
You should always charge a LiPo battery at a safe charge rate, typically 1C, matching the battery’s capacity in amps. The 1C rule protects both battery life and safety. Major manufacturers recommend this rate for most lipo battery charge rates, as higher charging can stress the lipo battery and increase risk.
Key Takeaways
Always charge LiPo batteries at the recommended 1C rate to protect battery life and prevent overheating or swelling.
Use chargers designed for LiPo batteries with balance charging and safety features, and never leave batteries unattended while charging.
Inspect batteries before charging, watch for warning signs like swelling or heat, and stop charging immediately if any appear to ensure safety.
Part 1: LiPo Battery Basics

1.1 What is a LiPo Battery
You encounter lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries in many battery pack solutions across industrial, medical, robotics, and consumer electronics sectors. LiPo batteries use a gel-like polymer electrolyte, making them lighter and more flexible than nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) or traditional lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. You benefit from their customizable shapes and thin profiles, which suit compact devices and weight-sensitive applications.
Here is a comparison of LiPo batteries with other lithium chemistries commonly used in battery packs:
Chemistry | Platform Voltage (V) | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
LiPo | 3.7 | 150-200 | 300-500 | Drones, RC, medical, robotics |
LiFePO4 | 3.2 | 90-120 | 2000+ | Medical, infrastructure, security |
NMC | 3.7 | 180-220 | 1000-2000 | Industrial, EV, consumer electronics |
LCO | 3.6 | 150-200 | 500-1000 | Smartphones, cameras |
LMO | 3.7 | 100-150 | 700-1500 | Power tools, robotics |
LTO | 2.4 | 70-80 | 7000+ | Grid storage, medical, robotics |
LiPo batteries stand out for their high discharge rates (often 35C-45C), low self-discharge, and lightweight design—about 60% the weight of NiMH batteries with similar capacity. You must use specialized chargers and handle LiPo batteries with care due to their unique internal structure and charge rate requirements.
1.2 Why Charge Rates Matter
You need to understand lipo battery charge rates to maximize battery performance and lifespan. The charge rate, often expressed as c-rate, determines how quickly you can safely recharge a lipo battery. Charging too quickly increases internal mechanical stress and heat, which can cause swelling, reduced capacity, or even thermal runaway—a dangerous condition that may lead to fire.
Tip: Always follow manufacturer guidelines for charge rate and use battery management systems to monitor voltage, current, and temperature.
Charging at the recommended rate (typically 1C) helps you avoid chemical changes that increase internal resistance and heat generation. Overcharging or deep discharging shortens battery life, especially in industrial and medical applications where reliability is critical. Proper charge rate management ensures your battery packs deliver consistent performance and safety across hundreds of cycles.
Part 2: LiPo Battery Charge Rates
2.1 The 1C Rule
You often see the term “1C” when working with lipo battery charge rates. The c-rate defines how quickly you can safely charge or discharge a lipo battery. For example, a 2200mAh lipo battery charged at 1C means you set the current to 2.2A. This rule is grounded in the chemical and physical limits of lipo batteries. Charging at 1C ensures the voltage per cell does not exceed 4.2V, which prevents overheating and swelling. The charging process uses a constant current/constant voltage (CC/CV) method. You start with a steady current until the battery reaches 4.2V per cell, then the charger holds the voltage while the current tapers off. This approach protects the battery from overcharging and extends its lifespan.
Most lipo battery charge rates default to 1C because many batteries do not specify a maximum charge rate. Charging faster than 1C increases the risk of heat buildup, swelling, and reduced cycle life. Always check the manufacturer’s label and use a quality charger designed for lipo batteries. Monitoring temperature during charging helps you avoid damage.
Note: Charging to 80% and discharging to 40% can further extend your battery’s lifespan.
2.2 Higher C-Rates
Some lipo batteries support higher c-rates, such as 2C or even 5C, but only if the manufacturer specifies this on the label. Manufacturers determine these ratings through controlled lab tests, monitoring temperature and voltage under load. High c-rate lipo battery charge rates are common in robotics, industrial, and medical sectors where fast charging is critical. However, charging above 1C can reduce battery life and increase risk if not managed properly.
Industry / Application | Typical C-Rate Range | Usage Notes / Safety Emphasis |
|---|---|---|
FPV Drone Racing | 30C–75C | High throttle, fast maneuvers |
RC Cars | 20C–50C | Size and motor dependent |
Robotics | 10C–30C | Steady/variable loads, safety margins |
Industrial / Professional | 15C–40C | Certified sources, strict protocols |
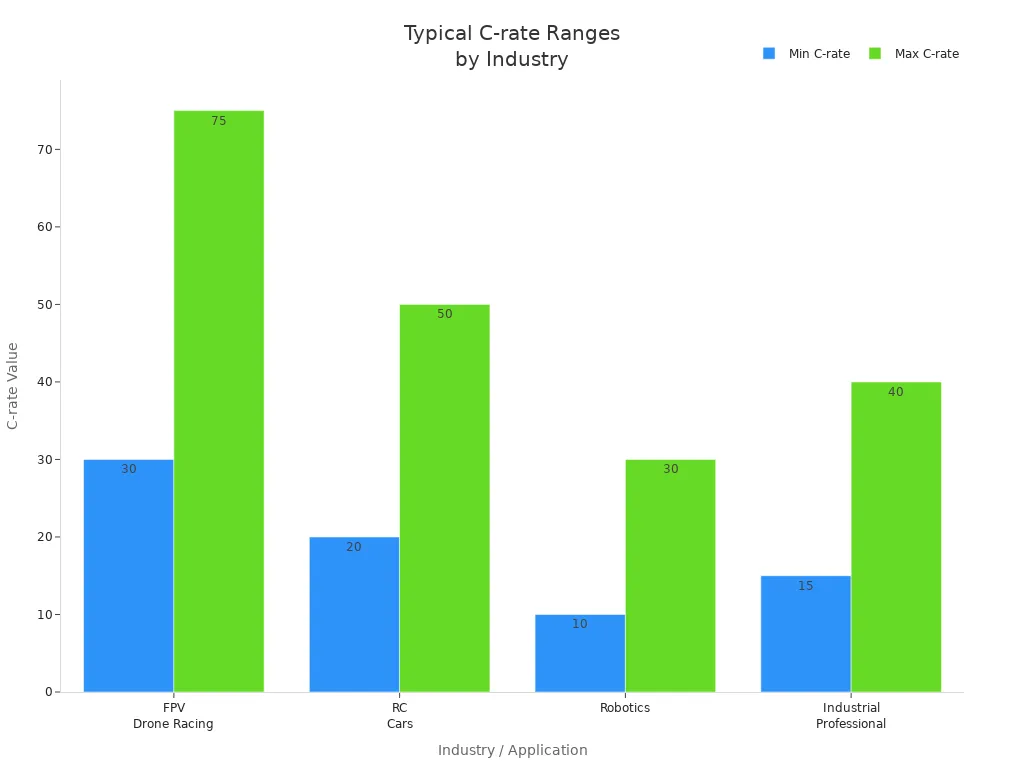
You should always use certified chargers, monitor for heat or swelling, and store lipo batteries in fireproof containers. Never exceed the recommended charge rate, and always prioritize safety in your charging setup.
Part 3: Calculate Charge Rates
3.1 Step-by-Step Calculation
You can calculate the safe charge rate for any lipo battery using a simple formula. The standard method uses the battery’s capacity and the C-rate. For most lipo batteries, the safe charge rate is 1C. This means you set the charging current (in amps) equal to the battery’s capacity (in ampere-hours). For example, a 3000mAh battery (which is 3Ah) should be charged at 3A for a 1C rate. Always check the battery label for the recommended charge rate before starting the charging process. Use a lipo-compatible charger that supports constant current/constant voltage charging methods.
Tip: Convert milliamp-hours (mAh) to ampere-hours (Ah) by dividing by 1000. For example, 5000mAh = 5Ah.
3.2 Example Calculations
Let’s look at how the calculation works in real-world scenarios. Suppose you have a 5000mAh (5Ah) lipo battery. For a 1C charge rate, set your charger to 5A. If the manufacturer allows a 2C rate, you can charge at 10A. However, always use the lower value if unsure. The table below compares different chargers and their performance with a 3S 5000mAh lipo battery:
Charger | Max Power (W) | Max Current (A) | Theoretical Charging Time | Practical Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Charger A | 100 | 5 | ~1 hour | Suitable for standard charging; current limited to 5A. |
Charger B | 150 | 10 | ~0.5 hour | Supports 2C fast charging; ensure battery supports higher charge rate. |
Charger C | 200 | 15 | ~0.5 hour | Power for larger packs; actual current limited by battery’s max C-rate. |
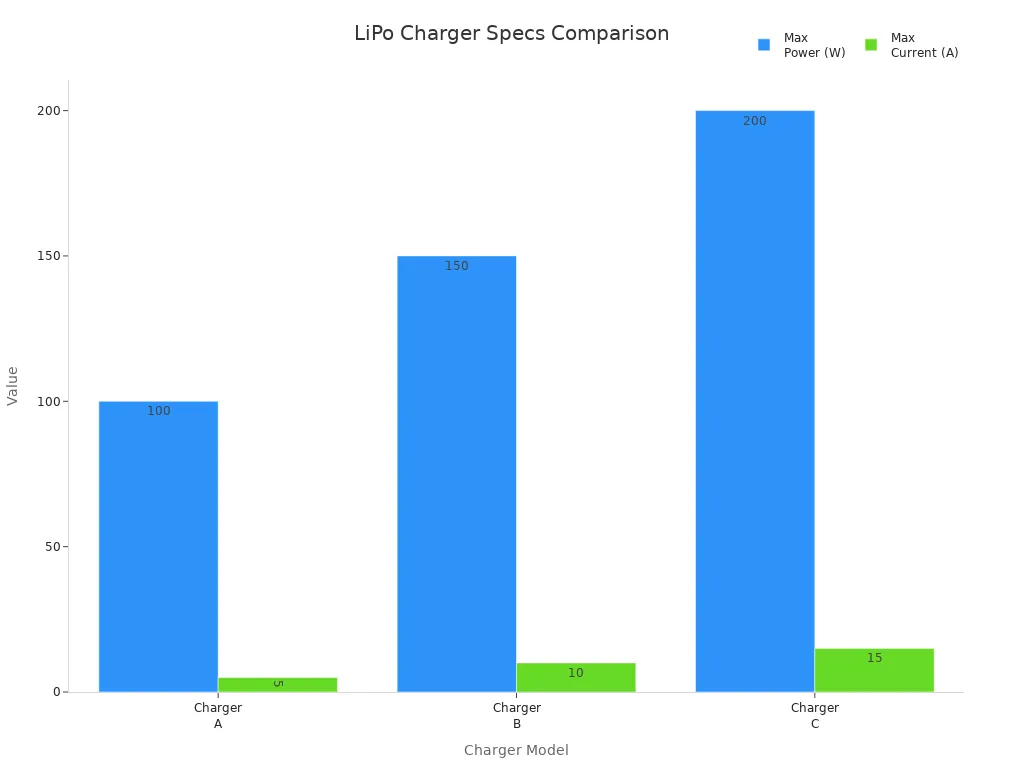
Common errors in calculating charge rates include using burst C-rates instead of continuous ratings, not adding a 20–30% safety margin, and ignoring signs of battery aging. You should always use continuous ratings, measure actual current draw, and monitor for swelling or heat during the charging process.
3.3 Online Tools
You can simplify charge rate calculations with online tools like the LiPo Battery Charge Rate Calculator by Ufine. This tool lets you enter battery type, voltage, capacity, and charge rate to estimate safe charging current and time. It also provides guidance on charging process efficiency, unit conversions, and best practices for lipo battery longevity. The calculator includes FAQs and expert tips to help you avoid common mistakes and ensure safe charging methods for all lithium chemistries.
Part 4: Battery Labels and C-Ratings
4.1 Reading Labels
You must read lipo battery labels carefully to ensure safe operation and compliance with industry standards. Manufacturers include key information to help you select the correct charge rate and avoid hazards. Most labels display the nominal voltage, which matches the cell count (for example, 7.4V for a 2-cell pack or 11.1V for a 3-cell pack). Always match this voltage when setting your charger to prevent fire risks.
You will also find the maximum safe charging current, typically limited to 1C. For example, a 1300mAh battery should be charged at or below 1.3A. Labels warn against charging if the voltage per cell drops below a minimum threshold, often 3.3V per cell. Balance charging using the correct connector, such as a JST XH, is emphasized for safety.
Manufacturers include additional safety instructions:
Never leave batteries unattended while charging.
Use only professional lipo chargers.
Charge in fireproof containers and avoid flammable surfaces.
Do not charge swollen or damaged batteries.
Avoid charging multiple packs in series.
Labels may also specify storage voltage (3.6V–3.9V per cell) and maximum charge voltage (4.2V per cell). In the European Economic Area, you will see the CE marking, which indicates compliance with EU directives. Other regions require certifications such as UL (USA/Canada), PSE (Japan), and KC (Korea).
Region / Country | Certification / Mark | Key Focus / Coverage |
|---|---|---|
EEA | CE Marking | EU safety, health, environmental directives |
USA, Canada | UL 1642 / 2054 | Structural and electrical safety |
Japan | PSE Certification | Electrical safety |
Korea | KC Certification | Electrical and thermal safety |
India | BIS Certification | Battery safety certification |
Taiwan | BSMI Certification | Electrical safety, EMC, labeling |
Brazil | INMETRO Certification | Energy and product safety |
China | CQC Certification | Public projects, high-end devices |
Saudi Arabia | SASO Certification | Product conformity |
Global (Transport) | UN38.3, MSDS | Shipping safety standards |
Tip: Always check for clear labeling, proper certifications, and up-to-date documentation before using any lipo battery in your application.
4.2 Spotting Overstated Claims
You need to stay alert for exaggerated C-rate claims on lipo battery packaging. Manufacturers sometimes inflate C ratings, such as labeling a battery 50C when it can only safely deliver 20–30C. No industry-wide standard exists for C-rate testing, so claims can be inconsistent.
Common signs of overstated C ratings include:
The battery cannot sustain the claimed amperage.
Voltage drops quickly under load.
The battery overheats, swells, or shows physical damage like puffing or casing rupture.
Rapid power loss or failure to deliver full capacity.
Overstated C ratings increase the risk of overheating, swelling, and even fire. You should always leave a safety margin below the claimed C rating. Rely on independent testing, user reviews, and real-world performance rather than packaging claims alone.
To verify C-rate authenticity, you can:
Purchase from reputable sellers.
Check for clear labeling, including brand, model, and certifications.
Compare claimed capacity to typical values for the battery model.
Inspect packaging for tampering or anti-counterfeiting features.
Use manufacturer authentication codes if available.
Test battery performance with controlled discharge and compare results to specifications.
Note: Measuring internal resistance with specialized equipment provides the most reliable indication of true discharge capability.
Part 5: Charge LiPo Batteries Safely

Charging lithium polymer batteries requires strict attention to safety protocols. You must follow industry best practices to protect your equipment, facility, and personnel. This section outlines essential steps to charge lipo batteries safely, focusing on inspection, charger selection, environment setup, and recognizing warning signs.
5.1 Pre-Charge Checks
Before you begin charging, always perform a thorough inspection of your lipo battery. This step reduces the risk of failure or fire and ensures compliance with industrial safety standards.
Visually inspect the battery for damage, swelling, or irregularities. Look for damaged leads, connectors, or shrinkwrap issues.
Do not use or charge any battery that shows signs of swelling or physical damage.
Check the battery pack voltage with a digital voltmeter. Confirm each cell is above 3.3V before charging.
Verify charger settings for correct voltage and current. Ensure the settings match the battery label.
Use only chargers designed for lipo batteries. Never use NiMH or NiCd chargers.
Always connect the battery with correct polarity to prevent short circuits.
Use balance charging systems to maintain equal voltage across all cells.
Allow the battery to cool to room temperature before charging.
Charge each battery pack individually. Avoid charging multiple packs in series.
Store batteries in cool, dry places between 40–80°F, away from children and pets.
Tip: Never leave lipo batteries unattended while charging. Keep a dry fire extinguisher or a bucket of dry sand nearby as a precaution.
These pre-charge checks help you avoid overheating, overcharging, imbalance, and physical damage—primary causes of lipo battery failure or fire.
5.2 Charger Selection
Selecting the right charger is critical for safety and battery longevity. You should prioritize chargers with features that match your lipo battery’s specifications and your operational needs.
Choose a charger compatible with your specific lipo battery type, size, voltage, and configuration.
Use a charger with adjustable charge rates to prevent overcharging or damage.
Select a charger that supports balance charging. This feature maintains equal voltage across all cells and prevents overcharge or undercharge.
Prioritize chargers with built-in safety features such as overcharge protection, short circuit protection, and temperature monitoring.
Purchase chargers from reputable brands known for quality and reliability.
Verify the charging interface matches your power source, whether AC or DC.
Consider additional features like LCD displays or customizable charging profiles for enhanced usability.
A high-quality balance charger ensures safe and efficient charging. Chargers with storage functions help maintain optimal voltage during storage, stabilizing battery chemistry and reducing degradation. Built-in cutoff features prevent over-discharging and enhance safety. Using inappropriate chargers can reduce battery lifespan or create safety hazards.
5.3 Safe Charging Environment
You must set up a controlled environment to charge lipo batteries safely, especially in industrial or medical settings. The right environment minimizes risks and supports compliance with safety regulations.
Charge lipo batteries only in approved locations, such as fire-resistant containers or LiPo safety bags rated up to 1200°C.
Use fireproof surfaces like ceramic, metal, or UL94 V-0 certified charging boxes.
Keep a Class D (lithium-rated) fire extinguisher nearby. Never use water to extinguish lithium fires.
Avoid charging near flammable materials. Keep the area clear of wood, cloth, or carpet.
Always attend the battery during charging to monitor for abnormalities.
Store batteries in cool, dry places to maintain integrity and reduce risk.
Use intelligent monitoring systems in industrial environments to predict and prevent thermal runaway.
Promote user education and training on battery safety protocols.
Safety Measure | Industrial/Medical | Robotics | Consumer Electronics | Infrastructure/Security |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Fireproof charging container | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
Class D fire extinguisher | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
Intelligent monitoring | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
User training | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
Balance charging | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
Note: If you notice swelling, venting, or heat during charging, stop immediately. Move the battery to a non-flammable area with insulated gloves and allow it to cool.
5.4 Warning Signs
Recognizing early warning signs helps you prevent incidents and respond quickly to potential hazards. You must remain vigilant during every charging session.
Swelling, ballooning, or deformity of the battery cells signals a serious issue.
Physical damage such as punctures, splits, or warping of the casing requires immediate attention.
High temperature during charging or use is a warning sign. Disconnect the battery and monitor it closely.
Unusual smells, hissing sounds, or smoke indicate imminent danger. Stop charging and move the battery to a safe area.
Never charge a battery that has been dropped or sustained impact.
Avoid charging batteries with voltage per cell below 3.3V.
If you observe any of these warning signs:
Stop charging and disconnect the battery immediately.
Move the battery or device to a fireproof or safe area, such as a concrete floor or metal tray.
Do not touch the battery if it is smoking or overheating. Wait until it cools down.
Call emergency services if the fire spreads or the situation escalates.
Dispose of the battery at a certified recycling center once it is fully cooled.
⚠️ Never throw damaged or swollen batteries in regular trash. Proper disposal prevents secondary fires and environmental hazards.
By following these precautions and maintaining a disciplined approach, you can charge lipo batteries safely and protect your facility, equipment, and personnel from unnecessary risks.
You protect your workplace and extend the life of every lipo battery by checking specifications, using LiPo-compatible chargers, and following safety steps.
Routine maintenance, balanced charging, and regulated disposal reduce risks.
Updated best practices, such as voltage management and BMS integration, lower incident rates and support compliance.
Practice | Benefit |
|---|---|
Voltage management | Fewer cell failures |
BMS integration | Early anomaly detection |
Maintenance protocols | Longer battery pack lifespan |
FAQ
What is the safest charge rate for LiPo batteries in industrial battery packs?
You should charge LiPo batteries at 1C unless the manufacturer specifies otherwise. This rate protects battery life and reduces risk in industrial and medical applications.
How do LiPo charge rates compare to other lithium chemistries?
Chemistry | Typical Charge Rate | Platform Voltage (V) | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
LiPo | 1C | 3.7 | 150–200 | 300–500 |
LiFePO4 | 0.5C–1C | 3.2 | 90–120 | 2000+ |
NMC | 0.5C–1C | 3.7 | 180–220 | 1000–2000 |
LCO | 0.5C–1C | 3.6 | 150–200 | 500–1000 |
LMO | 0.5C–1C | 3.7 | 100–150 | 700–1500 |
LTO | 2C | 2.4 | 70–80 | 7000+ |
What should you do if a LiPo battery swells during charging?
You must stop charging immediately. Move the battery to a fireproof area. Dispose of it at a certified recycling center after it cools.




