
Temperature plays a critical role in how lithium batteries in outdoor security cameras perform. You see reduced battery capacity in cold outdoor environments and faster battery aging in hot climates. For example, every 15°F increase above 77°F can halve battery life. Both heat and cold present unique challenges for lithium batteries in outdoor security cameras, making reliable outdoor battery operation a constant concern.
Key Takeaways
Cold temperatures slow down battery chemistry, reducing capacity and causing issues like lithium plating that can damage batteries and lower performance.
High temperatures speed up battery aging, increase safety risks like overheating, and reduce battery lifespan, so managing heat is crucial for safe operation.
Protect batteries by choosing the right chemistry, using weatherproof and insulated housings, placing cameras strategically, and performing regular maintenance to ensure reliable outdoor performance.
Part 1: Why Temperature Matters for Outdoor Camera Batteries

1.1 Chemical Reactions and Battery Life
Temperature matters for outdoor camera batteries because it directly influences the chemical reactions inside lithium-ion batteries. When you install lithium batteries in outdoor security cameras, you expose them to a wide range of ambient temperature conditions. These changes affect battery performance and reliability.
At low temperatures, the chemical reactions responsible for lithium-ion transfer slow down. This reduces efficiency and power output. The electrolyte inside the battery becomes more viscous, making it harder for lithium ions to move between the anode and cathode.
Charging lithium-ion batteries below freezing can cause lithium plating on the anode. This increases internal resistance and can permanently damage the battery.
High temperatures accelerate the breakdown of internal components and the electrolyte. This speeds up battery aging and increases the risk of thermal runaway, which can lead to safety hazards.
The table below compares how different lithium-ion chemistries respond to temperature extremes:
Battery Chemistry | Optimal Temperature Range | Cold Weather Performance | High Temperature Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
LCO | 0°C to 45°C | Poor | Moderate |
NMC | -20°C to 60°C | Good | Good |
LiFePO4 | -20°C to 60°C | Excellent | Excellent |
LMO | 0°C to 45°C | Poor | Moderate |
LTO | -30°C to 55°C | Excellent | Good |
Tip: Choose lithium-ion batteries with a wide operating temperature range for outdoor security cameras to maximize battery life and efficiency.
1.2 Common Failure Signs
You can spot temperature-related battery issues by watching for several common failure signs in outdoor security cameras:
Reduced battery runtime, especially in cold weather.
Unexpected shutdowns or frequent reboots.
Charging failures or slow charging rates.
Swelling, deformation, or leakage in the battery case.
Significant voltage drops during operation.
If you notice these symptoms, your batteries may be operating outside their optimal temperature range. Regular monitoring helps you maintain battery performance and avoid costly downtime.
Part 2: Cold Weather and Lithium Batteries in Outdoor Security Cameras

2.1 Reduced Capacity in Low Temperatures
You face significant challenges when operating lithium-ion batteries in outdoor security cameras during cold weather. Temperature drops below freezing slow the chemical reactions inside the battery, which directly affects performance. In cold weather conditions, you notice a decrease in battery capacity. Lithium-ion batteries typically operate at about 95-98% capacity at temperatures below 0°C (32°F), so you experience a capacity decrease of approximately 2-5%. Users in cold climates report a daily battery capacity drop rate between 1% and 4% when ambient temperature falls below 3°C.
Cold weather conditions slow lithium-ion movement, reducing efficiency.
Battery performance drops more noticeably in extreme cold compared to moderate cold.
You see moderate capacity reduction in lithium-ion batteries, which is less severe than in alkaline batteries.
Note: If you rely on outdoor security cameras for critical infrastructure, medical monitoring, or robotics, you must account for this capacity loss to maintain uninterrupted surveillance and operational reliability.
2.2 Lithium Plating and Internal Resistance
Cold weather increases internal resistance in lithium-ion batteries. As temperature drops, the electrolyte inside the battery thickens, making it harder for lithium ions to move between the anode and cathode. This increased resistance reduces the battery’s ability to deliver power, causing performance degradation in outdoor security cameras. Lithium batteries lose 10-20% capacity at 0°F but remain functional, unlike alkaline batteries which suffer greater losses.
Effect | Explanation |
|---|---|
Increased Internal Resistance | Cold weather thickens the electrolyte, slowing ion movement and increasing internal resistance. |
Voltage Drops and Power Output Loss | Higher resistance causes voltage drops, reducing battery power output. |
Reduced Capacity at Low Temperatures | Electrolyte viscosity increases, lowering efficiency and capacity. |
Potential for Cell Damage | Cold-induced stress and rapid temperature changes can damage battery components. |
Impact on Longevity | Freezing/thawing cycles and electrolyte solidification accelerate battery aging. |
Limited Operating Range | Even low-temperature lithium-ion batteries have operational limits and may fail if too cold. |
Lithium plating is another risk in cold weather. When you charge lithium-ion batteries below 0°C, metallic lithium plates permanently on the anode. This process reduces the lithium available for electrochemical reactions, decreasing battery capacity and efficiency. Charging at inappropriate rates below freezing worsens lithium plating, making the battery less stable and more prone to sudden failure. You may see your outdoor security camera stop working unexpectedly due to this issue.
Lithium plating occurs because lithium ions cannot efficiently absorb into the anode at low temperature.
The battery becomes less mechanically stable and more likely to fail.
Battery management systems help protect against temperature-related battery issues by monitoring and controlling charging rates.
Tip: For outdoor applications in harsh winter climates, select premium lithium-ion battery packs with advanced battery management systems to minimize the impact of cold weather and extend battery life.
2.3 Charging and Discharging Issues
Charging lithium-ion batteries in cold weather presents unique challenges. Low temperature slows electrochemical processes and increases risks such as lithium plating and internal short circuits. You must reduce charging rates to no more than 0.1C between 32°F and 14°F, and further reduce to 0.05C between 14°F and -4°F to avoid damage. It is best to allow batteries to warm to room temperature before you charge them. Some specialized lithium-ion batteries for outdoor security cameras include heating elements to enable safe charging in cold weather conditions.
Discharging also becomes less efficient in cold weather. You see reduced capacity and faster battery drain, which means you must avoid deep discharge during storage. Battery management systems and smart chargers with temperature sensors help monitor and adjust charging to protect battery health. These features are essential for outdoor security cameras used in medical, industrial, and infrastructure sectors where reliable performance is critical.
Charging below freezing increases risk of lithium plating and internal short circuits.
Discharging in cold weather drains batteries faster and reduces overall performance.
Smart chargers and battery management systems optimize charging and discharging based on ambient temperature.
Alert: Always monitor battery temperature and avoid charging lithium-ion batteries in extreme cold to prevent permanent damage and ensure reliable outdoor security camera operation.
Part 3: Heat Effects on Outdoor Security Camera Batteries

3.1 Faster Aging and Degradation
You encounter significant challenges when outdoor security cameras operate in high temperature environments. Lithium batteries perform best within an optimal temperature range of 15°C to 35°C. When temperatures rise above 35°C, chemical reactions inside the battery accelerate. This increased reaction rate leads to faster aging and severe degradation. You see a marked reduction in battery performance and lifespan, especially during prolonged exposure to heat.
Heat causes thermal degradation and chemical instability. The electrolyte inside the battery decomposes, generating gas and raising internal pressure. This process damages the battery’s internal structure and reduces its ability to store and deliver energy. In NMC lithium batteries, the cathode can release oxygen, which destabilizes the battery further. These chemical changes increase internal resistance and accelerate capacity loss. You notice that battery efficiency drops and the risk of temperature-related battery issues rises.
Temperature (°C) | Battery Performance | Aging Rate | Safety Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
15-35 | Optimal | Normal | Low |
36-59 | Reduced | Accelerated | Moderate |
60+ | Severe Degradation | Very High | High |
Tip: You should use thermal management systems to keep battery temperatures within the recommended operating temperature range. This strategy helps maintain battery efficiency and extends battery life in outdoor security camera applications.
3.2 Overheating and Safety Risks
High ambient temperature increases the risk of overheating and safety incidents in lithium battery packs. You face several common causes of overheating:
Physical damage, such as cracks or punctures, exposes flammable electrolyte and can trigger thermal runaway.
Electrical abuse, including overcharging or deep discharging, generates excessive heat and damages internal components.
Exposure to high temperature accelerates battery degradation and raises fire risk.
Manufacturing defects, such as improper assembly or contaminants, compromise battery integrity and may cause thermal runaway.
Thermal runaway is a critical safety risk. When internal battery failure occurs, uncontrollable heat generation can lead to fire, explosion, and toxic smoke. You must watch for warning signs like unusual heat, noise, smoke, odor, or swelling. Proper handling, storage, and charging procedures are essential to prevent these incidents. You should install battery management systems (BMS) to monitor temperature and protect against overheating.
Alert: Always monitor battery temperature and use BMS to reduce the risk of fire hazards and ensure safe operation of outdoor security cameras.
3.3 Efficiency Loss in High Temperatures
You notice a decline in battery efficiency when outdoor security cameras operate in high temperature environments. High ambient temperature above 100°F accelerates self-discharge and reduces battery lifespan. Cameras placed in direct sunlight or enclosed spaces experience reduced battery performance during hot months. Lithium batteries outperform alkaline batteries across temperature ranges, but they still suffer from accelerated degradation at high temperature.
You can mitigate heat impact by installing cameras in shaded or protected areas. This approach helps maintain battery efficiency and extends battery life. You should avoid placing cameras in locations with extreme temperature fluctuations. Battery management systems and smart installation strategies play a key role in optimizing battery performance and reliability.
Application Scenario | Heat Impact on Battery Efficiency | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
Medical Monitoring | High risk of efficiency loss | Use thermal management and BMS |
Industrial Robotics | Moderate risk | Install in shaded areas |
Security Systems | High risk in direct sunlight | Monitor temperature, use BMS |
Infrastructure | Moderate to high risk | Protect from heat sources |
Consumer Electronics | Moderate risk | Avoid enclosed hot spaces |
Note: You should always consider the operating temperature range and environmental conditions when selecting lithium battery packs for outdoor security cameras. This practice ensures reliable battery performance and reduces the risk of temperature-related battery issues.
Part 4: Best Practices for Outdoor Camera Batteries

4.1 Insulation and Environmental Protection
You can improve the temperature resilience of outdoor security cameras by focusing on insulation and environmental protection. Weatherproof housings shield your equipment from rain, snow, and direct sunlight, reducing exposure to extreme temperature swings. Insulated enclosures help maintain stable internal temperature, which supports optimal performance and extends battery life. Sealing cable entry points prevents moisture ingress, protecting outdoor camera batteries from electrical issues. For cold climates, select cold-rated batteries or consider hardwired power sources to maintain performance during winter. In hot regions, use enclosures with ventilation or cooling features to prevent overheating.
Tip: Protecting outdoor camera batteries with proper insulation and weatherproofing is one of the best practices for outdoor camera batteries. This approach helps you maintain seasonal maintenance tips for optimal battery performance year-round.
4.2 Placement and Installation Tips
Strategic placement plays a key role in protecting outdoor camera batteries from temperature extremes. Follow these best practices for outdoor camera batteries:
Install cameras under eaves or overhangs to shield them from rain and direct sunlight.
Avoid placing cameras in direct sunlight to prevent UV damage and overheating.
Mount cameras 8 to 10 feet off the ground for balanced field of view and protection from elements.
Position cameras away from prevailing winds to reduce exposure to wind-driven rain or debris.
Orient cameras facing south in cold climates to maximize winter sunlight and battery performance.
Secure cameras under roof eaves or sturdy branches to minimize snow accumulation.
Periodically check mounts for stability against weather conditions.
These placement strategies help you maintain optimal performance and support protecting outdoor camera batteries in all seasons.
4.3 Monitoring and Maintenance
Routine monitoring and maintenance are essential for protecting outdoor camera batteries and ensuring optimal performance. You should check battery charge status weekly to prevent deep discharge and capacity loss. Clean cameras and sensors weekly to maintain clear images and reliable operation. Test alarms and control panels monthly, and update software and firmware regularly. Inspect wiring and physical connections quarterly, and schedule a professional system checkup annually.
Maintenance Task | Recommended Frequency |
|---|---|
Check batteries | Weekly |
Clean cameras & sensors | Weekly |
Test alarms & control panels | Monthly |
Update software & firmware | Monthly |
Inspect wiring & physical connections | Quarterly |
Professional system checkup | Annually |
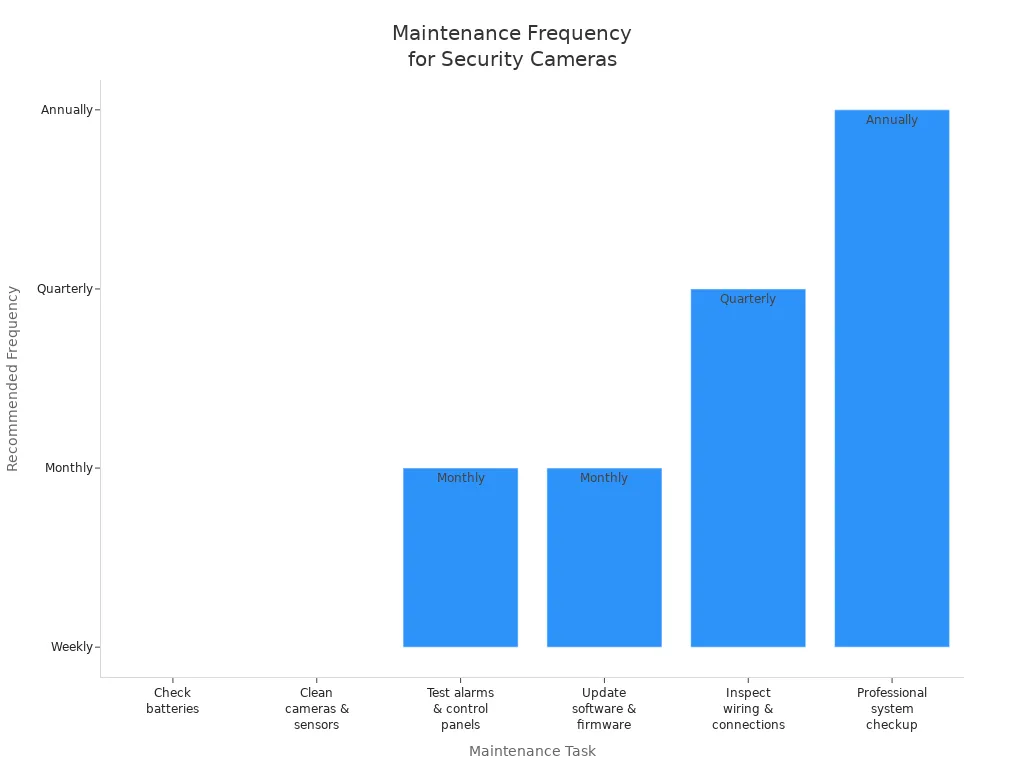
Note: Following seasonal maintenance tips for optimal battery performance ensures your outdoor security cameras operate reliably in any temperature. Consistent monitoring supports best practices for outdoor camera batteries and extends the life of your system.
You face unique challenges when using lithium batteries in outdoor security cameras. Temperature extremes—both heat and cold weather—reduce battery efficiency, shorten lifespan, and increase safety risks. To ensure reliable outdoor operation, select batteries rated for your climate, install weatherproof enclosures, and follow a strict maintenance schedule.
FAQ
1. What lithium battery chemistry works best for outdoor security cameras in extreme temperatures?
Chemistry | Cold Weather | Hot Weather | Application Sectors |
|---|---|---|---|
LiFePO4 | Excellent | Excellent | Security, Robotics, Medical |
NMC | Good | Good | Infrastructure, Industrial |
LTO | Excellent | Good | Medical, Robotics |
You should choose LiFePO4 or LTO for reliable performance in harsh climates.
2. How often should you replace lithium battery packs in outdoor cameras?
You should replace lithium battery packs every 2–3 years for optimal reliability. High temperatures or frequent deep discharge may shorten lifespan.
3. Where can you get custom lithium battery solutions for outdoor security cameras?
You can request a custom consultation from Large Power for tailored lithium battery packs.




