
You play a crucial role in shaping the future of recycling and sustainability for outdoor lighting lithium battery packs. Improper disposal of these batteries leads to significant environmental impact:
Chemicals from lithium batteries contaminate soil and water.
Landfill fires caused by battery waste release toxic gases and heavy metals.
The importance of recycling lithium batteries grows as environmental regulations tighten and businesses face increased scrutiny over their environmental performance.
Key Takeaways
Recycling lithium batteries prevents harmful chemicals from contaminating soil and water, protecting wildlife and human health.
Businesses can save money and generate income by recycling batteries, reclaiming valuable materials, and avoiding fines from improper disposal.
Adopting a circular economy approach enhances sustainability by promoting recycling and resource recovery, reducing waste in battery management.
Part1: Recycling and Sustainability
1.1 Environmental Impact
You face increasing pressure to address the environmental impact of lithium battery packs used in outdoor lighting. Recycling and sustainability are essential for your operations because improper disposal of lithium batteries can cause severe harm to the environment. When you send batteries to landfills, toxic metals leach into soil and water, threatening wildlife and human health. Incinerating batteries releases hazardous emissions, which contribute to air pollution and climate change.
Recycling lithium batteries prevents the leaching of toxic metals into soil and water, which can harm wildlife and human health.
It minimizes waste by ensuring that batteries do not end up in landfills, where they can leak harmful chemicals.
Recycling conserves natural resources by reducing the need for new materials, thus decreasing the environmental impact associated with mining.
Lithium battery waste poses long-term ecological risks. Heavy metals such as nickel, manganese, and cobalt disrupt soil ecosystems and reduce agricultural productivity. Water pollution occurs when electrolytes and toxic substances leak, compromising water quality and harming aquatic life. Air pollution from incineration of batteries releases hazardous emissions, increasing health risks for communities and contributing to global warming.
You can reduce these risks by adopting advanced lithium battery recycling practices. By focusing on recycling and sustainability, you help protect the environment and support your company’s long-term goals.
1.2 Benefits for Businesses
Recycling lithium batteries offers significant advantages for your business. You can generate income by selling scrap batteries to certified recyclers. This process allows you to reclaim valuable materials such as lithium, nickel, and cobalt, which reduces your production costs. Many governments offer financial incentives for recycling programs, which can further enhance your profitability. By complying with regulations, you avoid costly fines and penalties.
Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
Selling Scrap Batteries | Businesses can sell used batteries to recyclers for cash, generating income from waste. |
Reclaiming Valuable Materials | Recycling allows businesses to recover metals like lithium, nickel, and cobalt, reducing production costs. |
Government Incentives | Financial incentives from governments can lower the costs of recycling programs, enhancing profitability. |
Compliance with Regulations | Engaging in recycling helps avoid fines from non-compliance with disposal regulations, saving money. |
You also gain reputational and competitive advantages by implementing sustainable lithium battery recycling programs:
You protect your business from fees and penalties related to improper disposal.
You contribute to your company’s sustainability goals, which is increasingly important for investors.
You enhance your brand reputation through sustainable practices.
You position your company as a leader in corporate responsibility.
Environmentally conscious brands enjoy higher trust and loyalty from customers, giving you a competitive edge.
For more on how your company can approach sustainability, see Our Approach to Sustainability.
1.3 Regulatory Factors
You must navigate a complex regulatory landscape when managing lithium battery recycling and sustainability. Major markets such as the US, EU, and China have introduced strict requirements for recycling lithium batteries used in outdoor lighting and other sectors, including medical, robotics, security, infrastructure, consumer electronics, and industrial applications.
Carbon Footprint Declaration: Manufacturers must calculate and declare the carbon footprint of battery production to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Minimum Recycled Material Content: Starting from August 2028, certain batteries must contain a minimum percentage of recycled materials, including cobalt, lead, lithium, and nickel.
Durability and Disassembly: Regulations require extended battery lifespan and easier maintenance, reuse, and recycling.
Battery Safety: New measures limit hazardous substances and mandate testing to protect human health and the environment.
Supply Chain Due Diligence: Manufacturers must ensure responsible sourcing of raw materials, adhering to human rights and environmental standards. For more information, review our Conflict Minerals Statement.
End-of-Life Management: Regulations mandate specific collection targets and free collection systems for end users, along with minimum recycling requirements.
You can meet these requirements by choosing lithium battery chemistries that support recycling and sustainability. For example, LiFePO4 batteries offer a stable iron phosphate composition, making them easier to recycle and less hazardous to the environment. They do not contain harmful heavy metals, so proper disposal poses no negative health or environmental hazards. The stable cathode material in LiFePO4 batteries reduces the risk of overheating and fire, preventing thermal runaway and combustion.
Battery Type | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|
LiFePO4 | 5 to 10 years |
The longevity of LiFePO4 batteries in outdoor lighting applications enhances sustainability by decreasing the need for frequent replacements. This reduces waste and the environmental impact linked to battery production and disposal. By integrating lithium battery recycling into your operations, you can meet regulatory requirements, improve your environmental performance, and support a circular economy.
Tip: Prioritize lithium battery recycling and sustainability practices to future-proof your business and protect the environment.
Part2: Lithium Battery Recycling Methods
2.1 Current Technologies
You face a rapidly evolving landscape in lithium battery recycling. As outdoor lighting applications expand, you must understand the main recycling technologies to ensure responsible battery waste management and sustainable disposal practices. The most common methods include pyrometallurgy, hydrometallurgy, and several innovative approaches. Each method offers unique advantages for recycling lithium batteries and reducing environmental impact.
Technology | Description |
|---|---|
Pyrometallurgy | A high-temperature process that recovers metals from batteries through melting. |
Hydrometallurgy | A process that uses aqueous solutions to extract metals from battery materials. |
Innovative Methods | Includes mechanical assistance, bioleaching, and electroplating as emerging techniques. |
Pyrometallurgy uses heat to melt down battery components, allowing you to recover valuable metals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Hydrometallurgy relies on chemical solutions to dissolve and separate metals from battery waste. These processes support waste reduction and help you reclaim materials for new battery production, which lowers the economic impact of raw material sourcing.
Innovative methods like mechanical recycling, bioleaching, and electroplating continue to gain traction. Mechanical recycling involves shredding or grinding batteries to recover valuable materials. Bioleaching uses microorganisms to extract metals, while electroplating recovers metals through electrical currents. These methods improve the eco-friendliness of lithium battery recycling and support sustainable disposal practices.
You can see the effectiveness of these technologies in the recovery rates of key materials:
Material | Recovery Rate by 2027 | Recovery Rate by 2031 |
|---|---|---|
Cobalt | 90% | 95% |
Copper | 90% | 95% |
Lithium | 50% | 80% |
Nickel | 90% | 95% |
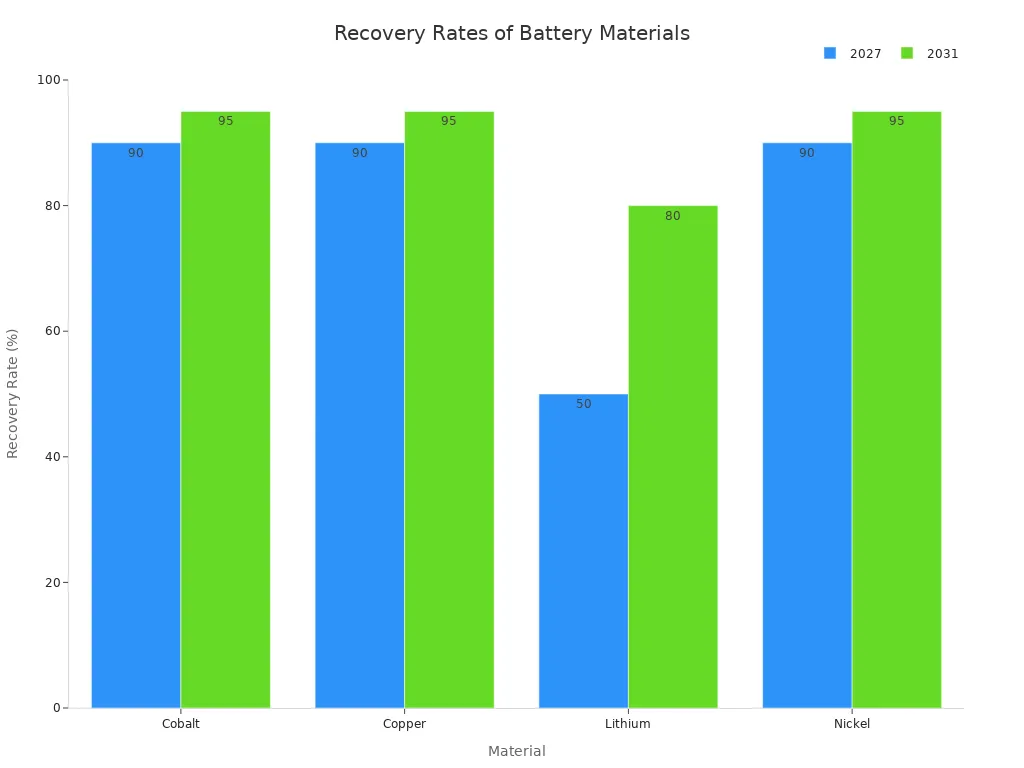
The recovery rates of minerals are calculated annually.
These rates consider the minerals contained in the battery or black mass.
The output materials are then used to manufacture new products.
You benefit from these high recovery rates by reducing your reliance on virgin materials and supporting responsible battery waste management. Recycling lithium batteries with these technologies helps you meet regulatory requirements and minimize environmental impact.
2.2 Future Trends
You must stay ahead of the curve as the future of lithium battery recycling brings new innovations. Advanced sorting technologies, mechanical recycling, solvent extraction, AI-powered sorting systems, and mechanochemical recycling are transforming the industry. These methods address challenges in recycling lithium batteries and improve both efficiency and safety.
Method | Description |
|---|---|
Advanced Sorting Technologies | Utilizes state-of-the-art methods like X-ray fluorescence and computer vision to enhance material separation efficiency. |
Mechanical Recycling | Involves physical processes to break down batteries, allowing for the recovery of valuable materials. |
Solvent Extraction | Uses organic solvents to selectively dissolve and recover metals from battery components. |
AI-Powered Sorting Systems | Leverages machine learning for accurate battery type identification and categorization. |
Mechanochemical Recycling | Combines efficiency and sustainability, making it a promising method for future battery recycling. |
Mechanical recycling allows you to recover valuable materials by shredding or grinding batteries. Solvent extraction uses organic solvents to dissolve metals from battery components, increasing the purity of recovered materials. AI-powered sorting systems use machine learning to identify and categorize battery types, which streamlines the recycling process and reduces errors. Mechanochemical recycling stands out for its efficiency and sustainability, making it a key player in the future of lithium battery recycling.
You also see the rise of safer chemistries, such as LiFePO4, NMC, LCO, and LMO, which simplify recycling and reduce environmental risks. For example, LiFePO4 batteries, with a platform voltage of 3.2V, energy density of 90-160 Wh/kg, and cycle life of 2000-7000 cycles, offer a safer and more sustainable option for outdoor lighting and other sectors like medical, robotics, security, infrastructure, consumer electronics, and industrial. These chemistries support sustainable lithium battery recycling and reduce the environmental impact of battery waste.
Chemistry | Platform Voltage | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|
LiFePO4 | 3.2V | 90-160 | 2000-7000 |
NMC | 3.7V | 150-220 | 1000-2000 |
LCO | 3.7V | 150-200 | 500-1000 |
LMO | 3.7V | 100-150 | 300-700 |
You can leverage these advances to improve your recycling initiatives and support sustainable disposal practices. The future of lithium battery recycling will rely on smart integration, automation, and safer chemistries to maximize resource recovery and minimize environmental impact.
2.3 Quality and Safety
You must prioritize quality and safety when recycling lithium batteries for outdoor lighting. The challenges in recycling lithium batteries often stem from the lack of standardized recycling procedures and the need for safe transportation. Different battery designs require varied recycling processes, which can lead to inefficiencies and safety risks.
Safety Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Lack of Standardized Recycling Procedures | Different designs of lithium batteries require varied recycling processes, leading to inefficiencies. |
Safe Transportation | Batteries contain flammable substances, necessitating careful handling to prevent dangerous fires. |
You can address these challenges by working with certified recyclers who follow strict protocols for safe lithium battery disposal. Proper battery recycling ensures that batteries meet quality standards for reuse in outdoor lighting and other critical applications. You should also implement a robust BMS (Battery Management System) to monitor battery health and safety during recycling and disposal.
Sustainable lithium battery recycling practices help you maintain compliance with environmental regulations and protect your workforce. You reduce the risk of fires and hazardous exposure by following safe lithium battery disposal guidelines. Responsible battery waste management not only safeguards the environment but also enhances your reputation as a leader in eco-friendly and sustainable disposal practices.
Tip: Always partner with certified recyclers and invest in staff training to ensure proper battery recycling and safe lithium battery disposal.
Part3: Practical Recycling Steps

3.1 Collection and Transport
You must establish robust collection and transport procedures for lithium battery packs used in outdoor lighting. Improper handling of batteries can lead to serious safety risks. Fires and explosions often occur during transport, especially in cargo and aviation settings. Excessive heat may trigger thermal runaway, causing batteries to ignite or explode. To minimize these risks, you should:
Remove batteries from devices and sort them by chemistry, such as LiFePO4, NMC, LCO, LMO, lithium-polymer/LiPo, and Solid-State Battery.
Package batteries securely to prevent short circuits and physical damage.
Use trained staff and certified carriers for safe transport.
Implement a BMS (Battery Management System) to monitor battery health during collection and transport.
You can improve your collection rate by following these steps. If you need a tailored solution for your business, click for custom consultation.
3.2 Certified Recyclers
You must partner with certified recyclers to ensure safe and environmentally responsible recycling of lithium batteries. You can identify reputable recycling centers by:
Using online platforms like Call2Recycle to locate nearby facilities.
Checking local government or environmental agency directories for authorized centers.
Contacting retail stores such as Best Buy, Home Depot, and Lowe’s for in-store recycling programs.
Certified recyclers should possess credentials such as R2 (Responsible Recycling), e-Stewards, and third-party auditing by organizations like CHWMEG. These certifications guarantee compliance with ethical guidelines and safety standards.
Key Principles of Ethical Guidelines for Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling |
|---|
Prioritize worker safety with proper training and protective equipment |
Ensure fair treatment and equal opportunities for employees |
Comply with labor laws and regulations |
Promote transparency and accountability in recycling practices |
Engage with local communities and stakeholders |
You should verify certifications before selecting a recycler to protect your business and the environment.
3.3 Circular Economy
You can maximize the impact of your recycling practices by adopting a circular economy approach for lithium battery packs. This strategy promotes recycling, regeneration, and upcycling, reducing waste and improving resource efficiency. Circular economy practices help you manage the lifecycle of batteries, mitigate supply chain issues, and support sustainability goals.
In regions like Australia, circular economy models for lithium-ion batteries have demonstrated significant economic value and improved end-of-life management. You benefit from robust collection systems and regional policies that enhance recycling rates and reduce environmental impact.
By integrating circular economy principles, you create a closed-loop system for lithium battery disposal and resource recovery. This approach supports your business in medical, robotics, security, infrastructure, consumer electronics, and industrial sectors.
Tip: Adopt circular economy strategies to future-proof your battery management practices and enhance your sustainability performance.
You improve sustainability by choosing lithium battery recycling over traditional mining.
Recycling Benefits | Traditional Mining Benefits | |
|---|---|---|
Emissions | Lower emissions | Higher emissions |
Land and Water Use | Less land and water use | More land and water use |
Ongoing innovation in lithium battery technology and collaboration drive better recycling and disposal. You should prioritize responsible battery management and request a custom battery consultation for tailored solutions.
FAQ
What lithium battery chemistries does Large Power recommend for outdoor lighting in industrial and infrastructure projects?
Large Power recommends LiFePO4, NMC, LCO, and LMO chemistries. See the table below for key specifications:
Chemistry | Platform Voltage | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|
LiFePO4 | 3.2V | 90-160 | 2000-7000 |
NMC | 3.7V | 150-220 | 1000-2000 |
LCO | 3.7V | 150-200 | 500-1000 |
LMO | 3.7V | 100-150 | 300-700 |
How can you ensure safe recycling and disposal of lithium battery packs in security and robotics applications?
You should partner with certified recyclers and use a BMS for monitoring. Large Power offers custom consultation for tailored recycling solutions.
Why should your business choose Large Power for lithium battery recycling in medical and consumer electronics sectors?
Large Power provides industry expertise, compliance with global standards, and custom solutions for medical and consumer electronics lithium battery recycling.




