right chemistry for your lithium-ion battery pack is critical for custom lifepo4 battery pack design. You must align the chemistry with your device’s power, safety, and longevity needs. Excell Battery supports OEM engineers by offering a range of chemistries, such as lithium-ion, LiFePO4, lithium-polymer/LiPo, and Solid-State Battery options. Each chemistry provides unique advantages for medical, robot, and industrial applications.
Chemistry Type | Energy Density | Cycle Life | Safety Level | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
LCO | High | Moderate | Moderate | Portable monitors, imaging |
NMC | High | High | Good | Robotics, mobile workstations |
LiFePO4 | Moderate | Very High | Excellent | Surgical tools, AEDs, ventilators |
LMO | Moderate | Moderate | Good | Infusion pumps, carts |
LTO | Low | Ultra High | Excellent | Backup power, oxygen concentrators |
Solid-State Battery | Very High | High | Superior | Implantable, wearable devices |
Lithium Metal Oxide | High | High | Good | Defibrillators, bone stimulators |
Lithium Power highlights the importance of pairing the right chemistry with a robust Smart Battery Management System to meet medical device requirements.
3.2 Ultra-Thin and Lightweight Cell Options
You can enhance device portability and comfort by choosing ultra-thin and lightweight battery cells. These cells are essential for custom lifepo4 battery pack design in wearable and implantable medical devices. They support continuous monitoring and telemedicine, while their customizable shapes fit unique device geometries.
Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
Compact and lightweight | Improves patient comfort and device ergonomics |
Customizable shapes and sizes | Enables integration into slim, flexible devices |
High energy density per volume | Extends device runtime without bulk |
Reliable rechargeability | Supports long-term use and frequent acceptance tests |
These battery cells must be safe, biocompatible, and provide power for extended periods.
Lightweight construction enhances safety precautions and overall device protection.
3.3 Safety and Certification
You must prioritize protection and safety precautions in every custom lifepo4 battery pack design. Overcharging, overheating, and volatile electrolytes can cause dangerous incidents. To ensure safety, always select battery cells that meet strict certifications:
Certification | Description |
|---|---|
UL1642 | Ensures safety of lithium battery cells in medical and industrial devices |
IEC62133 | Focuses on rechargeable battery safety, preventing overheating and leakage |
UN38.3 | Governs safe transportation of lithium batteries due to fire risk |
You should conduct acceptance tests at every stage to verify compliance and performance. These tests confirm that your battery cells meet all protection and safety requirements before integration into your lithium-ion battery pack.
Part4: Battery Management System Integration
A robust battery management system forms the backbone of any reliable lithium battery pack for medical devices. You need to ensure that every battery assembly delivers consistent performance, safety, and compliance. This section guides you through the essential features, communication protocols, and redundancy strategies that elevate your battery assembly from basic power storage to a smart, dependable energy solution.
4.1 Essential BMS Features
You must select a battery management system that addresses the unique demands of medical device applications. The right system monitors, protects, and optimizes every battery cell within your assembly. Here is a summary of the most critical features:
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Cell Balancing | Ensures equal charge levels across all battery cells, using dissipative balancing up to 150 mA. |
Comprehensive Protection | Provides voltage and current cutoff, thermal management, and automatic recovery from faults. |
Monitoring | Tracks individual cell parameters, lifetime statistics, and event history for each assembly. |
Safety Mechanisms | Includes overvoltage, undervoltage, and overcurrent protection to prevent dangerous conditions. |
You need cell balancing to maintain efficiency and maximize capacity throughout the battery’s life cycle. Constant monitoring of battery cells allows you to detect early signs of degradation or imbalance. Comprehensive protection features, such as voltage and current cutoffs, thermal management, and automatic fault recovery, help you avoid catastrophic failures. Safety mechanisms like overvoltage and undervoltage protection prevent battery cells from exceeding safe operating limits, while overcurrent protection guards against excessive charge or discharge rates.
🔎 Note: The battery management system continuously checks parameters against safety thresholds. When it detects a dangerous condition, it acts immediately to protect both the device and the patient.
4.2 Communication and Monitoring
Modern medical devices require advanced communication and monitoring capabilities within the battery management system. These features enable you to track battery health, predict maintenance needs, and ensure regulatory compliance. The system must support real-time data exchange with host devices and external analyzers.
Protocol | Application | Features |
|---|---|---|
SMBus | Biomedical instruments | Two-wire interface, supports multiple devices, includes timeouts and packet error checking |
Modbus | Industrial automation (including medical devices) | Simple, open protocol, organizes data in memory maps for efficient status and control |
You can use SMBus for seamless integration with biomedical instruments, benefiting from its error checking and multi-device support. Modbus offers a straightforward solution for industrial and medical automation, allowing efficient reading and writing of battery status and control parameters.
Advanced monitoring features further enhance your battery assembly. For example, battery model design and simulation help you estimate battery parameters under varying temperature conditions. Active cell balancing, using energy-efficient DC/DC converters, improves safety and performance compared to passive techniques. You should also consider the cost-benefit analysis of different balancing methods over the expected five-year lifespan of your battery assembly.
🟢 Tip: Real-time monitoring and predictive analytics support sustainability by extending battery life and reducing waste.
4.3 Safety and Redundancy
Safety and redundancy are non-negotiable in medical device battery assembly. You must implement multiple layers of protection to guarantee uninterrupted operation, especially for life-supporting equipment.
Redundancy Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Battery Redundancy Systems | Ensure continuous power for critical care equipment, protecting patient safety during outages. |
Modular Battery Solutions | Offer flexibility and quick replacement, minimizing downtime and maintaining backup power. |
Automated Switchover Mechanisms | Keep power supply stable, ensuring uninterrupted operation of life-saving devices. |
Dual AC Input Systems | Connect to two independent power circuits for rapid failover (under 10 ms). |
External UPS Systems | Provide battery backup emergency power and surge protection, requiring periodic battery replacement. |
Overcharge and Deep Discharge Protection | Advanced safety features in modular systems to prevent damage and ensure reliability. |
Real-time Monitoring | Each module includes monitoring for voltage, temperature, and current to ensure optimal performance. |
You should integrate protection circuits to prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits. Overheating prevention mechanisms minimize the risk of explosion or fire, maintaining stable performance over long periods. Continuous improvements in battery management reduce the risk of device failure, which is essential for life-supporting and monitoring devices.
⚠️ Alert: Always verify that your battery assembly includes real-time monitoring for voltage, temperature, and current. This step is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and safety in every application.
By prioritizing these safety and redundancy features, you ensure that your battery assembly meets the highest standards for reliability and patient safety. This approach supports compliance with international standards and extends the operational life of your medical devices.
You can achieve safe, reliable custom lithium battery packs for medical devices by following these steps:
Analyze requirements and define electrical needs.
Select optimal cell chemistry and robust BMS.
Validate with rigorous testing and certification.
Always document risk assessments and maintenance plans.
Consult battery experts for complex projects or custom battery consultation.
FAQ
What lithium battery chemistry should you choose for medical device applications?
Chemistry | Safety Level | Cycle Life | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
LiFePO4 | Excellent | Very High | Surgical tools, AEDs, ventilators |
Lithium-ion | Good | High | Portable monitors, imaging |
Solid-State Battery | Superior | High | Implantable, wearable devices |
You should select chemistry based on safety, cycle life, and device requirements.
How does a custom lithium battery pack improve reliability in industrial and medical environments?
You gain tailored protection, advanced monitoring, and compliance with global standards. Large Power offers custom battery consultation for optimized solutions.
What communication protocols do lithium battery management systems support for B2B integration?
You can use SMBus for biomedical instruments and Modbus for industrial automation. Both protocols enable real-time monitoring and control.




