You see transformation in healthcare and robotics as Solid-State Batteries drive safer, more reliable, and compact solutions. Hospitals now rely on surgical robots and diagnostic devices that benefit from increased operational life and intrinsic safety. The demand for advanced battery technology continues to rise, enhancing patient outcomes and supporting the shift toward personalized care.
Key Takeaways
Solid-state batteries enhance safety and reliability in healthcare devices, reducing risks like leakage and overheating.
These batteries offer higher energy density, allowing devices to operate longer between charges, which improves efficiency in healthcare and robotics.
Solid-state technology supports miniaturization, enabling the development of smaller, more flexible devices for advanced medical and robotic applications.
Part1: Impact
1.1 Healthcare Devices
You see solid-state batteries driving a new era of reliability and safety in medical devices. These batteries deliver years of service for implantable devices, such as pacemakers and neurostimulators. You benefit from lithium metal anodes and advanced cathode systems, which increase energy density and ensure dependable operation. Solid-state batteries meet strict requirements for safety, reliability, and long service life.
Solid-state batteries eliminate risks like leakage and uncontrolled heating.
You gain safe and reliable power for critical healthcare applications.
The technology supports compact designs, enabling smaller and less invasive devices.
Note: Solid-state batteries support eco-friendly healthcare solutions by reducing hazardous waste and improving device longevity. For more on sustainability, see our approach to sustainability.
You can see real-world applications in portable X-ray systems. Solid-state batteries enhance mobility, allowing you to perform diagnostics in various locations. The technology enables battery-operated X-ray scanners, which deliver short pulses of high-intensity radiation energy efficiently. This advancement improves patient care and streamlines workflows in hospitals and clinics.
1.2 Robotics Systems
You experience significant improvements in robotic systems with solid-state batteries. Surgical robots now operate with greater safety and efficiency. The compact nature of solid-state technology allows you to design smaller, more agile robots that fit into tight surgical spaces. These batteries provide consistent power, reducing downtime and maintenance.
Solid-state batteries offer higher energy density than traditional lithium battery packs.
You achieve longer operational cycles and faster charging times.
The technology supports eco-friendly robotics by minimizing environmental impact.
Tip: For custom solutions in robotics, explore our robotics battery solution.
You notice that solid-state batteries outperform lithium battery packs in both safety and performance. The absence of liquid electrolytes removes the risk of leakage or fire, which is critical in surgical environments. You also benefit from the ability to create more compact and lightweight robots, expanding the range of real-world applications in healthcare and beyond.
Part2: Solid-State Batteries Overview

2.1 Key Features
You gain a competitive edge by adopting solid-state batteries in your healthcare and robotics solutions. These batteries use solid electrolyte materials instead of liquid electrolytes, which fundamentally changes the safety and reliability profile of your devices. Solid-state batteries store three to four times more energy per unit weight than conventional lithium-ion batteries, making them a leading energy storage technology for compact and high-performance applications.
Solid-state batteries reduce the risk of dendrite formation, which enhances safety and stability during rapid charging cycles.
You benefit from multifunctional materials that increase versatility for medical, security, and industrial robotics.
The solid-state design supports groundbreaking innovations, such as thin-film solid-state batteries for miniaturized medical implants.
Solid-state batteries also utilize a thicker ceramic separator layer. This feature provides greater mechanical resistance to high temperatures, ensuring reliable operation even under stress or misuse. You can deploy these batteries in mission-critical environments where safety and longevity are essential.
2.2 Differences from Lithium Packs
You need to understand how solid-state batteries compare to traditional lithium-ion battery packs, including LiFePO4, NMC, and LCO chemistries. The table below highlights key differences in safety, lifespan, and performance:
Feature | Solid-State Batteries | Lithium-Ion Battery Packs (LiFePO4, NMC, LCO, LMO, LTO) |
|---|---|---|
Electrolyte Type | Solid electrolyte materials | Liquid electrolyte |
Risk of Thermal Runaway | Significantly reduced | High risk |
Flammability | Nonflammable | Flammable |
Dendrite Formation | Greater resistance | Lower resistance |
Energy Density | 3-4x higher | Standard |
Lifespan | Longer, but may face crack issues | Degrades over time due to cycling |
Charging Speed | Enhanced rapid charging capability | Standard |
Failure Rate | At least 10x lower | Higher |
Application Scenarios | Medical, robotics, security, infrastructure | Medical, industrial, consumer electronics |
Note: Solid-state batteries are less prone to leakage and fire hazards, making them ideal for surgical robots and implantable medical devices. You can request a custom battery consultation for your application needs here.
You see that solid-state batteries deliver faster charging, higher energy density, and superior safety compared to lithium battery packs. This technology enables you to design more reliable and compact devices for healthcare and robotics, supporting your business growth and operational excellence.
Part4: Advantages
4.1 Safety and Reliability
You prioritize safety and reliability in every healthcare and robotics project. Solid-state batteries address safety concerns by using a solid electrolyte, which enhances thermal stability and reduces the risk of short circuits or fire. You see this technology adopted in critical applications such as pacemakers, hearing aids, and drug delivery systems, where consistent performance is essential. Battery management ICs provide real-time monitoring and protection, ensuring safe operation and minimizing the risk of failure. The healthcare industry demands advanced solutions, and solid-state batteries deliver reliable energy output with minimal risk of leakage or thermal failure.
Solid-state batteries support devices that require uninterrupted operation.
You benefit from reduced maintenance and longer device lifespans.
4.2 Energy Density
You gain a significant advantage with the high energy density of solid-state batteries. This technology offers 350–700 Wh/kg, compared to 150–300 Wh/kg for lithium-ion battery packs. The table below highlights the difference:
Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) |
|---|---|
Solid-State Batteries | 350–700 |
Lithium-Ion Batteries | 150–300 |
Higher energy density means your devices operate longer between charges. In healthcare and robotics, this translates to fewer interruptions and improved workflow efficiency. You support continuous operation in mission-critical environments, which is vital for patient care and industrial automation.
4.3 Miniaturization
You drive innovations in miniaturization with solid-state batteries. Advanced micro/nano-fabrication techniques, such as 3D printing and atomic layer deposition, enable the creation of microbatteries with complex 3D structures. These batteries power tiny medical implants and compact robotic systems. You benefit from lightweight, ultra-compact designs that fit into wearable and implantable devices. Solid-state batteries provide high energy storage in a smaller volume, supporting flexible electronics and next-generation healthcare technologies.
Thinner, more flexible batteries promote new applications in wearables and smart microelectronics.
You enable advanced microsystems that previously lacked suitable power sources.
Tip: For custom solutions tailored to your robotics or healthcare applications, request a consultation with our experts.
Part5: Challenges
5.1 Manufacturing Scale
You face significant challenges when scaling solid-state battery production from development to high-volume manufacturing. The transition requires you to improve yields and reduce defect rates. Defectivity often disrupts stable yields, which increases costs and slows down your progress. You must implement advanced process control methods to detect and address defects early. This step is critical for ensuring reliability and efficiency in healthcare and robotics applications. You also encounter supply chain bottlenecks that impact your ability to deliver batteries on time.
A projected 30% supply deficit in battery-grade graphite by 2030 due to strict purity requirements.
Delays of 6-12 months in battery deliveries for electric vehicles, which can affect your robotics and medical device timelines.
China’s export restrictions on graphite in 2023 impacted 35% of global EV production, creating immediate shortages.
You need scalable manufacturing techniques to overcome these barriers and meet the growing demand in medical, robotics, and industrial sectors.
5.2 Cost Factors
You notice that solid-state batteries currently cost much more than traditional lithium-ion battery packs. The high price comes from expensive solid electrolytes, such as sulfides and oxides, and complex production processes. Only a few companies have the ability to produce these batteries at scale. The table below compares the cost per kWh:
Battery Type | Cost per kWh |
|---|---|
Solid-State Batteries | $400 – $600 |
Traditional Lithium-Ion | $100 – $150 |
Projected Solid-State | $150 – $200 by 2030 |
Future Solid-State | $100 or less |
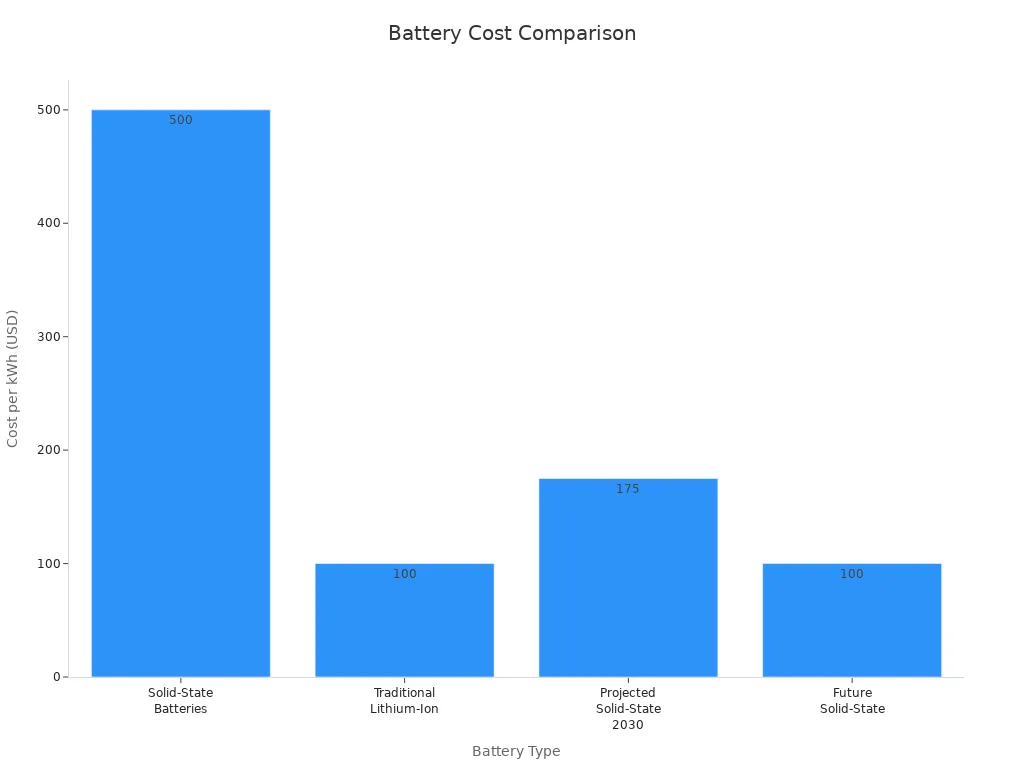
You expect costs to decrease as manufacturing scales. By the late 2020s, price parity with lithium-ion batteries is possible. In the early 2030s, you may see competitive pricing, making this technology more accessible for healthcare and robotics.
5.3 Regulatory Barriers
You must navigate evolving international standards and certification processes. As battery technology advances, you need updated testing protocols to ensure safety and market access. Regulatory bodies now require sophisticated certification focused on new material properties and long-term reliability. You invest in advanced testing facilities to comply with these standards and maintain trust in your products.
Updated testing protocols are necessary for new battery chemistries.
Certification standards now focus on energy density, safety, and reliability.
You must adapt quickly to changing regulations in healthcare and robotics markets.
Note: For custom consultation on regulatory compliance or scalable manufacturing, contact our team to discuss your specific needs.
You see solid-state batteries driving innovation in healthcare and robotics. You benefit from longer device life, flexible designs, and safer operations. Leading companies invest in partnerships to advance battery technology. To stay ahead, you should focus on R&D, strategic collaborations, and adapting to new market demands.
FAQ
What advantages do solid-state batteries offer over lithium battery packs in medical and robotics sectors?
You gain higher energy density, improved safety, and longer lifespan. Solid-state batteries reduce fire risk and support compact designs for advanced medical and robotics applications.
How does Large Power support custom solid-state battery solutions for B2B clients?
You access tailored battery solutions for medical, robotics, security, and industrial sectors. Large Power provides expert consultation. Request your custom battery solution here.
Which battery chemistries does Large Power compare when recommending solid-state technology?
You receive comparisons with LiFePO4, NMC, LCO, LMO, and LTO lithium packs. Large Power highlights solid-state benefits for mission-critical devices in healthcare, robotics, and infrastructure.




