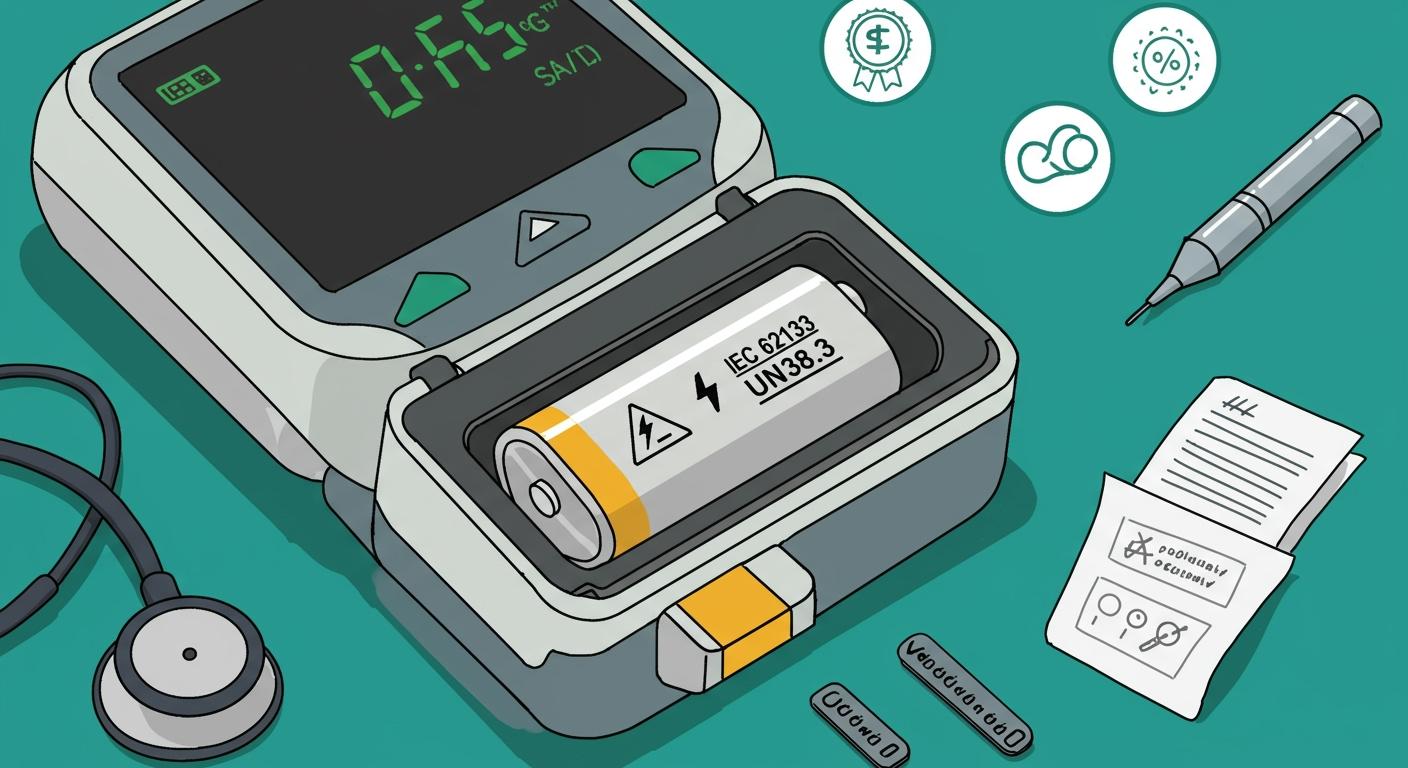
You must ensure that medical batteries comply with IEC and UN safety standards. These standards protect patients, guarantee device reliability, and support regulatory compliance. Global agencies demand strict testing for batteries used in healthcare.
Ignoring these requirements exposes your devices to safety risks, legal penalties, and loss of market access.
Key Takeaways
Compliance with IEC 62133 and UN38.3 standards ensures patient safety by preventing battery-related hazards in medical devices.
Meeting safety standards enhances device reliability, ensuring consistent performance in critical healthcare situations.
Regulatory approval is faster and easier when batteries meet IEC and UN standards, saving time and resources for manufacturers.
Non-compliance can lead to serious safety hazards, legal issues, and damage to brand reputation, risking market access.
Prioritizing compliance supports global market access, allowing safe shipping of medical batteries worldwide.
Part 1: Medical Batteries and Standards
1.1 IEC Standards Overview
You need to understand the role of the IEC 62133 standard when working with medical batteries. This standard sets strict safety requirements for lithium-ion battery safety in devices used in healthcare, robotics, security systems, infrastructure, and consumer electronics. The IEC 62133 standard focuses on everyday use and performance, making it essential for medical batteries that must operate reliably in critical situations.
Here is a table summarizing the key requirements of IEC 62133 for medical batteries:
Requirement Type | Description |
|---|---|
Safety Testing | Ensures safety against hazards like fire, explosion, or leakage during intended use and misuse. |
Compliance | Necessary for regulatory approval from bodies like the FDA. |
Testing Procedures | Includes specific tests for overcharging, over-discharging, short-circuiting, and thermal runaway. |
Labeling and Documentation | Requirements for proper labeling and documentation to verify compliance. |
You must meet these compliance requirements to ensure your batteries pass regulatory review and protect users.
1.2 UN38.3 Testing Requirements
The UN 38.3 standard applies to lithium batteries shipped across the globe. You need to follow this standard to guarantee safe transportation of medical batteries and lithium battery packs. The UN standard includes a series of tests that simulate real-world conditions during transit. These tests help prevent safety hazards such as fire or explosion.
Here are the main tests required by UN 38.3:
Test T1: Altitude Simulation – Simulates low pressure
Test T2: Thermal Test – Checks integrity during rapid temperature changes
Test T3: Vibration – Simulates vibration during transportation
Test T4: Shock – Simulates shock during transportation
Test T5: Short Circuit – Simulates an external short circuit
Test T6: Impact – Simulates impact and crush to the cell case
Test T7: Overcharge – Simulates overcharge on rechargeable batteries
Test T8: Forced Discharge – Simulates forced discharge of cells
Failures in these tests often result from poor sealing, thermal fatigue, or loose internal components. You must address these issues to achieve compliance and avoid shipment delays.
1.3 Relevance for Lithium-Ion Battery Safety
You rely on lithium-ion battery safety to protect patients and maintain device reliability. Both IEC and UN standards address risks like thermal runaway and fire. The IEC 62133 standard requires thermal abuse tests to prevent overheating, while the UN 38.3 standard mandates rigorous testing for transport safety.
Standard | Focus Area | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
IEC 62133 | Safety requirements for lithium-ion batteries | Outlines safety requirements and testing procedures, including thermal abuse tests to prevent thermal runaway. |
UN38.3 | Transport safety for lithium batteries | Mandates rigorous testing to ensure battery integrity during transport, addressing potential fire risks. |
You see these standards applied in medical, robotics, security systems, infrastructure, consumer electronics, and industrial sectors. Each application depends on reliable batteries that meet strict safety standards.
Below is a comparison of common lithium battery chemistries used in these sectors:
Chemistry | Platform Voltage (V) | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|
LiFePO4 | 3.2 | 90-160 | 2000-5000 |
NMC | 3.7 | 150-220 | 1000-2000 |
LCO | 3.7 | 150-200 | 500-1000 |
LMO | 3.7 | 100-150 | 500-1000 |
LTO | 2.4 | 70-110 | 7000-20000 |
Solid-State | 3.7-4.2 | 250-500 | 1000-5000 |
Lithium Metal | 3.0-3.6 | 300-500 | 500-1000 |
You must select the right chemistry and meet all safety standards to ensure compliance and protect your brand.
Part 2: Why Compliance Matters
2.1 Patient Safety
You protect patients when you follow safety standards for medical batteries. These standards help prevent injuries and fatalities linked to battery failures. You see real-world consequences when batteries do not meet safety requirements. For example:
From 1977 to June 2022, 69 deaths occurred due to button cell or coin battery ingestion, with 44 involving lithium batteries.
The NCPC reported that 50 of these deaths resulted from batteries burning through the esophagus.
Between January 2011 and December 2021, 25 fatalities were reported, with sources identified for seven cases.
You reduce these risks by meeting compliance requirements for lithium-ion battery safety. You ensure that batteries used in medical devices, robotics, and security systems do not pose hazards to patients or users. You also support safe transportation and handling, which is critical for devices shipped worldwide.
Following IEC and UN standards means you put patient safety first. You avoid preventable tragedies and build trust in your products.
2.2 Device Reliability
You rely on medical batteries to deliver consistent performance in critical situations. Safety standards like IEC 62133 and the UN 38.3 standard help you prevent battery failures that could lead to life-threatening emergencies. You benefit from:
Reliable operation of medical devices over years of use.
Protection against environmental factors such as temperature and humidity.
Verification of long-term performance, which is essential for devices in healthcare, infrastructure, and industrial sectors.
You see these standards applied to lithium battery packs in robotics, consumer electronics, and security systems. You avoid costly recalls and downtime by ensuring your batteries meet all safety requirements.
2.3 Regulatory Approval
You need regulatory approval to bring medical devices to market. Compliance with IEC and UN safety standards is essential for meeting the requirements of agencies like the FDA and ISO. You must show that your batteries pass rigorous testing and meet all safety requirements. You gain faster approval and avoid delays when you follow these standards.
Regulatory bodies demand proof of compliance before allowing medical devices into hospitals and clinics. You save time and resources by preparing your batteries for these reviews.
2.4 Global Market Access
You expand your reach when you meet international safety standards. You must comply with IEC 62133 and the UN 38.3 standard to ship medical batteries worldwide. You see different regions referencing these standards for market entry:
Standard | Importance for Market Access | Regions Referencing Standard |
|---|---|---|
IEC 62133 | Ensures battery safety, crucial for minimizing hazards and avoiding recalls or rejections. | CE marking in the EU, BIS in India, PSE in Japan |
UN38.3 | Ensures transport compliance, essential for safe shipping of medical devices. | Various international transport regulations |
You gain access to markets in Europe, Asia, and North America by meeting these compliance requirements. You avoid shipment delays and legal issues by ensuring safe transportation of lithium battery packs.
You position your products for success in medical, robotics, security, infrastructure, and consumer electronics sectors when you prioritize compliance.
Part 3: Risks of Non-Compliance

3.1 Safety Hazards
You face serious safety hazards when you ignore compliance requirements for medical batteries. Non-compliant lithium battery packs can cause dangerous incidents in hospitals, clinics, and other critical environments. You must understand the risks that arise from failing to meet IEC and UN safety standards.
Here are the most common safety hazards associated with non-compliant batteries:
Short-circuiting can trigger electrical explosions, intense heat, or fires.
Battery acid is extremely corrosive and can cause burns or damage to equipment and surfaces.
Flammable gases, such as hydrogen, may ignite easily and lead to explosions.
Battery bursts can result from excessive charging or gas build-up, causing chemical burns and injuries.
Heavy batteries can create physical hazards if not managed properly.
You see these risks in medical devices, robotics, security systems, and industrial equipment. For example, a battery burst in a portable medical monitor can harm patients and staff. In robotics, short-circuiting may damage sensitive electronics and disrupt operations.
Hazard Type | Description | Application Scenario |
|---|---|---|
Short-Circuiting | Electrical explosion, fire, heat | Medical monitors, robotics |
Battery Acid | Corrosive burns, equipment damage | Security systems, infrastructure |
Flammable Gases | Explosion risk | Industrial sensors, consumer electronics |
Battery Burst | Chemical burns, physical injury | Medical devices, robotics |
Weight | Physical hazard | Portable medical equipment |
You protect patients, staff, and property when you follow safety standards and ensure proper compliance.
3.2 Legal and Regulatory Issues
You expose your business to legal and regulatory consequences when you neglect compliance requirements. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and international transport authorities demand proof that your batteries meet IEC and UN standards. You risk fines, product recalls, and even bans from key markets if you fail to comply.
Non-compliant batteries often lead to device recalls in the medical industry. For instance:
ICU Medical recalled CSB batteries after discovering counterfeit units in critical devices.
These batteries were not tested for compatibility, which led to device failures.
Device failures interrupted essential medical treatments and put patient safety at risk.
You must meet all safety standards to avoid regulatory action and protect your business. You also need to maintain proper documentation and labeling to satisfy compliance requirements.
Regulatory Risk | Impact on Business | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
Product Recall | Financial loss, reputation damage | Counterfeit batteries in medical devices |
Market Ban | Loss of access to global markets | Non-compliance with IEC or UN standards |
Legal Penalties | Fines, lawsuits | Device failures causing patient harm |
You avoid costly recalls and legal trouble when you prioritize compliance and follow all safety standards.
3.3 Brand Reputation
You risk damaging your brand reputation when you sell non-compliant batteries. Customers and partners expect you to deliver safe, reliable products. A single safety incident or recall can erode trust and reduce your market share.
You see the impact of poor compliance in medical, robotics, and consumer electronics sectors. Device failures linked to non-compliant lithium battery packs can lead to negative press, loss of contracts, and long-term harm to your business.
Reputation Risk | Consequence | Sector Example |
|---|---|---|
Negative Press | Loss of customer trust | Medical devices, consumer electronics |
Contract Loss | Reduced business opportunities | Robotics, security systems |
Long-Term Harm | Decline in market share | Industrial, infrastructure |
You build a strong brand and gain customer loyalty when you meet all safety standards and compliance requirements.
Part 4: Achieving Compliance
4.1 Testing and Certification
You must follow a clear process to achieve compliance with international requirements for lithium battery packs. Accredited laboratory testing is mandatory for all lithium batteries used in medical, robotics, security systems, infrastructure, consumer electronics, and industrial sectors. You need to focus on battery safety testing to meet IEC and UN standards. The key tests ensure transport compliance and battery safety during the transport of dangerous goods.
Here is a table outlining the steps for testing and certification:
Step | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Conduct a gap analysis to identify missing components in compliance with FDA and UN 38.3 standards. |
2 | Ensure all necessary documentation is in place, including test records and safety certifications. |
3 | Complete all eight UN 38.3 key tests to demonstrate battery safety for shipping. |
4 | Submit documentation and test results to the FDA, ensuring compliance with relevant standards like IEC 62133. |
You must meet the documentation requirement for every stage. Accredited laboratory testing verifies safety features and ensures your batteries are ready for global shipment.
You protect your business and customers by following these steps. Compliance matters for every lithium system you produce.
4.2 Manufacturer Responsibilities
You have ongoing responsibilities to maintain compliance with IEC and UN standards. You must conduct detailed testing on battery designs to meet IEC 62133-2 safety criteria. Passing transportation-related tests certifies safe shipping across all transport modes. You need to monitor and update battery safety protocols to align with evolving standards.
You must adhere to safety standards set by organizations like IEC and UN.
You need to employ advanced thermal management systems to prevent thermal runaway in lithium systems.
You should use cooling mechanisms and temperature monitoring devices to maintain safe operating conditions.
You must provide documentation and evidence of compliance for every shipment.
You also need to address sustainability and ethical sourcing. Learn more about sustainability practices and conflict minerals in battery manufacturing. For enhanced safety, integrate battery management systems (BMS) to monitor and control lithium battery packs.
You ensure long-term safety and reliability by updating protocols and using advanced safety features. Your commitment to compliance supports safe transport of dangerous goods and protects your brand.
You strengthen your business when you prioritize compliance with IEC 62133 and UN38.3 standards. Manufacturers who follow these standards benefit from international recognition, reduced legal risks, and improved brand reputation.
Align with environmental sustainability goals
Protect your company from lawsuits
Enhance your market image
Standard | Purpose | Impact on Future Regulations |
|---|---|---|
IEC 62133 | Battery safety requirements | Sets benchmarks for future safety standards |
UL 2054 | Household and commercial battery safety | Influences medical device battery standards |
ISO 13485 | Medical device quality management | Guides regulatory frameworks for quality |
You stay ahead by hiring battery safety engineers and encouraging ongoing learning. Proactive compliance helps you adapt to regulatory changes and ensures patient protection.
FAQ
What is IEC 62133, and why does it matter for medical batteries?
IEC 62133 sets safety standards for rechargeable lithium battery packs. You must follow this standard to ensure batteries in medical devices operate safely and reliably. Regulatory agencies require compliance for market approval.
How does UN38.3 testing affect battery shipments?
UN38.3 testing verifies that lithium battery packs can withstand transport hazards. You need to pass these tests to ship batteries for medical, industrial, and consumer electronics worldwide. Failure to comply can result in shipment delays or bans.
Which lithium battery chemistries meet IEC 62133 and UN38.3 standards?
Chemistry | IEC 62133 | UN38.3 | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
LiFePO4 | Yes | Yes | Medical, robotics, infrastructure |
NMC | Yes | Yes | |
LCO | Yes | Yes | Medical, industrial |
Yes | Yes | Robotics, infrastructure | |
LTO | Yes | Yes | Medical, industrial |
Solid-State | Yes | Consumer electronics, security | |
Lithium Metal | Yes | Yes | Medical, industrial |
What documentation do you need for compliance?
You must provide test reports, certification documents, and safety data sheets. Regulatory bodies require these for lithium battery packs used in medical, robotics, and industrial sectors. Proper documentation speeds up approval and shipment.
How do safety standards protect your brand reputation?
You build trust when you meet IEC 62133 and UN38.3 standards. Safe lithium battery packs reduce recalls and negative press in medical, security, and consumer electronics markets. Customers prefer reliable products from compliant manufacturers.




